
A balloon filled with hydrogen gas is carried from earth to moon. Then the balloon will:
A. Neither fall nor rise
B. Fall with acceleration less than g
C. Fall with acceleration g
D. Rise with acceleration g
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to comment on the motion of the balloon filled with hydrogen gas and is carried from the earth to the moon. For this, we will use the concept that the gravity on the moon is one-sixth that of earth’s gravity.
Complete step by step answer:
Let the mass on the balloon be m
It is said that the balloon is initially carried from earth’s surface so a gravity g will act on the balloon and a force due to gravity will be acting downwards. Since the balloon has some air in so due to atmospheric pressure, a buoyant force acts on the balloon as shown in the diagram below.
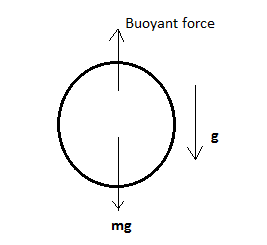
So the acceleration in the balloon will be equal to \[a = \dfrac{{mg - {F_B}}}{m} - - (i)\]
Now it is said that the balloon rises up to the moon and as we know that there is no environment present on the moon so there will be no atmospheric pressure acting on the balloon so there will be no buoyant force acting on the balloon and since gravity on the moon is one-sixth that of earth’s gravity as shown in the diagram.
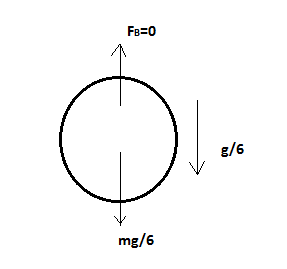
Now since no buyout force is acting on the balloon, hence we can say the balloon will fall with acceleration less than g.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Students must note that whenever an object or the balloon is descending a buyout force acts on the balloon in the upward direction and when the balloon rises up then the buyout force acts in the upward direction.
Complete step by step answer:
Let the mass on the balloon be m
It is said that the balloon is initially carried from earth’s surface so a gravity g will act on the balloon and a force due to gravity will be acting downwards. Since the balloon has some air in so due to atmospheric pressure, a buoyant force acts on the balloon as shown in the diagram below.

So the acceleration in the balloon will be equal to \[a = \dfrac{{mg - {F_B}}}{m} - - (i)\]
Now it is said that the balloon rises up to the moon and as we know that there is no environment present on the moon so there will be no atmospheric pressure acting on the balloon so there will be no buoyant force acting on the balloon and since gravity on the moon is one-sixth that of earth’s gravity as shown in the diagram.

Now since no buyout force is acting on the balloon, hence we can say the balloon will fall with acceleration less than g.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Students must note that whenever an object or the balloon is descending a buyout force acts on the balloon in the upward direction and when the balloon rises up then the buyout force acts in the upward direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




