
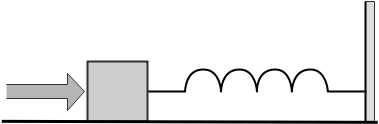
A block of mass $0.18kg$ is attached to a spring of force-constant $2N/m$. The coefficient of friction between the block and the floor is $0.1$. Initially, the block is at rest and the spring is unstretched. An impulse is given to the block as shown in the figure. The block slides a distance of \[0.06m\] and comes to rest for the first time. The initial velocity of the block $m/s$ is $V=\dfrac{N}{10}$. Then N is:
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 7

Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: An object undergoing motion always follows the law of conservation of energy. According to the law, the energy is transformed from one form to another; it cannot be destroyed or created. This law of energy conservation can be used to find the initial velocity of the object.
Formula used:
$KE=PE+frictional\,loss$
Complete answer:
As per the given data,
Mass is $0.18kg$
Spring constant $2N/m$
The friction coefficient $\left( \mu \right)$ is 0.1
Distance slide by the block ($x$) is $0.6m$
Initial velocity ($u$) is $\dfrac{N}{10}m/s$
As per the question a mass is attached with a spring which has it’s another end fixed at a certain point. Initially, both the block and string are at their original position. When an impulse is given to the block it slides a distance of \[0.06m\]. After this, the object comes to rest.
So by considering the law of conservation of energy, kinetic energy will be transferred into other forms of the energy. The kinetic energy which the object has will transform into the potential energy and some of the energy will be undergoing frictional loss due to the friction between the two surfaces.
Mathematically,
$KE=PE+frictional\,loss$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}+\mu mgx \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{k{{x}^{2}}}{m}+2\mu mgx \\
\end{align}$
\[\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{k{{x}^{2}}}{m}+2\mu mgx}\]
By putting the values as per the given data,
\[\begin{align}
& v=\sqrt{\dfrac{2{{(0.6)}^{2}}}{0.18}+2(0.1\times 0.6\times 10)} \\
& \Rightarrow v=0.4 \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{4}{10} \\
\end{align}\]
From the given data it is known that the initial velocity of the block is given as $\dfrac{N}{10}m/s$
So it can be concluded that,
\[v=\dfrac{4}{10}=\dfrac{N}{10}\]
By comparing we can come with the statement that the value of ‘N’ is 4.
$N=4$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The frictional force is the force which acts in the opposite direction of the applied force. It opposes the motion of the object. If an object has to be moved we have to apply a force greater than the frictional force (static frictional force).
Formula used:
$KE=PE+frictional\,loss$
Complete answer:
As per the given data,
Mass is $0.18kg$
Spring constant $2N/m$
The friction coefficient $\left( \mu \right)$ is 0.1
Distance slide by the block ($x$) is $0.6m$
Initial velocity ($u$) is $\dfrac{N}{10}m/s$
As per the question a mass is attached with a spring which has it’s another end fixed at a certain point. Initially, both the block and string are at their original position. When an impulse is given to the block it slides a distance of \[0.06m\]. After this, the object comes to rest.
So by considering the law of conservation of energy, kinetic energy will be transferred into other forms of the energy. The kinetic energy which the object has will transform into the potential energy and some of the energy will be undergoing frictional loss due to the friction between the two surfaces.
Mathematically,
$KE=PE+frictional\,loss$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}+\mu mgx \\
& \Rightarrow {{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{k{{x}^{2}}}{m}+2\mu mgx \\
\end{align}$
\[\Rightarrow v=\sqrt{\dfrac{k{{x}^{2}}}{m}+2\mu mgx}\]
By putting the values as per the given data,
\[\begin{align}
& v=\sqrt{\dfrac{2{{(0.6)}^{2}}}{0.18}+2(0.1\times 0.6\times 10)} \\
& \Rightarrow v=0.4 \\
& \Rightarrow v=\dfrac{4}{10} \\
\end{align}\]
From the given data it is known that the initial velocity of the block is given as $\dfrac{N}{10}m/s$
So it can be concluded that,
\[v=\dfrac{4}{10}=\dfrac{N}{10}\]
By comparing we can come with the statement that the value of ‘N’ is 4.
$N=4$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The frictional force is the force which acts in the opposite direction of the applied force. It opposes the motion of the object. If an object has to be moved we have to apply a force greater than the frictional force (static frictional force).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




