
A ball of mass $m$ is hung on a thread. The thread is taut and horizontal and the ball is released as shown. Find the tension in the string when it becomes vertical. Also, determine the angle between the thread and the vertical at which the tension in the string becomes equal to the weight in magnitude.


Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint:As the ball is released from its horizontal position, the ball will swing to and fro about its vertical axis. The weight of the ball will be directed downwards and the tension in the string will be directed upwards along the string but making an angle $\theta $ with the vertical, except when the mass is vertically below.
Formula used:
The magnitude of the weight of a body is given by, $W = mg$ where $m$ is the mass of the body and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch a figure depicting the motion of the ball when it is released.

Figure 1 represents the initial position of the ball of mass $m$. The ball is held horizontal before releasing.

Figure 2 represents the motion of the ball once it is released at some distance from its initial position. Here the weight of the ball is directed downwards but the tension in the string makes an angle $\theta $ with the vertical. So the tension will be equal to the cosine component of the weight of the ball i.e., $T = W\cos \theta $ .
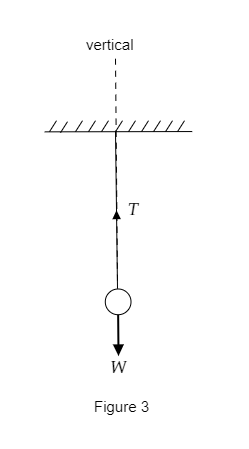
Figure 3 represents the position of the ball when the string is vertical. Here we see that the tension is directed upwards and the weight is directed downwards.
So at this position, the tension in the string will be equal in magnitude to the weight of the ball.
i.e., $T = W$
The weight of the ball can be expressed as $W = mg$ .
So at the vertical, we have $T = mg$ .
In figure 3 we also observe that the angle made by the string with the vertical has reduced to zero i.e. $\theta = 0^\circ $ as the string and the vertical are parallel to each other.
So the angle between the thread and the vertical is zero when the tension equals the magnitude of the weight of the ball.
Note:When the thread was held horizontal, the thread and the vertical were perpendicular to each other. The mass swings back and forth about the vertical because of the restoring force. The restoring force urges the mass to return to its initial position and it is directed opposite to the angular displacement $\theta $.
Formula used:
The magnitude of the weight of a body is given by, $W = mg$ where $m$ is the mass of the body and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch a figure depicting the motion of the ball when it is released.

Figure 1 represents the initial position of the ball of mass $m$. The ball is held horizontal before releasing.

Figure 2 represents the motion of the ball once it is released at some distance from its initial position. Here the weight of the ball is directed downwards but the tension in the string makes an angle $\theta $ with the vertical. So the tension will be equal to the cosine component of the weight of the ball i.e., $T = W\cos \theta $ .

Figure 3 represents the position of the ball when the string is vertical. Here we see that the tension is directed upwards and the weight is directed downwards.
So at this position, the tension in the string will be equal in magnitude to the weight of the ball.
i.e., $T = W$
The weight of the ball can be expressed as $W = mg$ .
So at the vertical, we have $T = mg$ .
In figure 3 we also observe that the angle made by the string with the vertical has reduced to zero i.e. $\theta = 0^\circ $ as the string and the vertical are parallel to each other.
So the angle between the thread and the vertical is zero when the tension equals the magnitude of the weight of the ball.
Note:When the thread was held horizontal, the thread and the vertical were perpendicular to each other. The mass swings back and forth about the vertical because of the restoring force. The restoring force urges the mass to return to its initial position and it is directed opposite to the angular displacement $\theta $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




