
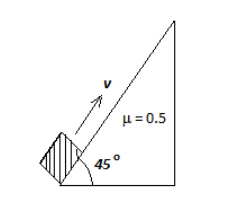
A block of mass \[1\,{\text{kg}}\] is projected from the lowest point up the inclined plane. If \[g = 10\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\] , the retardation experienced by the block is:
(A) \[\dfrac{{15}}{{\sqrt 2 }}\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
(B) \[\dfrac{5}{{\sqrt 2 }}\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
(C) \[\dfrac{{10}}{{\sqrt 2 }}\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
(D) Zero

Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: We will draw the diagram and break down the force components. The applied force is equal to the summation of frictional force and downward force along the inclined plane. We will substitute the required values and manipulate accordingly.
Step by step answer:In the given question, the following data are supplied, as follows:
The mass of the body is \[1\,{\text{kg}}\] .
Coefficient of static friction is \[0.5\] .
The angle of inclination of the plane is \[45^\circ \] .
For better understanding, we draw the diagram to illustrate in details:
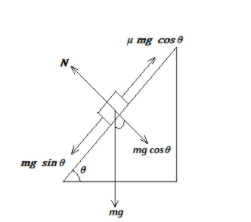
The weight of the block which is indicated as \[mg\] acts downward at right angle to the horizontal plane. The component of force which acts downward is \[mg\sin \theta \] and the normal reaction is indicated as \[mg\cos \theta \] . The frictional force which acts along the upward direction is indicated as \[\mu mg\cos \theta \] .
We are asked to find the retardation which is experienced by the block.
For this we will use the expression of force experienced by the block, which is the summation of two forces.
Mathematically we can write:
\[F = mg\sin \theta + \mu mg\cos \theta \] …… (1)
Where,
\[F\] indicates the force experienced by the block.
\[m\] indicates the mass of the block.
\[g\] indicates the acceleration due to gravity.
\[\theta \] indicates the inclination of the inclined plane.
\[\mu \] indicates coefficient of static friction.
Substituting the required values in the equation (1) we get:
\[
F = mg\sin \theta + \mu mg\cos \theta \\
\Rightarrow ma = mg\sin \theta + \mu mg\cos \theta \\
\Rightarrow 1 \times a = 1 \times 10 \times \sin 45^\circ + 0.5 \times 1 \times 10 \times \cos 45^\circ \\
\Rightarrow a = 10 \times \dfrac{1}
{{\sqrt 2 }} + 5 \times \dfrac{1}
{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
\]
Simplifying further we get:
\[
a = 10 \times \dfrac{1}
{{\sqrt 2 }} + 5 \times \dfrac{1}
{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{10}}
{{\sqrt 2 }} + \dfrac{5}
{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{15}}
{{\sqrt 2 }}\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}} \\
\]
Hence, the retardation experienced by the block is found to be \[\dfrac{{15}}{{\sqrt 2 }}\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\].
The correct option is (A).
Note: While solving this problem, you should have good knowledge of breaking down force components. Always keep in mind that the component adjacent to the angle is the cosine component. Higher the coefficient of static friction, higher is the frictional force. Frictional force always acts opposite to the applied force.
Step by step answer:In the given question, the following data are supplied, as follows:
The mass of the body is \[1\,{\text{kg}}\] .
Coefficient of static friction is \[0.5\] .
The angle of inclination of the plane is \[45^\circ \] .
For better understanding, we draw the diagram to illustrate in details:

The weight of the block which is indicated as \[mg\] acts downward at right angle to the horizontal plane. The component of force which acts downward is \[mg\sin \theta \] and the normal reaction is indicated as \[mg\cos \theta \] . The frictional force which acts along the upward direction is indicated as \[\mu mg\cos \theta \] .
We are asked to find the retardation which is experienced by the block.
For this we will use the expression of force experienced by the block, which is the summation of two forces.
Mathematically we can write:
\[F = mg\sin \theta + \mu mg\cos \theta \] …… (1)
Where,
\[F\] indicates the force experienced by the block.
\[m\] indicates the mass of the block.
\[g\] indicates the acceleration due to gravity.
\[\theta \] indicates the inclination of the inclined plane.
\[\mu \] indicates coefficient of static friction.
Substituting the required values in the equation (1) we get:
\[
F = mg\sin \theta + \mu mg\cos \theta \\
\Rightarrow ma = mg\sin \theta + \mu mg\cos \theta \\
\Rightarrow 1 \times a = 1 \times 10 \times \sin 45^\circ + 0.5 \times 1 \times 10 \times \cos 45^\circ \\
\Rightarrow a = 10 \times \dfrac{1}
{{\sqrt 2 }} + 5 \times \dfrac{1}
{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
\]
Simplifying further we get:
\[
a = 10 \times \dfrac{1}
{{\sqrt 2 }} + 5 \times \dfrac{1}
{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{10}}
{{\sqrt 2 }} + \dfrac{5}
{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{15}}
{{\sqrt 2 }}\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}} \\
\]
Hence, the retardation experienced by the block is found to be \[\dfrac{{15}}{{\sqrt 2 }}\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\].
The correct option is (A).
Note: While solving this problem, you should have good knowledge of breaking down force components. Always keep in mind that the component adjacent to the angle is the cosine component. Higher the coefficient of static friction, higher is the frictional force. Frictional force always acts opposite to the applied force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




