
A balloon of gross weight W newton descends with an acceleration$fm/{s^2}$. The weight that must be thrown out in order to give the balloon an equal upward acceleration will be.
A. $\dfrac{{Wf}}{g}$
B. $\dfrac{{2Wf}}{g}$
C. $\dfrac{{2Wf}}{{(g + f)}}$
D. $\dfrac{{W(g + f)}}{f}$
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Initially balloon is descending with acceleration ($fm/{s^2}$.) other than acceleration due to gravity(g). That hints us that there is some other force acting on the balloon other than its weight. Since it is in air that force will be air fluid force or buoyancy force and let it be denoted by B. Now when we remove some mass(x) from the balloon it becomes lighter and starts moving up. By free body diagram and equating forces we can solve this question.
Complete step by step answer:
Initial weight be W and buoyancy force is B.
W acts in downward direction while B acts in upward direction and it is clear that W is dominating initially as the balloon is moving downward.
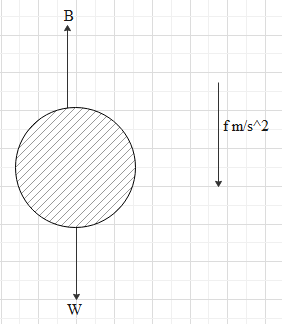
By balancing forces we get
$W - B = \dfrac{W}{g}f$ …eq 1
Where $\dfrac{W}{g}$ is initial mass before removing weight
Let us assume ‘x’ mass is removed from balloon and it started moving up with same acceleration then mass becomes $\dfrac{W}{g} - x$
Equation will be
$B - (\dfrac{W}{g} - x)g = (\dfrac{W}{g} - x)f$ …eq 2
By adding eq 1 and eq 2 we get
$\eqalign{
& xg = 2\dfrac{W}{g}f - xf \cr
& x(g + f) = 2\dfrac{W}{g}f \cr
& x = \dfrac{{2\dfrac{W}{g}f}}{{(g + f)}} \cr} $
Since they asked us to find out the weight removed we multiply mass removed with ‘g’ to get weight
So weight is
$xg = \dfrac{{2Wf}}{{(g + f)}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Generally in case of fluids it is assumed that buoyancy force is always in upward direction. But that convention is false. It is always directed from high pressure to low pressure or high force region to low force region. Here since at lower altitudes pressure is higher than higher altitude pressure buoyancy is directed upwards.
Complete step by step answer:
Initial weight be W and buoyancy force is B.
W acts in downward direction while B acts in upward direction and it is clear that W is dominating initially as the balloon is moving downward.

By balancing forces we get
$W - B = \dfrac{W}{g}f$ …eq 1
Where $\dfrac{W}{g}$ is initial mass before removing weight
Let us assume ‘x’ mass is removed from balloon and it started moving up with same acceleration then mass becomes $\dfrac{W}{g} - x$
Equation will be
$B - (\dfrac{W}{g} - x)g = (\dfrac{W}{g} - x)f$ …eq 2
By adding eq 1 and eq 2 we get
$\eqalign{
& xg = 2\dfrac{W}{g}f - xf \cr
& x(g + f) = 2\dfrac{W}{g}f \cr
& x = \dfrac{{2\dfrac{W}{g}f}}{{(g + f)}} \cr} $
Since they asked us to find out the weight removed we multiply mass removed with ‘g’ to get weight
So weight is
$xg = \dfrac{{2Wf}}{{(g + f)}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Generally in case of fluids it is assumed that buoyancy force is always in upward direction. But that convention is false. It is always directed from high pressure to low pressure or high force region to low force region. Here since at lower altitudes pressure is higher than higher altitude pressure buoyancy is directed upwards.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




