
A ball of mass 0.4 kg hits a brick wall. The ball strikes when it is moving horizontally to the left at $30m{{s}^{-1}}$ and rebounds horizontal at $20m{{s}^{-1}}$. Find the impulse of the force exerted on the ball by the wall.
$\text{A}\text{. 20Ns}$
$\text{B}\text{. 4Ns}$
$\text{C}\text{. 14 Ns}$
$\text{D}\text{. 8Ns}$
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: When a large force acts on a body for short time duration, the change it produces in its momentum is known as impulse. In our daily life, we come across many problems where force and time are difficult to ascertain separately. The impulse, in such cases, becomes an important measurable quantity.
Impulse can be calculated by determining change in momentum of the ball after rebounding from the wall.
Formula Used:
Impulse $\vec{I}=m\Delta \vec{v}$
Complete answer:
Impulse is the change in momentum produced, when a large force acts on a body for a short period of time. In such cases, it is difficult to determine force and time duration separately. That is where impulse comes into play as change in momentum can be calculated. Mathematically, we can write impulse
$\vec{I}=m\Delta \vec{v}$
Where m is the mass of the body and $\Delta \vec{v}$ is the change in the velocity vector.
We are given that mass of the ball is 0.4 kg, its initial velocity, $30m{{s}^{-1}}$ and final velocity, $20m{{s}^{-1}}$ in direction opposite to initial velocity.
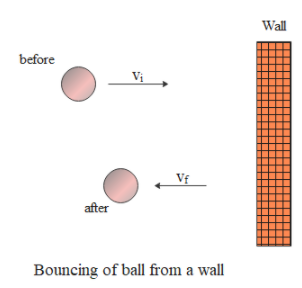
Therefore change in velocity of the ball
$\Delta \vec{v}={{\vec{v}}_{f}}-{{\vec{v}}_{i}}$
Assuming direction of initial velocity as positive, we get
$\Delta \vec{v}=(-20m{{s}^{-1}})-30m{{s}^{-1}}=-50m{{s}^{-1}}$
We substitute this result and get
$\vec{I}=(0.4kg)\times (-50m{{s}^{-1}})$
$\vec{I}=-20\text{ }kg\text{ }m{{s}^{-1}}=-20Ns$
Thus the impulse of the force exerted by brick wall on the ball is
$\Rightarrow \left| {\vec{I}} \right|=20Ns$
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:
Velocity is a vector quantity and when it bounces back from the wall its direction changes. Thus, when we calculate change in velocity vector, direction must be considered.
Since, momentum is a vector quantity, impulse is also a vector.
Impulse can be calculated by determining change in momentum of the ball after rebounding from the wall.
Formula Used:
Impulse $\vec{I}=m\Delta \vec{v}$
Complete answer:
Impulse is the change in momentum produced, when a large force acts on a body for a short period of time. In such cases, it is difficult to determine force and time duration separately. That is where impulse comes into play as change in momentum can be calculated. Mathematically, we can write impulse
$\vec{I}=m\Delta \vec{v}$
Where m is the mass of the body and $\Delta \vec{v}$ is the change in the velocity vector.
We are given that mass of the ball is 0.4 kg, its initial velocity, $30m{{s}^{-1}}$ and final velocity, $20m{{s}^{-1}}$ in direction opposite to initial velocity.

Therefore change in velocity of the ball
$\Delta \vec{v}={{\vec{v}}_{f}}-{{\vec{v}}_{i}}$
Assuming direction of initial velocity as positive, we get
$\Delta \vec{v}=(-20m{{s}^{-1}})-30m{{s}^{-1}}=-50m{{s}^{-1}}$
We substitute this result and get
$\vec{I}=(0.4kg)\times (-50m{{s}^{-1}})$
$\vec{I}=-20\text{ }kg\text{ }m{{s}^{-1}}=-20Ns$
Thus the impulse of the force exerted by brick wall on the ball is
$\Rightarrow \left| {\vec{I}} \right|=20Ns$
Hence, option A is correct.
Note:
Velocity is a vector quantity and when it bounces back from the wall its direction changes. Thus, when we calculate change in velocity vector, direction must be considered.
Since, momentum is a vector quantity, impulse is also a vector.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




