
A ball is held at rest in position A in figure by two light cords. The horizontal cord is cut and the ball starts swinging as a pendulum. The ratio of the tension in the supporting cord in position B, to that in position A is
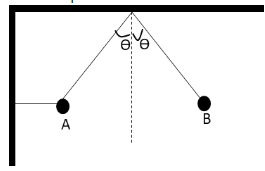
A. \[{\sin ^2}\theta \]
B. \[{\cos ^2}\theta \]
C. \[{\tan ^2}\theta \]
D. $1:1$

Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: Draw the free body diagram of the balls in position A and B. Use the expression for Newton’s second law of motion. Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the balls in at positions A and B and determine the values of tensions in the cords and then take the ratio of these tensions in the asked manner to calculate the final answer.
Formula used:
The expression for Newton’s second law of motion is
\[{F_{net}} = ma\]
Here, \[{F_{net}}\] is net force acting on the object, \[m\] is mass of the object and \[a\] is acceleration of the object.
Complete step by step answer:
Let \[m\] be the mass of the two balls. Let us draw the free body diagram of the two balls is as follows:
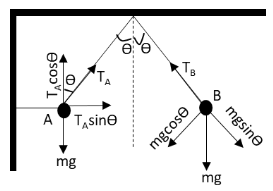
In the above free body diagram, \[mg\] is the weight of the two balls, \[{T_A}\] is the tension in the cord holding the ball at position A and \[{T_B}\] is the tension in the cord holding the ball at position B.
Let is apply Newton’s second law of motion to the ball at position A.
\[{T_A}\cos \theta = mg\]
\[ \Rightarrow {T_A} = \dfrac{{mg}}{{\cos \theta }}\]
Let is apply Newton’s second law of motion to the ball at position B.
\[{T_B} = mg\cos \theta \]
Now let us determine the ratio of the tensions in the cords.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{T_B}}}{{{T_A}}} = \dfrac{{mg\cos \theta }}{{\dfrac{{mg}}{{\cos \theta }}}}\]
\[ \therefore \dfrac{{{T_B}}}{{{T_A}}} = {\cos ^2}\theta \]
Therefore, the ratio of the tension in the cord in position B to that in position A is \[{\cos ^2}\theta \].
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The students should be careful while drawing the free body diagram of eh balls at positions A and B. If this free body diagram is not drawn correctly with the correct directions and positions of all the forces then the expressions for the tensions in the cords will be incorrect and hence the final answer will also be incorrect.
Formula used:
The expression for Newton’s second law of motion is
\[{F_{net}} = ma\]
Here, \[{F_{net}}\] is net force acting on the object, \[m\] is mass of the object and \[a\] is acceleration of the object.
Complete step by step answer:
Let \[m\] be the mass of the two balls. Let us draw the free body diagram of the two balls is as follows:

In the above free body diagram, \[mg\] is the weight of the two balls, \[{T_A}\] is the tension in the cord holding the ball at position A and \[{T_B}\] is the tension in the cord holding the ball at position B.
Let is apply Newton’s second law of motion to the ball at position A.
\[{T_A}\cos \theta = mg\]
\[ \Rightarrow {T_A} = \dfrac{{mg}}{{\cos \theta }}\]
Let is apply Newton’s second law of motion to the ball at position B.
\[{T_B} = mg\cos \theta \]
Now let us determine the ratio of the tensions in the cords.
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{T_B}}}{{{T_A}}} = \dfrac{{mg\cos \theta }}{{\dfrac{{mg}}{{\cos \theta }}}}\]
\[ \therefore \dfrac{{{T_B}}}{{{T_A}}} = {\cos ^2}\theta \]
Therefore, the ratio of the tension in the cord in position B to that in position A is \[{\cos ^2}\theta \].
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: The students should be careful while drawing the free body diagram of eh balls at positions A and B. If this free body diagram is not drawn correctly with the correct directions and positions of all the forces then the expressions for the tensions in the cords will be incorrect and hence the final answer will also be incorrect.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




