
A block is kept on the floor of an elevator at rest. The elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$. Find the displacement of the block during the first 0.2 s after the start. (Take g = 10 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$)
${\text{A}}{\text{.}}$ 30 cm
${\text{B}}{\text{.}}$ Zero
${\text{C}}{\text{.}}$ 20 cm
${\text{D}}{\text{.}}$ 25 cm
Answer
611.1k+ views
Hint- Here, we will proceed by determining whether the block remains on the floor of the elevator or it detaches from it according to whether $a > g$ or $g > a$. Then, we will use the kinematic laws of motion in a straight line.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Formula Used- ${\text{s}} = {\text{ut}} + \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{a}}{{\text{t}}^2}$.
Given, Initial velocity of the block, u = 0 m/s
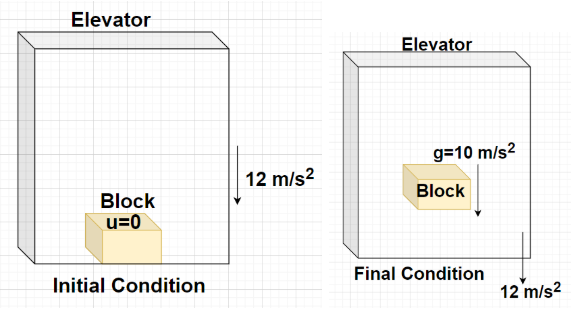
It is given that the elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ which is greater than the acceleration due to gravity (i.e., g = 10 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$). So, the block which was initially kept on the floor of the elevator will no longer remain on the floor as shown in the figure. This means that the block will be experiencing a free-fall motion and will be moving in the downward direction with an acceleration equal to acceleration due to gravity (i.e., g = 10 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$).
According to Kinematic Laws of motion,
${\text{s}} = {\text{ut}} + \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{a}}{{\text{t}}^2}{\text{ }} \to {\text{(1)}}$ where s denotes the distance travelled by the body, u denotes the initial velocity of the body, t denotes the time taken by the body and a denotes the acceleration of the body.
Let us take the downward direction as a positive direction.
Here, u = 0 m/s, a = 10 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ and t = 0.2 s
By putting the above values in equation (1), we get
Distance travelled by the block during the first 0.2 s after the start, ${\text{s}} = {\text{0}} \times {\text{0}}{\text{.2}} + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {10} \right){\left( {0.2} \right)^2} = \left( 5 \right)\left( {0.04} \right) = 0.2{\text{ m}} = 0.2 \times 100{\text{ cm}} = 20{\text{ cm}}$
Therefore, the distance travelled by the block during the first 0.2 s after the start is 20 cm.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note- In this problem (where $a > g$), if instead of 12 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ we are given with 9 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ as the acceleration with which the elevator descends. Now we have $g > a$ case, so the block will remain on the floor of the elevator only. This means that the elevator and block descends with the same acceleration (i.e., 9 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$).
Complete step-by-step solution -

Formula Used- ${\text{s}} = {\text{ut}} + \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{a}}{{\text{t}}^2}$.
Given, Initial velocity of the block, u = 0 m/s
It is given that the elevator starts descending with an acceleration of 12 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ which is greater than the acceleration due to gravity (i.e., g = 10 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$). So, the block which was initially kept on the floor of the elevator will no longer remain on the floor as shown in the figure. This means that the block will be experiencing a free-fall motion and will be moving in the downward direction with an acceleration equal to acceleration due to gravity (i.e., g = 10 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$).
According to Kinematic Laws of motion,
${\text{s}} = {\text{ut}} + \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{a}}{{\text{t}}^2}{\text{ }} \to {\text{(1)}}$ where s denotes the distance travelled by the body, u denotes the initial velocity of the body, t denotes the time taken by the body and a denotes the acceleration of the body.
Let us take the downward direction as a positive direction.
Here, u = 0 m/s, a = 10 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ and t = 0.2 s
By putting the above values in equation (1), we get
Distance travelled by the block during the first 0.2 s after the start, ${\text{s}} = {\text{0}} \times {\text{0}}{\text{.2}} + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {10} \right){\left( {0.2} \right)^2} = \left( 5 \right)\left( {0.04} \right) = 0.2{\text{ m}} = 0.2 \times 100{\text{ cm}} = 20{\text{ cm}}$
Therefore, the distance travelled by the block during the first 0.2 s after the start is 20 cm.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note- In this problem (where $a > g$), if instead of 12 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ we are given with 9 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$ as the acceleration with which the elevator descends. Now we have $g > a$ case, so the block will remain on the floor of the elevator only. This means that the elevator and block descends with the same acceleration (i.e., 9 m/${{\text{s}}^2}$).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




