
A bead of mass \[m\] can slide on a thin vertical rod, with sliding friction coefficient $\mu = 0.4$. The rod is translated horizontally with a constant acceleration $a$. For what value of $a$ will an observer on earth see equal horizontal and vertical components of the acceleration of the bead?
Answer
490.2k+ views
Hint: This question is based on the concept of sliding friction. So, in this question first we need to find the value of the horizontal and the vertical component of force and with the help of it, we need to find the horizontal and the vertical component of acceleration. Then we will equate the two components, as they are given equal in the question.
Complete step by step answer:
The diagram of this question is,
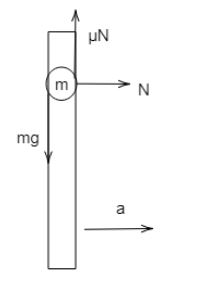
Given, the bead is sliding vertically down with friction which will oppose it.The following are the forces acting on the bead:
(A) The normal force $N$ exerted on it by the rod in the horizontal direction.
(B) The force of sliding friction $\mu N$ which acts vertically upward.
(C) Its weight $mg$ in the vertically downward direction.
Net force in the vertical direction ${F_V} = Mg - \mu N$.
Net force in the horizontal direction ${F_H} = Ma$.
The normal force is $N = ma$, as the normal force is acting in the horizontal direction.Now, we need the value of $a$ for which the observer on earth can see equal horizontal and vertical components of the acceleration of the bead. So, horizontal component of acceleration $ = $ vertical component of acceleration
$\dfrac{{Mg - \mu N}}{M} = \dfrac{{Ma}}{M}$
On putting $N = ma$,
$\dfrac{{Mg - \mu Ma}}{M} = \dfrac{{Ma}}{M}$
$\Rightarrow Mg - \mu Ma = Ma$
On cancelling $M$ on both the sides,
$g - \mu a = a$
$\Rightarrow a + \mu a = g$
On taking $a$ as common on LHS,
$a(1 + \mu ) = g$
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{g}{{1 + \mu }}$
We know that $g = 9.8\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$ and $\mu = 0.4$(given),
$a = \dfrac{{9.8}}{{1 + 0.4}}$
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{9.8}}{{1.4}}$
$\therefore a = 7\,{m}{s^2}$
Hence, the value of $a$ for which an observer on earth can see equal horizontal and vertical components of the acceleration of the bead is $a = 7\,{m}{s^2}$.
Note: Normal force is contact force. Normal force is also known as a normal reaction force. This force acts only when an object is in contact with another object. But if there is no contact between two objects then the normal force does not act. The SI unit of normal force is Newton.
Complete step by step answer:
The diagram of this question is,

Given, the bead is sliding vertically down with friction which will oppose it.The following are the forces acting on the bead:
(A) The normal force $N$ exerted on it by the rod in the horizontal direction.
(B) The force of sliding friction $\mu N$ which acts vertically upward.
(C) Its weight $mg$ in the vertically downward direction.
Net force in the vertical direction ${F_V} = Mg - \mu N$.
Net force in the horizontal direction ${F_H} = Ma$.
The normal force is $N = ma$, as the normal force is acting in the horizontal direction.Now, we need the value of $a$ for which the observer on earth can see equal horizontal and vertical components of the acceleration of the bead. So, horizontal component of acceleration $ = $ vertical component of acceleration
$\dfrac{{Mg - \mu N}}{M} = \dfrac{{Ma}}{M}$
On putting $N = ma$,
$\dfrac{{Mg - \mu Ma}}{M} = \dfrac{{Ma}}{M}$
$\Rightarrow Mg - \mu Ma = Ma$
On cancelling $M$ on both the sides,
$g - \mu a = a$
$\Rightarrow a + \mu a = g$
On taking $a$ as common on LHS,
$a(1 + \mu ) = g$
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{g}{{1 + \mu }}$
We know that $g = 9.8\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}$ and $\mu = 0.4$(given),
$a = \dfrac{{9.8}}{{1 + 0.4}}$
$\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{9.8}}{{1.4}}$
$\therefore a = 7\,{m}{s^2}$
Hence, the value of $a$ for which an observer on earth can see equal horizontal and vertical components of the acceleration of the bead is $a = 7\,{m}{s^2}$.
Note: Normal force is contact force. Normal force is also known as a normal reaction force. This force acts only when an object is in contact with another object. But if there is no contact between two objects then the normal force does not act. The SI unit of normal force is Newton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




