
A, B and C represents switches in ‘on’ position and A’, B’ and C’ represents them in ‘off’ position. Construct a switching circuit representing the polynomial $ABC + AB'C + A'B'C$. Using Boolean algebra, prove that the given polynomial can be simplified to $C\left( {A + B'} \right)$. Construct an equivalent switching circuit.
Answer
624.9k+ views
Hint: Use the property of Boolean algebra which are $A.A = A,{\text{ }}A.A' = 0,{\text{ }}A\left( {1 + B'} \right) = A,{\text{ & }}\left( {A + A'} \right) = 1$ for solving this problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
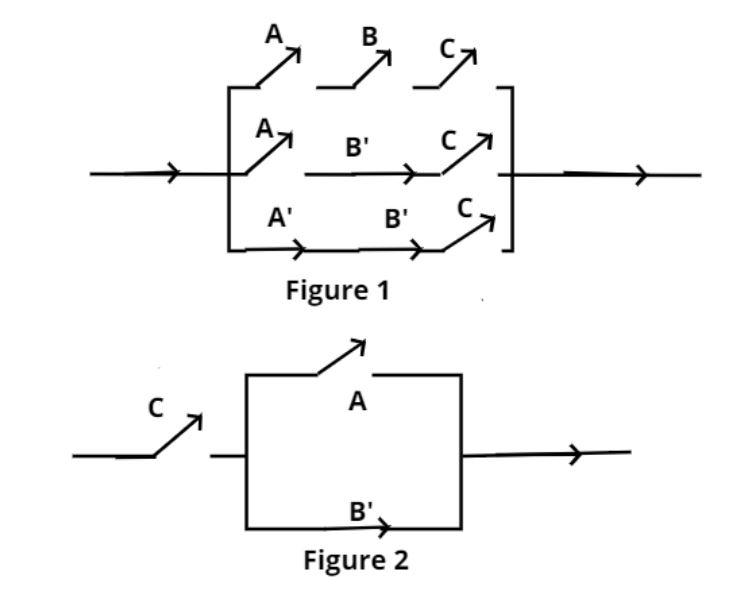
Given polynomial is $ABC + AB'C + A'B'C$ switching circuit representing the given polynomial is shown in figure (1), where A, B and C represents switches in ‘on’ position and A’, B’ and C’ represents them in ‘off’ position
Now we have to prove that
$ABC + AB'C + A'B'C = C\left( {A + B'} \right)$
Consider L.H.S
$ABC + AB'C + A'B'C$
Take AC common from first two terms
$ \Rightarrow AC\left( {B + B'} \right) + A'B'C$
As we know in Boolean algebra value of $\left( {B + B'} \right)$ is equal to one
$ \Rightarrow AC\left( {B + B'} \right) + A'B'C = AC + A'B'C$
Now take C as common
$ \Rightarrow AC + A'B'C$ = $C\left( {A + A'B'} \right).............\left( 1 \right)$
Now $\left( {A + A'B'} \right)$ is written as$\left( {A + A'} \right)\left( {A + B'} \right)$, property of Boolean algebra.
Because we know in Boolean algebra the value of $A.A = A,{\text{ }}A.A' = 0,{\text{ & }}A\left( {1 + B'} \right) = A$
So,
$
\left( {A + A'} \right)\left( {A + B'} \right) = A.A + A.B' + A.A' + A'B' \\
= A + AB' + 0 + A'B' \\
= A\left( {1 + B'} \right) + A'B' = A + A'B' \\
$
Therefore
$\left( {A + A'B'} \right) = \left( {A + A'} \right)\left( {A + B'} \right)$
Therefore from equation (1)
$ \Rightarrow ABC + AB'C + A'B'C = C\left( {A + A'B'} \right) = C\left( {A + A'} \right)\left( {A + B'} \right)$
Now as we know in Boolean algebra value of $\left( {A + A'} \right)$ is equal to one
$ \Rightarrow ABC + AB'C + A'B'C = C\left( {A + B'} \right)$
=R.H.S
Hence Proved.
And the equivalent representation is shown in figure (2), where A, B and C represents switches in ‘on’ position and A’, B’ and C’ represents them in ‘off’ position.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions always remember some of the basic properties of the Boolean algebra which is stated above then using these properties simplify the given polynomial, we will get the required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given polynomial is $ABC + AB'C + A'B'C$ switching circuit representing the given polynomial is shown in figure (1), where A, B and C represents switches in ‘on’ position and A’, B’ and C’ represents them in ‘off’ position

Now we have to prove that
$ABC + AB'C + A'B'C = C\left( {A + B'} \right)$
Consider L.H.S
$ABC + AB'C + A'B'C$
Take AC common from first two terms
$ \Rightarrow AC\left( {B + B'} \right) + A'B'C$
As we know in Boolean algebra value of $\left( {B + B'} \right)$ is equal to one
$ \Rightarrow AC\left( {B + B'} \right) + A'B'C = AC + A'B'C$
Now take C as common
$ \Rightarrow AC + A'B'C$ = $C\left( {A + A'B'} \right).............\left( 1 \right)$
Now $\left( {A + A'B'} \right)$ is written as$\left( {A + A'} \right)\left( {A + B'} \right)$, property of Boolean algebra.
Because we know in Boolean algebra the value of $A.A = A,{\text{ }}A.A' = 0,{\text{ & }}A\left( {1 + B'} \right) = A$
So,
$
\left( {A + A'} \right)\left( {A + B'} \right) = A.A + A.B' + A.A' + A'B' \\
= A + AB' + 0 + A'B' \\
= A\left( {1 + B'} \right) + A'B' = A + A'B' \\
$
Therefore
$\left( {A + A'B'} \right) = \left( {A + A'} \right)\left( {A + B'} \right)$
Therefore from equation (1)
$ \Rightarrow ABC + AB'C + A'B'C = C\left( {A + A'B'} \right) = C\left( {A + A'} \right)\left( {A + B'} \right)$
Now as we know in Boolean algebra value of $\left( {A + A'} \right)$ is equal to one
$ \Rightarrow ABC + AB'C + A'B'C = C\left( {A + B'} \right)$
=R.H.S
Hence Proved.
And the equivalent representation is shown in figure (2), where A, B and C represents switches in ‘on’ position and A’, B’ and C’ represents them in ‘off’ position.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions always remember some of the basic properties of the Boolean algebra which is stated above then using these properties simplify the given polynomial, we will get the required answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




