
A ball is thrown vertically upward; it has a speed of 10m/s when it has reached one half of its maximum height. How high does the ball rise? (Taking $g = 10m/{s^2}$)
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint – To solve such types of questions we need to solve using equations of motion. We will put the final velocity zero and calculate the height by putting the value of height half of the maximum height using the variable h and use the information provided in the problem to get the right answer.
Formula used: ${v^2} - {u^2} = 2as$
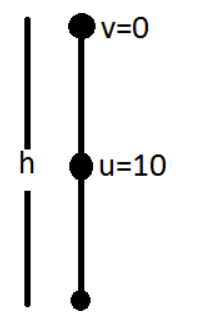
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, initial speed of ball=10m/s
Let the maximum height be h.
We know that, ${v^2} - {u^2} = 2as$
Putting the value of v= 0, u = 10, a = g = 10, ${\text{s = }}\dfrac{{\text{h}}}{{\text{2}}}$.
$
0 = {u^2} - 2g(h/2) \\
h = \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{g} = \dfrac{{{{(10)}^2}}}{{10}} = 10m \\
$
Hence, the answer to this question is 10m.
Note – In such types of questions, we should consider the upper ward direction as positive and downward direction negative. Displacement in the nth second, $S = u + \dfrac{a}{2}(2n - 1)$. We need to use equations of motion when the acceleration is constant. Since, acceleration due to gravity is constant on earth so we have used equations of motion. Equations of motion are: $v = u + at,\,\,S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2},\,\,{v^2} - {u^2} = 2as$.
We suggest students to know the derivation of these equations. It will clear your concept more deeply and knowing these equations will help you further.
Formula used: ${v^2} - {u^2} = 2as$

Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, initial speed of ball=10m/s
Let the maximum height be h.
We know that, ${v^2} - {u^2} = 2as$
Putting the value of v= 0, u = 10, a = g = 10, ${\text{s = }}\dfrac{{\text{h}}}{{\text{2}}}$.
$
0 = {u^2} - 2g(h/2) \\
h = \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{g} = \dfrac{{{{(10)}^2}}}{{10}} = 10m \\
$
Hence, the answer to this question is 10m.
Note – In such types of questions, we should consider the upper ward direction as positive and downward direction negative. Displacement in the nth second, $S = u + \dfrac{a}{2}(2n - 1)$. We need to use equations of motion when the acceleration is constant. Since, acceleration due to gravity is constant on earth so we have used equations of motion. Equations of motion are: $v = u + at,\,\,S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2},\,\,{v^2} - {u^2} = 2as$.
We suggest students to know the derivation of these equations. It will clear your concept more deeply and knowing these equations will help you further.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




