
A bacterial infection in an internal wound grows as $N\prime (t)={{N}_{O}}{{\exp }^{(t)}}$, where the time ‘t’ is in hours. A dose of antibiotic, taken orally, needs one hour to reach the wound. Once it reaches there, the bacterial population goes down as $\dfrac{dN}{dt}=-5{{N}^{2}}$. What will be the plot of $\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}$ vs t after one hour?
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint:. To solve this question, first find out the bacterial growth at time equals to one hour. The bacterial growth from one hour onwards is already given. Then find out the bacterial at time equals to t hours. You have to use integration and then find the type of equation.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that,
A bacterial infection in an internal wound grows as ${{N}^{'}}(t)={{N}_{O}}{{\exp }^{(t)}}$, where the time ‘t’ is in hours. A dose of antibiotic, which is taken orally, needs one hour to reach the wound and once it reaches there, the bacterial population becomes $\dfrac{dN}{dt}=-5{{N}^{2}}$. We have to find out the plot of $\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}$ vs t after one hour.
So, from $0$ to $1$ hour, the bacterial growth is $N\prime ={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{t}}$.
So, at $t=1$ hour, the bacterial growth will be $N\prime =e{{N}_{0}}$.
And from one hour onwards, the bacterial growth becomes $\dfrac{dN}{dt}=-5{{N}^{2}}$.
In the given equation $\dfrac{dN}{dt}=-5{{N}^{2}}$, let’s take ${{N}^{2}}$ to the denominator in the left side and $dt$ to the right side. Then we will get:
$\dfrac{dN}{{{N}^{2}}}=-5dt$
Let the bacterial growth at t time be ‘N’.
So, by integrating the above reaction from ${{N}_{0}}e$ to $N$, we will get:
$\int\limits_{{{N}_{0}}e}^{N}{\dfrac{dN}{{{N}^{2}}}=\int\limits_{1}^{t}{-5dt}}$
Then, $\int\limits_{{{N}_{0}}e}^{N}{{{N}^{-2}}dN=-5\int\limits_{1}^{t}{dt}}$
Then, after multiplying ${{N}_{0}}$ on both side we get:
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}-\dfrac{1}{e}=5{{N}_{0}}(t-1)$
Then, $\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}=5{{N}_{0}}(t-1)+\dfrac{1}{e}$
And, the final equation will be:
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}=5{{N}_{0}}t+\left( \dfrac{1}{e}-5{{N}_{0}} \right)$
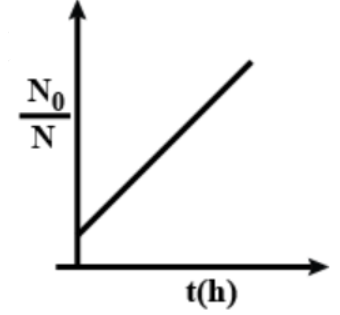
Here, if we consider $\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}$ as y-axis, $5{{N}_{0}}$ as m, $t$ as the x-axis and $\left( \dfrac{1}{e}-5{{N}_{0}} \right)$ as c, the plot equation will be $y=mx+c$ which represent an increasing straight line. And option A shows an increasing straight line (i.e. positive slope) in the plot.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
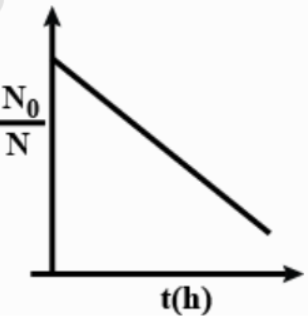
Note: The possible mistake is that you can get confused with option B which shows a negative slope but is a straight line. The plot equation for such a plot can be represented by $y=mx-c$ and it is generally shown by a decreasing straight line in the plot.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that,
A bacterial infection in an internal wound grows as ${{N}^{'}}(t)={{N}_{O}}{{\exp }^{(t)}}$, where the time ‘t’ is in hours. A dose of antibiotic, which is taken orally, needs one hour to reach the wound and once it reaches there, the bacterial population becomes $\dfrac{dN}{dt}=-5{{N}^{2}}$. We have to find out the plot of $\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}$ vs t after one hour.
So, from $0$ to $1$ hour, the bacterial growth is $N\prime ={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{t}}$.
So, at $t=1$ hour, the bacterial growth will be $N\prime =e{{N}_{0}}$.
And from one hour onwards, the bacterial growth becomes $\dfrac{dN}{dt}=-5{{N}^{2}}$.
In the given equation $\dfrac{dN}{dt}=-5{{N}^{2}}$, let’s take ${{N}^{2}}$ to the denominator in the left side and $dt$ to the right side. Then we will get:
$\dfrac{dN}{{{N}^{2}}}=-5dt$
Let the bacterial growth at t time be ‘N’.
So, by integrating the above reaction from ${{N}_{0}}e$ to $N$, we will get:
$\int\limits_{{{N}_{0}}e}^{N}{\dfrac{dN}{{{N}^{2}}}=\int\limits_{1}^{t}{-5dt}}$
Then, $\int\limits_{{{N}_{0}}e}^{N}{{{N}^{-2}}dN=-5\int\limits_{1}^{t}{dt}}$
Then, after multiplying ${{N}_{0}}$ on both side we get:
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}-\dfrac{1}{e}=5{{N}_{0}}(t-1)$
Then, $\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}=5{{N}_{0}}(t-1)+\dfrac{1}{e}$
And, the final equation will be:
$\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}=5{{N}_{0}}t+\left( \dfrac{1}{e}-5{{N}_{0}} \right)$
Here, if we consider $\dfrac{{{N}_{0}}}{N}$ as y-axis, $5{{N}_{0}}$ as m, $t$ as the x-axis and $\left( \dfrac{1}{e}-5{{N}_{0}} \right)$ as c, the plot equation will be $y=mx+c$ which represent an increasing straight line. And option A shows an increasing straight line (i.e. positive slope) in the plot.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The possible mistake is that you can get confused with option B which shows a negative slope but is a straight line. The plot equation for such a plot can be represented by $y=mx-c$ and it is generally shown by a decreasing straight line in the plot.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




