
A & B are the points (2, 0) & (0, 2) respectively. The coordinates of the point P on the line $2x+3y+1=0$ are:
(a) (7, -5) if $\left| \text{PA - PB} \right|$ is maximum
(b) $\left( \dfrac{1}{5},\dfrac{1}{5} \right)$ if $\left| \text{PA - PB} \right|$ is maximum
(c) (7, -5) if $\left| \text{PA - PB} \right|$ is minimum
(d) $\left( \dfrac{1}{5},\dfrac{1}{5} \right)$ if $\left| \text{PA - PB} \right|$ is minimum
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: Let us suppose that joining the three points P, A & B constructs a triangle so using the triangle inequalities that sum of two sides is greater than the third side so $PB+AB>PA$. Rearranging this inequation will give us $\left| PA-PB \right|$ < $AB$. Now, find the distance between A & B and we can consider $\left| PA-PB \right|$ as the equation of a line passing through A, B. After substituting this equation of a line AB and the distance between A & B we get $p+q=2$. And point P (p, q) lies on the line $2x+3y+1=0$ so we have two equations in ${{x}_{1}}\And {{y}_{1}}$ i.e. $p+q=2$ & $2p+3q+1=0$ so solve these two equations and find the value of p & q.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the below figure, we have shown a line $2x+3y+1=0$ and points A & B and point P (a, b).
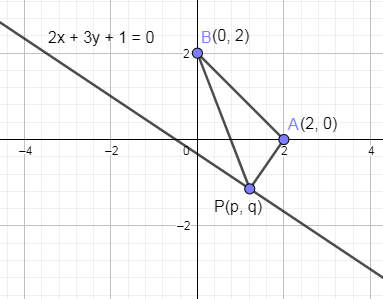
We have assumed that the three points are joined to form a triangle so we are going to use properties of the triangle that sum of the two sides is greater than the third side.
$PB+AB>PA$
Rearranging the above inequality we get,
$\left| PA-PB \right|$ < $AB$
$\left| PA-PB \right|$ is maximum when $PA-PB=AB$. So PA – PB is the same as the equation of line AB.
We know that equation of a line passing through $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is:
$y-{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
Using the above equation of a line passing through two points we can write the equation of a line passing through A (2, 0) & B (0, 2).
$\begin{align}
& y-0=\dfrac{2-0}{0-2}\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=-1\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow x+y=2 \\
\end{align}$
Now, point P passes through this line AB so plugging this value of point P (p, q) in the above equation we get,
$p+q=2$
And point P (p, q) also passes through the line $2x+3y+1=0$ so plugging this point P in the given line we get,
$2p+3q+1=0$
Solving two equations:
$p+q=2$………… Eq. (1)
$2p+3q+1=0$………. Eq. (2)
Multiply first equation by 2 and then subtract this new equation from the second equation we get,
$\begin{matrix}
2p+3q+1=0 \\
\dfrac{-\left( p+q-2=0 \right)\times 2}{q+5=0} \\
\end{matrix}$
Simplifying the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& q+5=0 \\
& \Rightarrow q=-5 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting this value of q in eq. (1) we get,
$p+q=2$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow p-5=2 \\
& \Rightarrow p=7 \\
\end{align}$
From the above solution, the value of point P is (7, -5).
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Note: You can verify that the point P that we have got is satisfying the maximum condition or not.
We have shown above that $\left| PA-PB \right|$ is maximum when $\left| PA-PB \right|=AB$.
The point P that we have solved above is (7, -5).
Verifying that $PA-PB=AB$ by finding PA, PB and AB then put these values in this relation.
Points A & B given as A (2, 0) & B (0, 2).
We know that distance between two points $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is equal to:
$AB=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Using the above formula, we can find the distances PA, PB and AB.
$PA=\sqrt{{{\left( 7-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -5 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{25+25}=5\sqrt{2}$
$PB=\sqrt{{{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -5-2 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{49+49}=7\sqrt{2}$
$AB=\sqrt{{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}}=2\sqrt{2}$
$\begin{align}
& \left| PA-PB \right|=\left| 5\sqrt{2}-7\sqrt{2} \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \left| PA-PB \right|=\left| -2\sqrt{2} \right|=2\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
From the above, we have established that $\left| PA-PB \right|=AB$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the below figure, we have shown a line $2x+3y+1=0$ and points A & B and point P (a, b).

We have assumed that the three points are joined to form a triangle so we are going to use properties of the triangle that sum of the two sides is greater than the third side.
$PB+AB>PA$
Rearranging the above inequality we get,
$\left| PA-PB \right|$ < $AB$
$\left| PA-PB \right|$ is maximum when $PA-PB=AB$. So PA – PB is the same as the equation of line AB.
We know that equation of a line passing through $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is:
$y-{{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
Using the above equation of a line passing through two points we can write the equation of a line passing through A (2, 0) & B (0, 2).
$\begin{align}
& y-0=\dfrac{2-0}{0-2}\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y=-1\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow x+y=2 \\
\end{align}$
Now, point P passes through this line AB so plugging this value of point P (p, q) in the above equation we get,
$p+q=2$
And point P (p, q) also passes through the line $2x+3y+1=0$ so plugging this point P in the given line we get,
$2p+3q+1=0$
Solving two equations:
$p+q=2$………… Eq. (1)
$2p+3q+1=0$………. Eq. (2)
Multiply first equation by 2 and then subtract this new equation from the second equation we get,
$\begin{matrix}
2p+3q+1=0 \\
\dfrac{-\left( p+q-2=0 \right)\times 2}{q+5=0} \\
\end{matrix}$
Simplifying the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& q+5=0 \\
& \Rightarrow q=-5 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting this value of q in eq. (1) we get,
$p+q=2$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow p-5=2 \\
& \Rightarrow p=7 \\
\end{align}$
From the above solution, the value of point P is (7, -5).
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Note: You can verify that the point P that we have got is satisfying the maximum condition or not.
We have shown above that $\left| PA-PB \right|$ is maximum when $\left| PA-PB \right|=AB$.
The point P that we have solved above is (7, -5).
Verifying that $PA-PB=AB$ by finding PA, PB and AB then put these values in this relation.
Points A & B given as A (2, 0) & B (0, 2).
We know that distance between two points $A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\And B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is equal to:
$AB=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$
Using the above formula, we can find the distances PA, PB and AB.
$PA=\sqrt{{{\left( 7-2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -5 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{25+25}=5\sqrt{2}$
$PB=\sqrt{{{\left( 7 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -5-2 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{49+49}=7\sqrt{2}$
$AB=\sqrt{{{\left( 2 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}}=2\sqrt{2}$
$\begin{align}
& \left| PA-PB \right|=\left| 5\sqrt{2}-7\sqrt{2} \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \left| PA-PB \right|=\left| -2\sqrt{2} \right|=2\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
From the above, we have established that $\left| PA-PB \right|=AB$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




