
A ball is bouncing down a set of stairs. The coefficient of restitution is$e$. The height of each step is $d$and the ball bounces one step at each bounce. After each bounce the ball rebounds to a height $h$above the next lower step. Neglect width of each step, in comparison to $h$and assume the impacts to be effectively head on. Which of the following relations is correct? (Given that$h > d$)
A. $\dfrac{h}{d} = 1 - {e^2}$
B. $\dfrac{h}{d} = 1 - e$
C. $\dfrac{h}{d} = \dfrac{1}{{1 - {e^2}}}$
D. $\dfrac{h}{d} = \dfrac{1}{{1 - e}}$
Answer
576.6k+ views
Hint: Use the kinematic equation relating the final velocity, initial velocity, acceleration and time of the object. Also use the coefficient of restitution of an object in terms of the speed of approach and the speed of separation. Determine the velocity of approach and velocity of rebound of the ball using the kinematic equation. Substitute it in the formula for the coefficient of restitution and solve it.
Formula used:
The kinematic equation relating the final velocity $v$, initial velocity $u$, acceleration $g$ and displacement $s$ is as follows:
${v^2} = {u^2} + 2gs$ …… (1)
The coefficient of restitution is given by
$e = \dfrac{{speed\,of\,separation}}{{speed\,of\,approach}}$ …… (2)
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the ball is bouncing down a set of stairs. The height of each step is $d$. After each bounce the ball rebounds to a height $h$above the next lower step and $e$is the Coefficient of Restitution
The diagram representing the situation explained in the question is as follows:
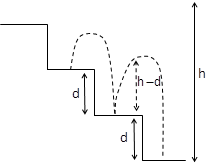
The initial velocity $u$ of the ball in the free fall is zero.
$u = 0\,{\text{m/s}}$
Hence, the velocity $v$ with which the ball hits the floor is given by using equation (1).
${v^2} = 0 + 2gh$
$ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {2gh} $
The displacement of the ball when it rebounds is $(h - d)$.
Hence, the velocity ${v_1}$ with which the ball rebounds from the floor is given by using equation (2).
$v_1^2 = 0 + 2g\left( {h - d} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {v_1} = \sqrt {2g\left( {h - d} \right)} $
We can determine the coefficient of restitution using equation (2).
Substitute ${v_1}$ for $speed\,of\,separation$ and $v$ for $speed\,of\,approach$ in equation (2).
$e = \dfrac{{{v_1}}}{v}$
Substitute $\sqrt {2g(h - d)} $ for ${v_1}$ and for $v$ in the above equation.
$e = \dfrac{{\sqrt {2g\left( {h - d} \right)} }}{{\sqrt {2gh} }}$
$ \Rightarrow e = \sqrt {\dfrac{{h - d}}{h}} $
Take square on both sides of the above equation.
$ \Rightarrow {e^2} = \dfrac{{h - d}}{h}$
$ \Rightarrow {e^2} = 1 - \dfrac{d}{h}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{h} = {e^2} - 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{d} = \dfrac{1}{{{e^2} - 1}}\]
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:
The students should keep in mind that the solution given above is correct because the ball is bouncing on the set of stairs normally, that is the velocity of the ball is perpendicular to the horizontal stair. If the ball is bouncing on the stairs making some angle with the stair and not normally, then we have to consider the components of velocity of the ball.
Formula used:
The kinematic equation relating the final velocity $v$, initial velocity $u$, acceleration $g$ and displacement $s$ is as follows:
${v^2} = {u^2} + 2gs$ …… (1)
The coefficient of restitution is given by
$e = \dfrac{{speed\,of\,separation}}{{speed\,of\,approach}}$ …… (2)
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the ball is bouncing down a set of stairs. The height of each step is $d$. After each bounce the ball rebounds to a height $h$above the next lower step and $e$is the Coefficient of Restitution
The diagram representing the situation explained in the question is as follows:
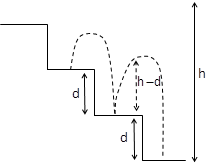
The initial velocity $u$ of the ball in the free fall is zero.
$u = 0\,{\text{m/s}}$
Hence, the velocity $v$ with which the ball hits the floor is given by using equation (1).
${v^2} = 0 + 2gh$
$ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {2gh} $
The displacement of the ball when it rebounds is $(h - d)$.
Hence, the velocity ${v_1}$ with which the ball rebounds from the floor is given by using equation (2).
$v_1^2 = 0 + 2g\left( {h - d} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {v_1} = \sqrt {2g\left( {h - d} \right)} $
We can determine the coefficient of restitution using equation (2).
Substitute ${v_1}$ for $speed\,of\,separation$ and $v$ for $speed\,of\,approach$ in equation (2).
$e = \dfrac{{{v_1}}}{v}$
Substitute $\sqrt {2g(h - d)} $ for ${v_1}$ and for $v$ in the above equation.
$e = \dfrac{{\sqrt {2g\left( {h - d} \right)} }}{{\sqrt {2gh} }}$
$ \Rightarrow e = \sqrt {\dfrac{{h - d}}{h}} $
Take square on both sides of the above equation.
$ \Rightarrow {e^2} = \dfrac{{h - d}}{h}$
$ \Rightarrow {e^2} = 1 - \dfrac{d}{h}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{h} = {e^2} - 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{h}{d} = \dfrac{1}{{{e^2} - 1}}\]
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:
The students should keep in mind that the solution given above is correct because the ball is bouncing on the set of stairs normally, that is the velocity of the ball is perpendicular to the horizontal stair. If the ball is bouncing on the stairs making some angle with the stair and not normally, then we have to consider the components of velocity of the ball.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




