
A battery consists of a variable number ′n′ of identical cells (having internal resistance ′r′ each) which are connected in series. The terminals of the battery are short-circuited and the current I is measured. Which of the graphs shows the correct relationship between I and n?
A.
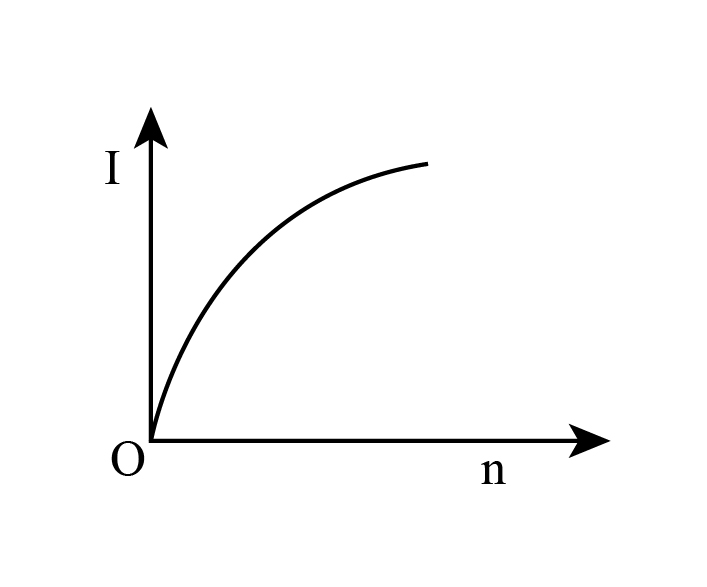
B.
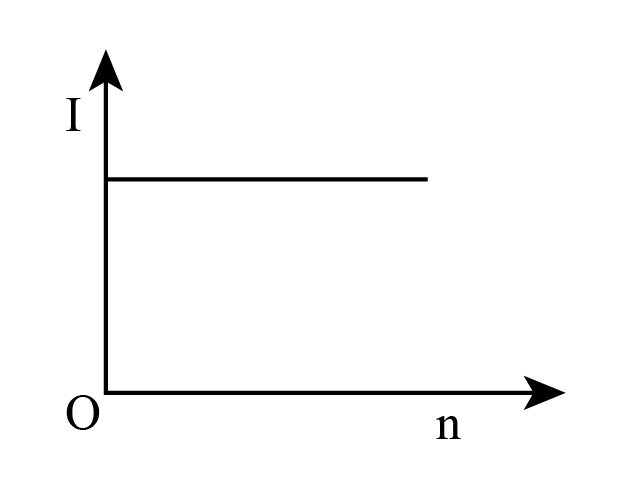
C.
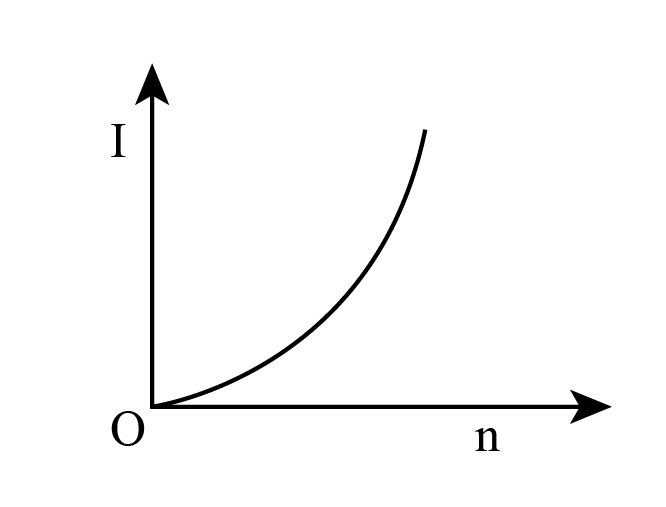
D.
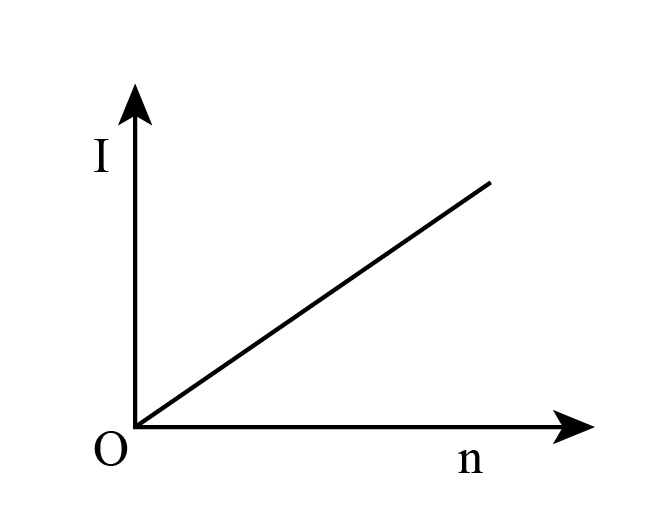




Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint:
The above problem can be resolved using the mathematical formula for the current through the cell. When the number of identical small cells, such that each of these cells is having the same value of internal resistance and the same magnitude of supplied voltage (E). Then the mathematical formula significantly shows that the current's magnitude is independent of the number of cells.
Complete step by step solution
The expression for the magnitude of current is,
\[I = \dfrac{{nE}}{r}\]
Here, n is the number of identical cells, E is the value of EMF of the cell, r is the value of internal resistance and I is the magnitude of current through the cell.
From the above given expression, it is clear that the magnitude of current is directly proportional to the magnitude of EMF and is inversely proportional to the internal resistance, by keeping the variable n as constant.
Then, the above expression is written in the form as,
\[\begin{array}{l}
I = \dfrac{{nE}}{r}\\
\Rightarrow I \propto \dfrac{E}{r}
\end{array}\]
The magnitude of current (I) does not depend on the number of identical cells (n), hence n is constant. Then the graph in option (B) represents the correct situation.
Therefore, the graph B is the correct graph and option (B) is correct.
Note:
Try to understand the meaning and concept involved in the formula for the EMF and the cell's internal resistance. Moreover, the fundamental relation is also useful in maintaining the automotive circuit’s design analysis and the components. Furthermore, it also has significance in the manufacturing of batteries.
The above problem can be resolved using the mathematical formula for the current through the cell. When the number of identical small cells, such that each of these cells is having the same value of internal resistance and the same magnitude of supplied voltage (E). Then the mathematical formula significantly shows that the current's magnitude is independent of the number of cells.
Complete step by step solution
The expression for the magnitude of current is,
\[I = \dfrac{{nE}}{r}\]
Here, n is the number of identical cells, E is the value of EMF of the cell, r is the value of internal resistance and I is the magnitude of current through the cell.
From the above given expression, it is clear that the magnitude of current is directly proportional to the magnitude of EMF and is inversely proportional to the internal resistance, by keeping the variable n as constant.
Then, the above expression is written in the form as,
\[\begin{array}{l}
I = \dfrac{{nE}}{r}\\
\Rightarrow I \propto \dfrac{E}{r}
\end{array}\]
The magnitude of current (I) does not depend on the number of identical cells (n), hence n is constant. Then the graph in option (B) represents the correct situation.
Therefore, the graph B is the correct graph and option (B) is correct.
Note:
Try to understand the meaning and concept involved in the formula for the EMF and the cell's internal resistance. Moreover, the fundamental relation is also useful in maintaining the automotive circuit’s design analysis and the components. Furthermore, it also has significance in the manufacturing of batteries.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




