
A block is in equilibrium. The tension in the string is $\left( {\mu < \tan \theta } \right)$
A. $mg\left( {\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta } \right)$
B. $mg\left( {\sin \theta + \mu \cos \theta } \right)$
C. $mg\sin \theta $
D. Zero

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: It is given in the question that the block is in equilibrium. An object will be at equilibrium when the linear momentum of its center of mass and the angular momentum about its center of mass will be constant. Here, we will resolve the weight $mg$ of the block to calculate the tension in the string.
Complete step by step answer:
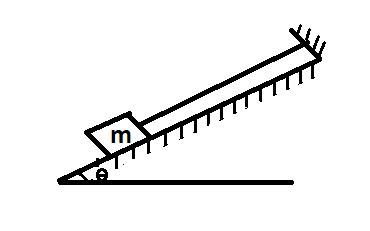
Consider a block of mass $m$ which is attached to a rigid support. This block is placed on an inclined plane which is making an angle $\theta $ with the surface. Let $mg$ be the weight of the block.
Now, if we resolve the weight $mg$ of the block into two components
$mg\,\cos \theta $ which is perpendicular to the plane of the block.
$mg\,\sin \theta $ which is along the plane of the block.
Now, the force along the inclined plane will be zero. Also, the force which is perpendicular to the inclined plane is also zero.
Now, let us denote the force in the upward direction of the mass $m$ as $N$ .
Therefore, for the direction of friction, the tendency of the motion of block is given by
$N = mg\,\cos \theta $
Now, if we cut the wire with which the block is attached to a rigid support. Therefore, the mass will move downward due to gravity.
Now, the tendency of the relative motion is $\mu N$ and it is opposite to the acceleration due to gravity.
Therefore, the tension $T$ in the block is given by
$T = mg\,\sin \theta - \mu \,mg\,\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \,T = mg\left( {\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta } \right)$
Therefore, the tension in the string is $mg\left( {\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta } \right)$ .
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
When the system will be in equilibrium, therefore, the tension in the string will be pointed away from the mass, that is, in the direction of the string.
When the system will be in equilibrium, the sum of all the forces will be zero.
$ \Rightarrow \,\sum F = 0$
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a block of mass $m$ which is attached to a rigid support. This block is placed on an inclined plane which is making an angle $\theta $ with the surface. Let $mg$ be the weight of the block.
Now, if we resolve the weight $mg$ of the block into two components
$mg\,\cos \theta $ which is perpendicular to the plane of the block.
$mg\,\sin \theta $ which is along the plane of the block.
Now, the force along the inclined plane will be zero. Also, the force which is perpendicular to the inclined plane is also zero.
Now, let us denote the force in the upward direction of the mass $m$ as $N$ .
Therefore, for the direction of friction, the tendency of the motion of block is given by
$N = mg\,\cos \theta $
Now, if we cut the wire with which the block is attached to a rigid support. Therefore, the mass will move downward due to gravity.
Now, the tendency of the relative motion is $\mu N$ and it is opposite to the acceleration due to gravity.
Therefore, the tension $T$ in the block is given by
$T = mg\,\sin \theta - \mu \,mg\,\cos \theta $
$ \Rightarrow \,T = mg\left( {\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta } \right)$
Therefore, the tension in the string is $mg\left( {\sin \theta - \mu \cos \theta } \right)$ .
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
When the system will be in equilibrium, therefore, the tension in the string will be pointed away from the mass, that is, in the direction of the string.
When the system will be in equilibrium, the sum of all the forces will be zero.
$ \Rightarrow \,\sum F = 0$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




