
A ball is dropped from a certain height and at the exact same moment, a rock is fired horizontally from the exact same height above the ground level. Assuming that air resistance is negligible, which object will strike the ground at a faster velocity?
A) The ball will hit at a faster velocity.
B) The rock will hit at a faster velocity.
C) They will hit with the same velocity.
D) The answer to this question depends on precisely how fast the rock is fired.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint:Even though the rock and the ball are dropped at the same instant and from the same height since the rock is thrown horizontally, the rock will take a parabolic path to reach the ground while the dropped ball falls vertically down. The velocity of the rock will thus have a vertical component and a horizontal component.
Formulas used:
-The velocity of a body in free fall is given by, $v = \sqrt {2gh} $ where $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height from which the body falls.
-The displacement of a body is given by, $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ where $u$ is the initial velocity of the body, $t$ is the time taken and $a$ is its acceleration.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch a figure representing the motion of the ball and the rock.
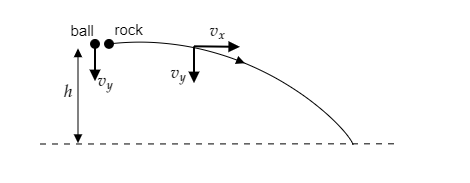
As seen from the above figure, the ball is dropped vertically down and the rock is thrown horizontally from a height $h$.
The velocity of the rock has a vertical component ${v_y}$ and a horizontal component ${v_x}$ .
The velocity of the ball will only have a vertical component ${v_y}$.
Step 2: Express the displacement equation of the ball and the rock in the x-direction and y-direction.
For the ball, there is no displacement in the x-direction.
So the vertical displacement of the ball in the y-direction is expressed as
${s_y} = h = - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ --------- (1)
Now for the rock, the horizontal displacement is expressed as ${s_x} = {v_x}t$ --------- (2)
The vertical displacement of the ball is expressed as $h = - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ -------- (3)
Now we observe that the vertical displacement is the same for both the ball and the rock. So the vertical velocities are also the same and will be equal to the velocity under free fall i.e., ${v_y} = \sqrt {2gh} $ .
Step 3: Express the magnitude of the net velocity of the ball and the rock.
The magnitude of the net velocity of the ball will be its vertical velocity ${v_y} = \sqrt {2gh} $ .
But as the rock has a horizontal component to its net velocity it will be $v = \sqrt {{v_x}^2 + {v_y}^2} $ .
This will be greater than that of the ball i.e., $v > {v_y}$ .
So the rock will hit the ground at a faster velocity.
Hence the correct option is B.
Note:Both the ball and the rock can be considered as projectiles but the ball lacks the horizontal component. The horizontal component of the velocity of the rock is what makes it move forwards and the vertical component is what makes it move downwards. Along the horizontal direction, the velocity remains constant and the rock has no horizontal acceleration. The vertical acceleration of both the ball and the rock will be the acceleration due to gravity $g$.
Formulas used:
-The velocity of a body in free fall is given by, $v = \sqrt {2gh} $ where $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height from which the body falls.
-The displacement of a body is given by, $s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ where $u$ is the initial velocity of the body, $t$ is the time taken and $a$ is its acceleration.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch a figure representing the motion of the ball and the rock.

As seen from the above figure, the ball is dropped vertically down and the rock is thrown horizontally from a height $h$.
The velocity of the rock has a vertical component ${v_y}$ and a horizontal component ${v_x}$ .
The velocity of the ball will only have a vertical component ${v_y}$.
Step 2: Express the displacement equation of the ball and the rock in the x-direction and y-direction.
For the ball, there is no displacement in the x-direction.
So the vertical displacement of the ball in the y-direction is expressed as
${s_y} = h = - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ --------- (1)
Now for the rock, the horizontal displacement is expressed as ${s_x} = {v_x}t$ --------- (2)
The vertical displacement of the ball is expressed as $h = - \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}$ -------- (3)
Now we observe that the vertical displacement is the same for both the ball and the rock. So the vertical velocities are also the same and will be equal to the velocity under free fall i.e., ${v_y} = \sqrt {2gh} $ .
Step 3: Express the magnitude of the net velocity of the ball and the rock.
The magnitude of the net velocity of the ball will be its vertical velocity ${v_y} = \sqrt {2gh} $ .
But as the rock has a horizontal component to its net velocity it will be $v = \sqrt {{v_x}^2 + {v_y}^2} $ .
This will be greater than that of the ball i.e., $v > {v_y}$ .
So the rock will hit the ground at a faster velocity.
Hence the correct option is B.
Note:Both the ball and the rock can be considered as projectiles but the ball lacks the horizontal component. The horizontal component of the velocity of the rock is what makes it move forwards and the vertical component is what makes it move downwards. Along the horizontal direction, the velocity remains constant and the rock has no horizontal acceleration. The vertical acceleration of both the ball and the rock will be the acceleration due to gravity $g$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




