
A block is lying on an inclined plane which makes \[60^\circ \] with the horizontal. If coefficient of friction between block and plane is 0.25 and \[g = 10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\], then acceleration of the block when it moves along the plane will be
A. \[2.50\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
B. \[5.00\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
C. \[7.4\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
D. \[8.66\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
Answer
561.6k+ views
Hint: Use the expression for Newton’s second law of motion. Also use the formula for frictional force in terms of coefficient of friction and normal force. Draw the free body diagram of the block on the inclined plane. First apply Newton’s second law of motion to the block in the vertical direction and then in the horizontal direction. Substitute the value of normal force and calculate the value of acceleration of the block.
Formulae used:
The expression for Newton’s second law of motion is given by
\[{F_{net}} = ma\] …… (1)
Here, \[{F_{net}}\] is the net force acting on an object, \[m\] is mass of the object and \[a\] is acceleration of the object.
The frictional force \[{F_f}\] between an object and surface is given by
\[{F_f} = \mu N\] …… (2)
Here, \[\mu \] is a coefficient of friction between the object and surface and \[N\] is the normal force exerted by the surface on the object.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the angle of inclination of the inclined plane with the horizontal is \[60^\circ \].The coefficient of friction between the inclined surface and the block is 0.25.
\[\mu = 0.25\]
We are asked to calculate the acceleration of the block along the inclined plane.Let \[m\] be the mass of the block.Let us first draw a free body diagram of the block.
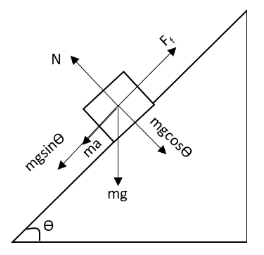
In the above free body diagram, \[mg\] is the weight of the block, \[N\] is the normal force acting on the block, \[{F_f}\] is the frictional force on the block and \[ma\] is the force due to acceleration \[a\] of the block.Let us apply Newton’s second law of motion to the block in the vertical direction.
\[N = mg\cos \theta \]
Let us apply Newton’s second law of motion to the block in the horizontal direction.
\[mg\sin \theta - {F_f} = ma\]
Substitute \[\mu N\] for \[{F_f}\] in the above equation.
\[mg\sin \theta - \mu N = ma\]
Substitute \[mg\cos \theta \] for \[N\] in the above equation.
\[mg\sin \theta - \mu \left( {mg\cos \theta } \right) = ma\]
\[ \Rightarrow g\sin \theta - \mu g\cos \theta = a\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = g\left( {\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta } \right)\]
Substitute \[10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\] for \[g\], \[60^\circ \] for \[\theta \] and \[0.25\] for \[\mu \] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow a = \left( {10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}} \right)\left[ {\sin 60^\circ - \left( {0.25} \right)\cos 60^\circ } \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \left( {10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} - \left( {0.25} \right)\dfrac{1}{2}} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 5\left[ {1.732 - 0.25} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 7.41\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
\[ \therefore a \approx 7.4\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
Therefore, the acceleration of the block is \[7.4\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\].
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: The students should keep in mind that in the free body diagram we have considered the direction of acceleration of the block on the inclined plane as positive X-direction and applied Newton’s law accordingly. One can also take the direction of the frictional force as the positive X-direction. Using both ways, we will end with the same answer for acceleration of the block.
Formulae used:
The expression for Newton’s second law of motion is given by
\[{F_{net}} = ma\] …… (1)
Here, \[{F_{net}}\] is the net force acting on an object, \[m\] is mass of the object and \[a\] is acceleration of the object.
The frictional force \[{F_f}\] between an object and surface is given by
\[{F_f} = \mu N\] …… (2)
Here, \[\mu \] is a coefficient of friction between the object and surface and \[N\] is the normal force exerted by the surface on the object.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the angle of inclination of the inclined plane with the horizontal is \[60^\circ \].The coefficient of friction between the inclined surface and the block is 0.25.
\[\mu = 0.25\]
We are asked to calculate the acceleration of the block along the inclined plane.Let \[m\] be the mass of the block.Let us first draw a free body diagram of the block.

In the above free body diagram, \[mg\] is the weight of the block, \[N\] is the normal force acting on the block, \[{F_f}\] is the frictional force on the block and \[ma\] is the force due to acceleration \[a\] of the block.Let us apply Newton’s second law of motion to the block in the vertical direction.
\[N = mg\cos \theta \]
Let us apply Newton’s second law of motion to the block in the horizontal direction.
\[mg\sin \theta - {F_f} = ma\]
Substitute \[\mu N\] for \[{F_f}\] in the above equation.
\[mg\sin \theta - \mu N = ma\]
Substitute \[mg\cos \theta \] for \[N\] in the above equation.
\[mg\sin \theta - \mu \left( {mg\cos \theta } \right) = ma\]
\[ \Rightarrow g\sin \theta - \mu g\cos \theta = a\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = g\left( {\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta } \right)\]
Substitute \[10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\] for \[g\], \[60^\circ \] for \[\theta \] and \[0.25\] for \[\mu \] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow a = \left( {10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}} \right)\left[ {\sin 60^\circ - \left( {0.25} \right)\cos 60^\circ } \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \left( {10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} - \left( {0.25} \right)\dfrac{1}{2}} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 5\left[ {1.732 - 0.25} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 7.41\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
\[ \therefore a \approx 7.4\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\]
Therefore, the acceleration of the block is \[7.4\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\].
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: The students should keep in mind that in the free body diagram we have considered the direction of acceleration of the block on the inclined plane as positive X-direction and applied Newton’s law accordingly. One can also take the direction of the frictional force as the positive X-direction. Using both ways, we will end with the same answer for acceleration of the block.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




