
A block is kept on a inclined plane of inclination θ of length l .The velocity of particle at the bottom of inclined is (the coefficient of friction is μ)
A. $\sqrt {\left[ {2gl\left( {\mu \cos \theta - \sin \theta } \right)} \right]} $
B. $\sqrt {\left[ {2gl\left( {\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta } \right)} \right]} $
C. $\sqrt {\left[ {2gl\left( {\sin \theta + \mu \cos \theta } \right)} \right]} $
D. $\sqrt {\left[ {2gl\left( {\cos \theta + \mu \sin \theta } \right)} \right]} $
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: This question utilizes the concept of mechanics and friction. First we draw the free body diagram and find the total acceleration acting on the body. Using the acceleration, we then proceed to find out the velocity of the particle at the bottom of the inclined plane.
Formulae used:
${v^2} = {u^2} + 2aS$
where \[v\] is the final velocity, $u$ is the initial velocity, $a$ is the acceleration and $S$ is the distance covered.
$f = \mu N$
where $f$ is the frictional force, $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction and $N$ is the normal
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given question, angle of inclination is $\theta $, Length of the plane $S = l$, Coefficient of friction is $\mu $ and Initial velocity is $u = 0$. Let normal be $N$.A free body diagram is drawn to understand the question better.
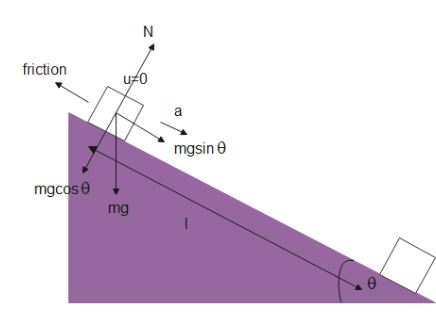
From the diagram, Total force on the block will be
$ \Rightarrow F = mg\sin \theta - f$
since $F = ma$ , we get
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{mg\sin \theta - f}}{m}$ -------(i)
where $f$ is the frictional force.
We know that
$f = \mu N$
From the figure,
$N = mg\cos \theta $
Thus, eq (i) becomes
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{mg\sin \theta - \mu mg\cos \theta }}{m} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{mg(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )}}{m} \\ $
$ \Rightarrow a = g(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )$ ----------------(ii)
Now, using the equation ${v^2} = {u^2} + 2aS$ and substituting the values, we have
$ \Rightarrow {v^2} = {(0)^2} + 2al$
Substituting the value of acceleration from eq (ii), we get
$\Rightarrow {v^2} = 2lg(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta ) \\
\therefore v = \sqrt {2gl(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )} \\ $
Therefore, the correct option is (B).
Note: Be extra careful when resolving a vector in inclined planes. Many times, students mix up $\sin \theta $ and $\cos \theta $ . This results in wrong answers. Also, remember that we have been asked about the velocity in the bottom of the inclined plane, so do not use the formula $v = u + at$ to find the velocity.
Formulae used:
${v^2} = {u^2} + 2aS$
where \[v\] is the final velocity, $u$ is the initial velocity, $a$ is the acceleration and $S$ is the distance covered.
$f = \mu N$
where $f$ is the frictional force, $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction and $N$ is the normal
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given question, angle of inclination is $\theta $, Length of the plane $S = l$, Coefficient of friction is $\mu $ and Initial velocity is $u = 0$. Let normal be $N$.A free body diagram is drawn to understand the question better.

From the diagram, Total force on the block will be
$ \Rightarrow F = mg\sin \theta - f$
since $F = ma$ , we get
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{mg\sin \theta - f}}{m}$ -------(i)
where $f$ is the frictional force.
We know that
$f = \mu N$
From the figure,
$N = mg\cos \theta $
Thus, eq (i) becomes
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{mg\sin \theta - \mu mg\cos \theta }}{m} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{mg(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )}}{m} \\ $
$ \Rightarrow a = g(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )$ ----------------(ii)
Now, using the equation ${v^2} = {u^2} + 2aS$ and substituting the values, we have
$ \Rightarrow {v^2} = {(0)^2} + 2al$
Substituting the value of acceleration from eq (ii), we get
$\Rightarrow {v^2} = 2lg(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta ) \\
\therefore v = \sqrt {2gl(\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta )} \\ $
Therefore, the correct option is (B).
Note: Be extra careful when resolving a vector in inclined planes. Many times, students mix up $\sin \theta $ and $\cos \theta $ . This results in wrong answers. Also, remember that we have been asked about the velocity in the bottom of the inclined plane, so do not use the formula $v = u + at$ to find the velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




