
A beaker with a liquid of density \[1.4\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] is in balance over one pan of weighing machine. If a solid of mass \[10\,{\text{g}}\] and density \[8\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] is now hung from the top of that pan with a thread and sinking fully in the liquid without touching the bottom, the extra weight to be put on the other pan for balance will be
A. \[10.0g\]
B. \[8.25g\]
C. \[11.75g\]
D. \[ - 1.75g\]

Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: Use Newton’s second law of motion. Calculate the upward thrust on the solid mass and the tension in the thread. These two forces together give the extra weight that should be added.
Formulae used:
The expression for Newton’s second law is
\[{F_{net}} = ma\] …… (1)
Here, \[{F_{net}}\] is the net force on the object, \[m\] is the mass of the object and \[a\] is the acceleration of the object.
The upward thrust \[F\] of an object in any fluid is
\[F = \rho Vg\] …… (2)
Here, \[\rho \] is the density of the liquid, \[V\] is the volume of the object and \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity.
The density \[\rho \] of an object is given by
\[\rho = \dfrac{m}{V}\] …… (3)
Here, \[m\] is the mass of the object and \[V\] is the volume of the object.
Complete step by step answer:
The density of the fluid in the liquid is \[1.4\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\]. When the beaker is placed on the weighing machine, the weight of the beaker is balanced. Then a solid mass is added in the liquid.
The mass of the solid mass is \[10\,{\text{g}}\] and its density is \[8\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\].
Calculate the extra weight that should be placed in the pan in order to again balance the weighing machine.
The forces acting on the solid mass in the liquid are shown in the following diagram:
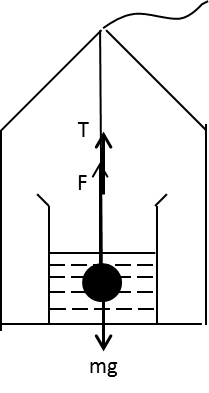
The weight \[mg\] of the mass acts in the downward direction, the tension \[T\] in the thread acts in the upward direction and the thrust \[F\] force on the mass in the liquid acts in the upward direction.
Since the solid mass is in a steady position in the liquid, it will have no acceleration.
Rewrite equation (3) for the density \[{\rho _m}\] of the solid mass.
\[{\rho _m} = \dfrac{m}{V}\]
Rearrange the above equation for the volume \[V\] of the solid mass.
\[V = \dfrac{m}{{{\rho _m}}}\]
Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the solid mass in the liquid.
\[T + F - mg = 0\] …… (4)
Calculate the upward thrust force \[F\] on the solid mass.
Substitute \[\dfrac{m}{{{\rho _m}}}\]for \[V\] in the above equation (3).
\[F = \rho \dfrac{m}{{{\rho _m}}}g\]
Substitute \[1.4\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] for \[\rho \], \[8\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] for \[{\rho _m}\] and \[10\,{\text{g}}\] for \[m\] in the above equation.
\[F = \left( {1.4\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}} \right)\dfrac{{10\,{\text{g}}}}{{8\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}}}g\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = 1.75g\]
Hence, the thrust force on the solid mass is \[1.75g\].
Rearrange equation (4) for \[T\].
\[T = mg - F\]
Substitute \[10\,{\text{g}}\] for \[m\] and \[1.75g\] for \[F\] in the above equation.
\[T = \left( {10\,{\text{g}}} \right)g - 1.75g\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = 8.25g\]
Hence, the tension in the thread is \[8.25g\].
Therefore, the extra weight \[W\] that should be added in other pan is
\[W = F + T\]
Substitute \[1.75g\] for \[F\] and \[8.25g\] for \[T\] in the above equation.
\[W = 1.75g + 8.25g\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = 10g\]
Therefore, the extra weight that should be added is \[10g\].
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:In the formula for the upward thrust, \[V\] is the volume of the solid mass in the liquid and not of the liquid.
Formulae used:
The expression for Newton’s second law is
\[{F_{net}} = ma\] …… (1)
Here, \[{F_{net}}\] is the net force on the object, \[m\] is the mass of the object and \[a\] is the acceleration of the object.
The upward thrust \[F\] of an object in any fluid is
\[F = \rho Vg\] …… (2)
Here, \[\rho \] is the density of the liquid, \[V\] is the volume of the object and \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity.
The density \[\rho \] of an object is given by
\[\rho = \dfrac{m}{V}\] …… (3)
Here, \[m\] is the mass of the object and \[V\] is the volume of the object.
Complete step by step answer:
The density of the fluid in the liquid is \[1.4\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\]. When the beaker is placed on the weighing machine, the weight of the beaker is balanced. Then a solid mass is added in the liquid.
The mass of the solid mass is \[10\,{\text{g}}\] and its density is \[8\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\].
Calculate the extra weight that should be placed in the pan in order to again balance the weighing machine.
The forces acting on the solid mass in the liquid are shown in the following diagram:

The weight \[mg\] of the mass acts in the downward direction, the tension \[T\] in the thread acts in the upward direction and the thrust \[F\] force on the mass in the liquid acts in the upward direction.
Since the solid mass is in a steady position in the liquid, it will have no acceleration.
Rewrite equation (3) for the density \[{\rho _m}\] of the solid mass.
\[{\rho _m} = \dfrac{m}{V}\]
Rearrange the above equation for the volume \[V\] of the solid mass.
\[V = \dfrac{m}{{{\rho _m}}}\]
Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the solid mass in the liquid.
\[T + F - mg = 0\] …… (4)
Calculate the upward thrust force \[F\] on the solid mass.
Substitute \[\dfrac{m}{{{\rho _m}}}\]for \[V\] in the above equation (3).
\[F = \rho \dfrac{m}{{{\rho _m}}}g\]
Substitute \[1.4\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] for \[\rho \], \[8\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\] for \[{\rho _m}\] and \[10\,{\text{g}}\] for \[m\] in the above equation.
\[F = \left( {1.4\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}} \right)\dfrac{{10\,{\text{g}}}}{{8\,{\text{g}} \cdot {\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}}}g\]
\[ \Rightarrow F = 1.75g\]
Hence, the thrust force on the solid mass is \[1.75g\].
Rearrange equation (4) for \[T\].
\[T = mg - F\]
Substitute \[10\,{\text{g}}\] for \[m\] and \[1.75g\] for \[F\] in the above equation.
\[T = \left( {10\,{\text{g}}} \right)g - 1.75g\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = 8.25g\]
Hence, the tension in the thread is \[8.25g\].
Therefore, the extra weight \[W\] that should be added in other pan is
\[W = F + T\]
Substitute \[1.75g\] for \[F\] and \[8.25g\] for \[T\] in the above equation.
\[W = 1.75g + 8.25g\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = 10g\]
Therefore, the extra weight that should be added is \[10g\].
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:In the formula for the upward thrust, \[V\] is the volume of the solid mass in the liquid and not of the liquid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




