
A block is placed on a rough horizontal plane. A time dependent horizontal force \[F = kt\] acts on the block, where \[k\] is a positive constant. The acceleration - time graph of the block is:
A.
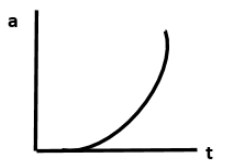
B.
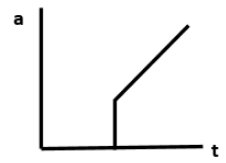
C.
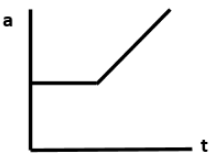
D.
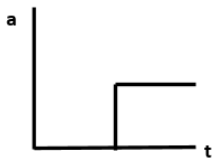


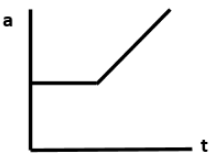

Answer
561.6k+ views
Hint: The given block is placed on a rough horizontal plane. Therefore, there will be some friction produced between the block and the rough horizontal plane when the block is in tendency to move( is applied by a certain force equal to the frictional force) and when the block starts moving under the action of the external force \[F\](is applied by a force which exceeds the frictional force).
Complete answer:
The frictional force is a retarding force that comes into play when there is a relative motion between the contact surfaces or there is a tendency of relative motion. When a block is placed on a rough horizontal plane and applied with a force \[F = kt\], there are two frictional forces that come into play.
Static friction: It is the opposing force that comes into play during the tendency of one body to move on another body. It is a self-adjusting force and is equal to the applied force.
Kinetic friction: It is the opposing force which comes into play during the motion of a body on another body
Static friction is produced when the surfaces of contact are in a tendency of relative motion. Here, the external time dependent force \[F\] applied is equal to the frictional force. As soon as the force \[F\]exceeds the frictional force, the block comes into motion. The maximum value of static friction is called the limiting friction. During static friction, the acceleration \[a\] keeps on increasing at constant time until it reaches the limiting friction. After the limiting friction, the acceleration \[a\] increases linearly with time \[t\]. This represents Kinetic friction.
Hence, option B is the correct answer.
Note: The static friction is only produced when the surfaces of contact are in a tendency of relative motion. It is produced when the external force \[F\] applied is not enough to overcome the frictional force. The static friction is equal and opposite to the force applied on the body. The body begins to slide only when the applied force is equal to the limiting friction. The Kinetic friction is less than the limiting friction.
Complete answer:
The frictional force is a retarding force that comes into play when there is a relative motion between the contact surfaces or there is a tendency of relative motion. When a block is placed on a rough horizontal plane and applied with a force \[F = kt\], there are two frictional forces that come into play.
Static friction: It is the opposing force that comes into play during the tendency of one body to move on another body. It is a self-adjusting force and is equal to the applied force.
Kinetic friction: It is the opposing force which comes into play during the motion of a body on another body
Static friction is produced when the surfaces of contact are in a tendency of relative motion. Here, the external time dependent force \[F\] applied is equal to the frictional force. As soon as the force \[F\]exceeds the frictional force, the block comes into motion. The maximum value of static friction is called the limiting friction. During static friction, the acceleration \[a\] keeps on increasing at constant time until it reaches the limiting friction. After the limiting friction, the acceleration \[a\] increases linearly with time \[t\]. This represents Kinetic friction.
Hence, option B is the correct answer.
Note: The static friction is only produced when the surfaces of contact are in a tendency of relative motion. It is produced when the external force \[F\] applied is not enough to overcome the frictional force. The static friction is equal and opposite to the force applied on the body. The body begins to slide only when the applied force is equal to the limiting friction. The Kinetic friction is less than the limiting friction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




