
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. After some time, it returns to the thrower. Draw the velocity time-graph and speed-time graph.
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: As we know that velocity is a vector quantity and speed is a scalar quantity. As we throw the ball up in the sky, the direction of its velocity is upwards until it reaches its maximum height. In that span the magnitude of the ball's velocity will decrease with time. Which can be given by the equation \[v = u + at\].
Complete step-by-step solution:As we have discussed that speed is scalar and velocity is vector i.e. it has both direction and magnitude. It means speed will always be positive but velocity can be negative (depending on the sign convention).
According to the first equation of motion \[v = u + at\] .
It clarifies that whenever acceleration is there the change in velocity is linearly dependent on time.
Where:
\[v\] is velocity after time t.
\[a\] acceleration of the body
\[u\] initial velocity of the body
\[t\] is the time in seconds.
Suppose initial velocity is \[u\] and \[g\] be acceleration due to gravity and taking upward as positive.
Then velocity can be given as:
\[v = u + gt\]
Thus, from this relation we can plot the graphs.
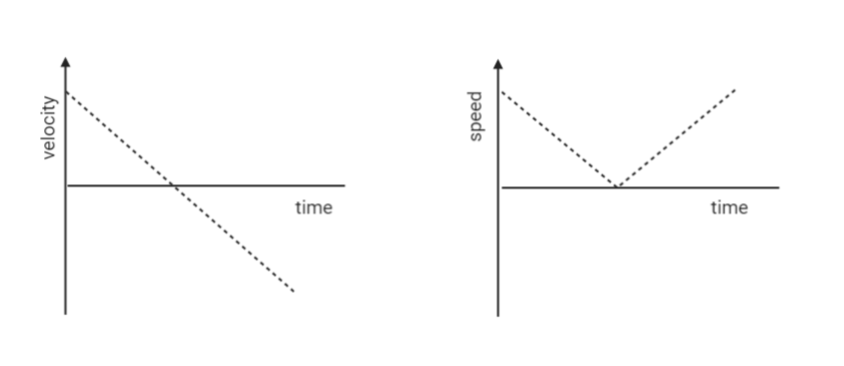
Note:- Points to remember while solving such questions:
- Objects that are projected from, and land on the same horizontal surface will have a vertically symmetrical path.
- The time it takes from an object to be projected and land is called the time of flight. This depends on the initial velocity of the projectile and the angle of projection.
- When the projectile reaches an upward vertical velocity of zero, that’s the maximum height of the projectile and then gravity will take the object downward.
- The horizontal displacement of the projectile is called the range of the projectile, and depends on the initial velocity of the object.
Complete step-by-step solution:As we have discussed that speed is scalar and velocity is vector i.e. it has both direction and magnitude. It means speed will always be positive but velocity can be negative (depending on the sign convention).
According to the first equation of motion \[v = u + at\] .
It clarifies that whenever acceleration is there the change in velocity is linearly dependent on time.
Where:
\[v\] is velocity after time t.
\[a\] acceleration of the body
\[u\] initial velocity of the body
\[t\] is the time in seconds.
Suppose initial velocity is \[u\] and \[g\] be acceleration due to gravity and taking upward as positive.
Then velocity can be given as:
\[v = u + gt\]
Thus, from this relation we can plot the graphs.

Note:- Points to remember while solving such questions:
- Objects that are projected from, and land on the same horizontal surface will have a vertically symmetrical path.
- The time it takes from an object to be projected and land is called the time of flight. This depends on the initial velocity of the projectile and the angle of projection.
- When the projectile reaches an upward vertical velocity of zero, that’s the maximum height of the projectile and then gravity will take the object downward.
- The horizontal displacement of the projectile is called the range of the projectile, and depends on the initial velocity of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




