
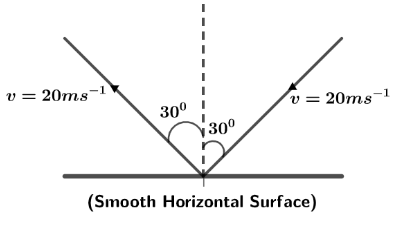
A ball moving with speed $20\,m{s^{ - 1}}$ collides with a smooth surface as shown in the figure. The magnitude of change in velocity of the ball will be
A. $10\sqrt 3 \,m{s^{ - 1}}$
B. $20\sqrt 3\,m{s^{ - 1}} $
C. $\dfrac{{40}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\,m{s^{ - 1}}$
D. $40\,m{s^{ - 1}}$

Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this question, we will calculate the velocities in vector form in two dimensional Cartesian XY plane and then resolve its components in each direction in both initial and final velocities then will find the change in velocity hence using magnitude formula, we will find the magnitude of change in velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw the components of initial and final velocities in free body diagram, we can see from the geometry of diagram such that,
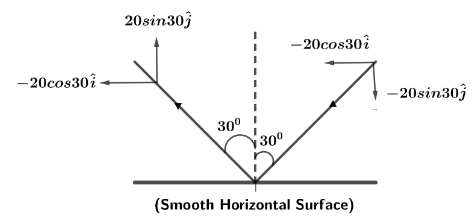
Initial velocity in vector form can be written as
${v_{initial}} = ( - 20\sin {30^0}\hat i - 20\cos {30^0}\hat j)$
Since, X component and the Y component both are in negative direction.
Now, the final velocity from the diagram can be written in vector form as
${v_{final}} = ( - 20\sin {30^0}\hat i + 20\cos {30^0}\hat j)$
Now, as we need to find the change in velocity which can be written as
Change in velocity $\Delta v = {v_{final}} - {v_{initial}}$ or
$\Delta v = ( - 20\sin {30^0}\hat i + 20\cos {30^0}\hat j) - ( - 20\sin {30^0}\hat i - 20\cos {30^0}\hat j)$
$\Rightarrow \Delta v = 40\cos {30^0}\hat j$
Put the value of $\cos {30^0} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$ we get
$\Delta v = 40 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\hat j$
$\Rightarrow \Delta v = 20\sqrt 3 \hat j$
Now, the magnitude of change in velocity can be written as
$\left| {\Delta v} \right| = 20\sqrt 3 $
So, the change in velocity of the ball is $\left| {\Delta v} \right| = 20\sqrt 3 $.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: It should be remembered that, the velocity component in Y direction only changes while ball continues to move with same velocity in X direction, and if a vector is written in the form of $\vec v = a\hat i + b\hat j + c\hat k$ , then the magnitude of this vector is calculated by the formulas as $\left| {\vec v} \right| = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} $.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw the components of initial and final velocities in free body diagram, we can see from the geometry of diagram such that,

Initial velocity in vector form can be written as
${v_{initial}} = ( - 20\sin {30^0}\hat i - 20\cos {30^0}\hat j)$
Since, X component and the Y component both are in negative direction.
Now, the final velocity from the diagram can be written in vector form as
${v_{final}} = ( - 20\sin {30^0}\hat i + 20\cos {30^0}\hat j)$
Now, as we need to find the change in velocity which can be written as
Change in velocity $\Delta v = {v_{final}} - {v_{initial}}$ or
$\Delta v = ( - 20\sin {30^0}\hat i + 20\cos {30^0}\hat j) - ( - 20\sin {30^0}\hat i - 20\cos {30^0}\hat j)$
$\Rightarrow \Delta v = 40\cos {30^0}\hat j$
Put the value of $\cos {30^0} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$ we get
$\Delta v = 40 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}\hat j$
$\Rightarrow \Delta v = 20\sqrt 3 \hat j$
Now, the magnitude of change in velocity can be written as
$\left| {\Delta v} \right| = 20\sqrt 3 $
So, the change in velocity of the ball is $\left| {\Delta v} \right| = 20\sqrt 3 $.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: It should be remembered that, the velocity component in Y direction only changes while ball continues to move with same velocity in X direction, and if a vector is written in the form of $\vec v = a\hat i + b\hat j + c\hat k$ , then the magnitude of this vector is calculated by the formulas as $\left| {\vec v} \right| = \sqrt {{a^2} + {b^2} + {c^2}} $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




