
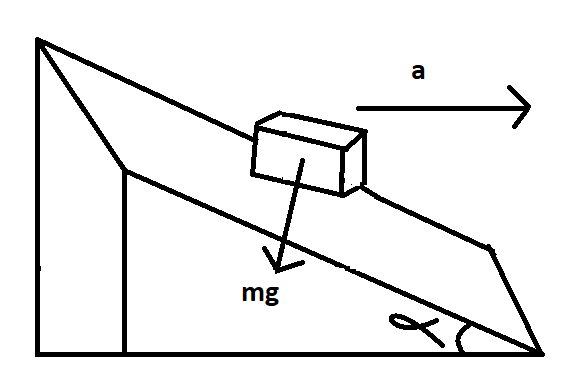
A block is kept on a frictionless inclined surface with an angle of inclination $\alpha $. The incline is given an acceleration ‘a’ to keep the block stationary, then ‘a’ is equal to.

Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint: The components of all the forces should be resolved by drawing a free body diagram. For the block moving with an acceleration ‘a’ a pseudo acceleration of equal magnitude acts on the inclined surface in the opposite direction.
Step by step answer:
The question involves the use of a free body placed on an inclined plane. The action and reaction forces acting on a body are always equal and in the opposite direction to each other. Here we will first draw a simplified Free body Diagram for the block kept on a frictionless inclined surface.
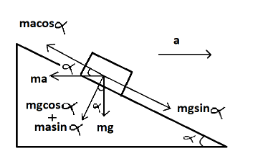
The angle of inclination is $\alpha $ and the mass of the block is given m. The force acting on the block vertically downward would be $mg$. On resolving the components of $mg$, we get $mg\sin \alpha $and $mg\cos \alpha $.
The inclination has an acceleration ‘a’ so there will be a pseudo force exerted by the block on the inclined surface acting in the opposite direction which is $ma$ . On resolving the components of $ma$ we get $ma\cos \alpha $and $ma\sin \alpha $.
We will equate the resolved components of forces $ma$and $mg$ acting on the block,
$R=mg\cos \theta $
$ma\cos \alpha =mg\sin \alpha $
$a=\dfrac{g\sin \alpha }{\cos \alpha }$
$a=g\tan \alpha $
Therefore, for the block to remain stationary the acceleration of the incline should be
$a=g\tan \alpha $
The correct answer is $a=g\tan \alpha $
Additional information:
For a body of mass m kept on an inclined plane at angle $\theta $ , normal reaction is given by $R=mg\cos \theta $
Note: While drawing the free body diagrams students should be careful with drawing the correct direction since it is an inclined plane. The weight $mg$ is straight downwards and the reaction force would be upwards perpendicular to the incline.
Step by step answer:
The question involves the use of a free body placed on an inclined plane. The action and reaction forces acting on a body are always equal and in the opposite direction to each other. Here we will first draw a simplified Free body Diagram for the block kept on a frictionless inclined surface.

The angle of inclination is $\alpha $ and the mass of the block is given m. The force acting on the block vertically downward would be $mg$. On resolving the components of $mg$, we get $mg\sin \alpha $and $mg\cos \alpha $.
The inclination has an acceleration ‘a’ so there will be a pseudo force exerted by the block on the inclined surface acting in the opposite direction which is $ma$ . On resolving the components of $ma$ we get $ma\cos \alpha $and $ma\sin \alpha $.
We will equate the resolved components of forces $ma$and $mg$ acting on the block,
$R=mg\cos \theta $
$ma\cos \alpha =mg\sin \alpha $
$a=\dfrac{g\sin \alpha }{\cos \alpha }$
$a=g\tan \alpha $
Therefore, for the block to remain stationary the acceleration of the incline should be
$a=g\tan \alpha $
The correct answer is $a=g\tan \alpha $
Additional information:
For a body of mass m kept on an inclined plane at angle $\theta $ , normal reaction is given by $R=mg\cos \theta $
Note: While drawing the free body diagrams students should be careful with drawing the correct direction since it is an inclined plane. The weight $mg$ is straight downwards and the reaction force would be upwards perpendicular to the incline.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




