
A ball is projected from a point on the floor with a speed of $ 15{\text{ m/s}} $ at an angle of $ {60^ \circ } $ with the horizontal. Will it hit a vertical wall $ 5{\text{ m}} $ away from the point of projection and perpendicular to the plane of projection without hitting the floor? Will the answer differ if the wall is $ {\text{22 m}} $ away?
Answer
478.2k+ views
Hint: In this question, a ball is projected, and we need to find out will it hit a vertical wall at a certain distance away from the point of projection. To solve this question, we need to find the range of the projectile. If the range of a projectile is greater than the distance of the wall from the point of projection, then the ball hits the wall else it will hit the floor first
Horizontal Range of a projectile, $ {\text{R = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{u}}^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g} $
Where $ {\text{u}} $ is the velocity of the projection
$ \theta $ is the angle of projectile with the horizontal
$ g = 9.8{\text{ m/}}{{\text{s}}^2} $ (Acceleration due to gravity).
Complete answer:
We are given,
The velocity of the projection of ball, $ {\text{u}} = 15{\text{ m/s}} $
The angle of projection of the ball, $ \theta = {60^ \circ } $
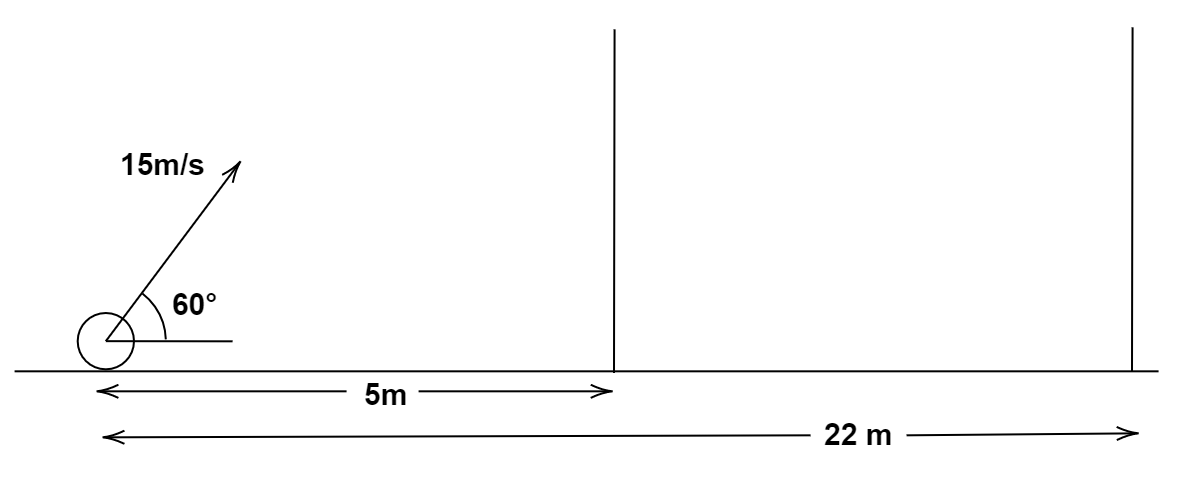
We need to find out if the ball hits the vertical wall at a distance of $ 5{\text{ m}} $ away from the point of projection.
If the range of the projectile is greater than $ 5{\text{ m}} $ then the projectile hits the wall else, it does not hit the wall.
Thus, we need to find out the range of the projectile of the ball
Range, $ {\text{R = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{u}}^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g} $
Now substituting the values in the formula we get,
$ R = \dfrac{{{{\left( {15} \right)}^2}\sin {{120}^ \circ }}}{{9.8}} $
Substituting $ \sin {120^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{225 \times \sqrt 3 }}{{2 \times 9.8}} $
On solving we get,
$ R = 19.88{\text{ m}} $
As the range $ R $ is greater than $ 5{\text{ m}} $ the ball will definitely hit the vertical wall
For the second part of the question,
The wall is placed at a distance of $ {\text{22 m}} $ from the point of projection
Since the range of a projectile of ball, $ R = 19.88{\text{ m}} $ is less than $ {\text{22 m}} $ so the wall is not within the horizontal range of the ball
Hence, the ball will not hit the wall in the second case.
Note:
The horizontal range value is maximum if the angle of projection $ \theta = {45^ \circ } $ and for the same value of initial velocity horizontal range of a projectile for complementary angle is same. The formula $ {\text{R = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{u}}^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g} $ is only valid for the case when projectile is projected obliquely on the surface of the earth.
Horizontal Range of a projectile, $ {\text{R = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{u}}^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g} $
Where $ {\text{u}} $ is the velocity of the projection
$ \theta $ is the angle of projectile with the horizontal
$ g = 9.8{\text{ m/}}{{\text{s}}^2} $ (Acceleration due to gravity).
Complete answer:
We are given,
The velocity of the projection of ball, $ {\text{u}} = 15{\text{ m/s}} $
The angle of projection of the ball, $ \theta = {60^ \circ } $

We need to find out if the ball hits the vertical wall at a distance of $ 5{\text{ m}} $ away from the point of projection.
If the range of the projectile is greater than $ 5{\text{ m}} $ then the projectile hits the wall else, it does not hit the wall.
Thus, we need to find out the range of the projectile of the ball
Range, $ {\text{R = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{u}}^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g} $
Now substituting the values in the formula we get,
$ R = \dfrac{{{{\left( {15} \right)}^2}\sin {{120}^ \circ }}}{{9.8}} $
Substituting $ \sin {120^ \circ } = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} $
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{225 \times \sqrt 3 }}{{2 \times 9.8}} $
On solving we get,
$ R = 19.88{\text{ m}} $
As the range $ R $ is greater than $ 5{\text{ m}} $ the ball will definitely hit the vertical wall
For the second part of the question,
The wall is placed at a distance of $ {\text{22 m}} $ from the point of projection
Since the range of a projectile of ball, $ R = 19.88{\text{ m}} $ is less than $ {\text{22 m}} $ so the wall is not within the horizontal range of the ball
Hence, the ball will not hit the wall in the second case.
Note:
The horizontal range value is maximum if the angle of projection $ \theta = {45^ \circ } $ and for the same value of initial velocity horizontal range of a projectile for complementary angle is same. The formula $ {\text{R = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{u}}^2}\sin 2\theta }}{g} $ is only valid for the case when projectile is projected obliquely on the surface of the earth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




