
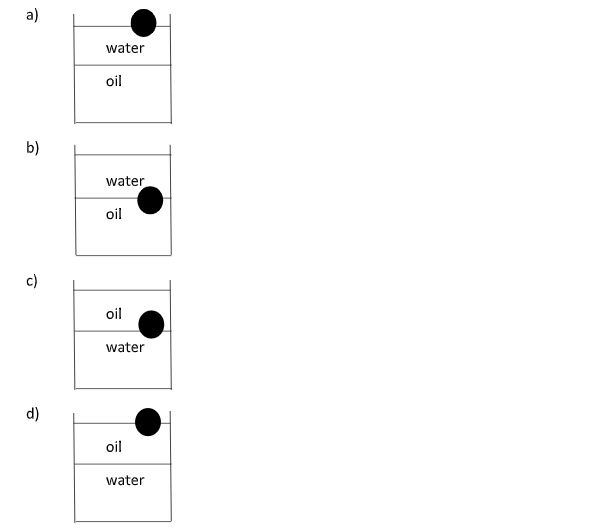
A ball is made of a material of density $\rho $ where ${\rho _{oil}} < \rho < {\rho _{water}}$ . Here ${\rho _{oil}}$ and ${\rho _{water}}$ represent the densities of oil and water respectively and they are immiscible. The ball is in equilibrium in a mixture of oil and water. Represent the equilibrium position of the ball in the mixture.

Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: A body will sink in a fluid if the density of the body is greater than that of the fluid and it will float on the surface of the fluid if the body’s density is less than the density of the fluid.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Explain the equilibrium position of the ball in the oil-water mixture using the Archimedes’ principle.
A ball of density $\rho $ is placed in an oil-water mixture. It is given that the ball’s density is less than the density of water, i.e., $\rho < {\rho _{water}}$ , also the density of the ball is more than the density of oil, i.e., $\rho > {\rho _{oil}}$ .
Archimedes’ principle states that the buoyant force acting upward on a body which is fully or partially immersed in a fluid (liquid or gas) will be equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body.
This suggests that when a denser object is immersed in a fluid, the weight of the fluid displaced by the object will be more than the upward buoyant force acting on it and thus the object sinks in the fluid. When a less dense object is immersed in a fluid, the weight displaced by the object will be less than the upward buoyant force and thus the less dense object floats on the surface of the fluid.
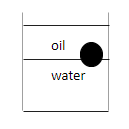
Here, according to the Archimedes’ principle, the ball will float on the surface of the water and it will sink in oil since, ${\rho _{oil}} < \rho < {\rho _{water}}$ .
Therefore, the correct representation of the equilibrium position of the ball in the oil-water mixture will be option (C).
Note:
The density of an object is its mass per unit volume. If an object is heavy for its size it will have a high density (eg: pebble) and if an object is lighter for its size it will have less density (eg: popcorn). The density of an object determines if it sinks or not.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Explain the equilibrium position of the ball in the oil-water mixture using the Archimedes’ principle.
A ball of density $\rho $ is placed in an oil-water mixture. It is given that the ball’s density is less than the density of water, i.e., $\rho < {\rho _{water}}$ , also the density of the ball is more than the density of oil, i.e., $\rho > {\rho _{oil}}$ .
Archimedes’ principle states that the buoyant force acting upward on a body which is fully or partially immersed in a fluid (liquid or gas) will be equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body.
This suggests that when a denser object is immersed in a fluid, the weight of the fluid displaced by the object will be more than the upward buoyant force acting on it and thus the object sinks in the fluid. When a less dense object is immersed in a fluid, the weight displaced by the object will be less than the upward buoyant force and thus the less dense object floats on the surface of the fluid.
Here, according to the Archimedes’ principle, the ball will float on the surface of the water and it will sink in oil since, ${\rho _{oil}} < \rho < {\rho _{water}}$ .
Therefore, the correct representation of the equilibrium position of the ball in the oil-water mixture will be option (C).

Note:
The density of an object is its mass per unit volume. If an object is heavy for its size it will have a high density (eg: pebble) and if an object is lighter for its size it will have less density (eg: popcorn). The density of an object determines if it sinks or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




