
(a) A park in the shape of a quadrilateral ABCD, has \[\angle C={{90}^{\circ }}\] AB = 9m, BC = 12m, CD = 5 and AD = 8m. How much area does it occupy?
(b) Find the area of a quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 3cm, BC = 4cm, CD = 4cm, DA = 5cm and AC = 5cm.
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: For both parts (a) and (b) draw the quadrilateral ABCD, mentioned with the sides. Now divide the quadrilaterals in two triangles. The area of the two triangles will give the total area of the quadrilateral ABCD. We might have to use Heron’s formula given by,
Area of triangle = \[\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\] and also the formula for area of right angled triangle, which is given by \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] base \[\times \] height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(a) From the figure, it is given a quadrilateral ABCD.
We have been given that,
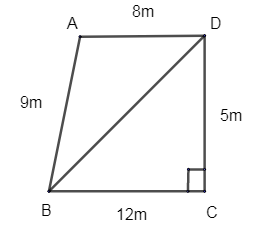
AB = 9cm, BC = 12m, CD = 5m and AD = 8m.
Total area = area of \[\Delta ABD\] + area of \[\Delta BCD\]
From the figure, let us find the area of \[\Delta BCD\].
We have been given BC = 12cm and DC = 5cm. It is right angled at C. Thus \[\Delta BCD\] is a right-angled triangle.
Area of \[\Delta BCD\] = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] base \[\times \] height
Area of \[\Delta BCD\] = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] BC \[\times \] DC = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] 12 \[\times \] 5 = 6 \[\times \] 5 = 30\[{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore ar\left( \Delta BCD \right)=30{{m}^{2}}\]
As \[\Delta BCD\] is a right-angled triangle, by Pythagoras theorem,
\[B{{D}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+D{{C}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore BD=\sqrt{B{{C}^{2}}+D{{C}^{2}}}\].
\[\therefore BD=\sqrt{{{12}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}}=\sqrt{144+25}=\sqrt{169}=13\]m.
\[\therefore \] BD = 13m.
Now let us find the area of \[\Delta ABD\], using Heron’s formula.
We know all the sides of the triangle,
AD = 8m, AB = 9m, BD = 13m.
Thus Heron’s formula gives the area as,
Area of triangle = \[\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\], where a, b, c are the sides of the triangle where a = AD = 8m, b = AB = 9m, c = BD = 13m.
s is the semi – perimeter of the triangle, where,
\[s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}=\dfrac{8+9+13}{2}=\dfrac{30}{2}=15\]m.
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABD=\sqrt{15\left( 15-8 \right)\left( 15-9 \right)\left( 15-13 \right)}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABD=\sqrt{15\times 7\times 6\times 2}=\sqrt{3\times 5\times 7\times 3\times 2\times 2}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABD=\sqrt{9\times 4\times 35}=6\sqrt{35}{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABD=6\sqrt{35}{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \] Total area of the park = \[ar\left( \Delta BCD \right)+ar\left( \Delta ABD \right)\].
\[\therefore \] Total area of the park = \[30+6\sqrt{35}\].
\[\therefore \] Total area of the park = \[30+6\times 5.91=65.46{{m}^{2}}\].
Thus, we got the total area of the park as \[65.46{{m}^{2}}\].
(b) We have been given the side of the quadrilateral as AB = 3cm, BC = 4cm, CD = 4cm, DA = 5cm and AC = 5cm.
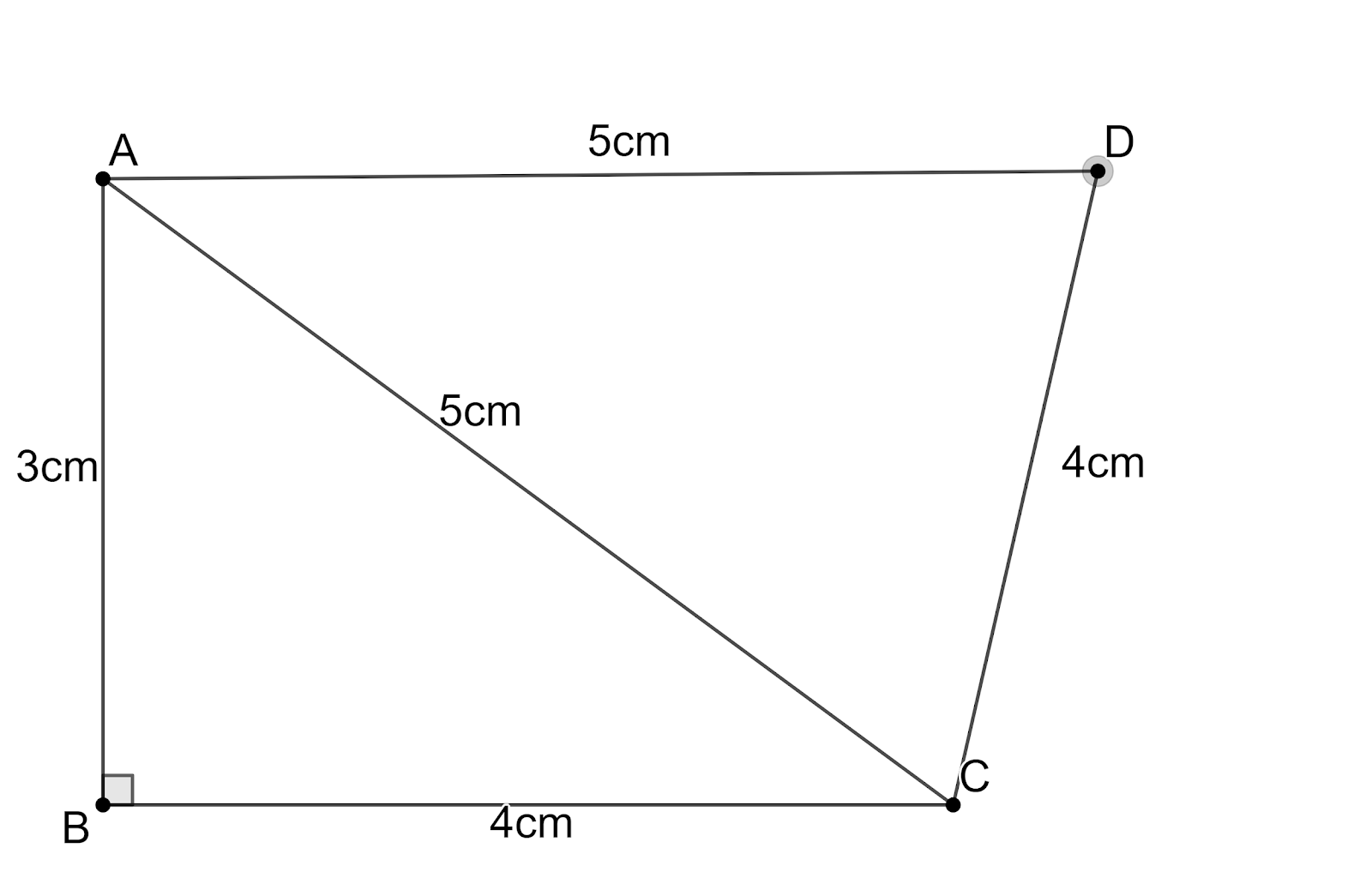
\[\therefore \] Area of quadrilateral ABCD = area of \[\Delta ABC\] + area of \[\Delta ADC\].
We can use Heron’s formula for finding area,
Area of triangle = \[\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\]
First let us find the area of \[\Delta ABC\].
From the figure, a = AB = 3cm,
b = BC = 4cm,
c = AC = 5cm.
\[\therefore s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}=\dfrac{3+4+5}{2}=\dfrac{12}{2}\]= 6cm
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABC\] = \[\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\]
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABC\] = \[\sqrt{6\left( 6-3 \right)\left( 6-4 \right)\left( 6-5 \right)}=\sqrt{6\times 3\times 2\times 1}=\sqrt{36}=6c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABC\] = \[6c{{m}^{2}}\]
Now let us find the area of \[\Delta ABC\].
From the figure, a = AD = 5cm
b = DC = 4cm,
c = AC = 5cm.
\[\therefore s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}=\dfrac{5+4+5}{2}=\dfrac{14}{2}\]= 7cm
\[\therefore ar\left( \Delta ADC \right)=\sqrt{7\left( 7-5 \right)\left( 7-4 \right)\left( 7-5 \right)}=\sqrt{7\times 2\times 3\times 2}=2\sqrt{21}c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore ar\left( \Delta ADC \right)=2\sqrt{21}c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of the quadrilateral ABCD = \[ar\left( \Delta ABC \right)+ar\left( \Delta ADC \right)\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of the quadrilateral ABCD = \[6+2\sqrt{21}\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of the quadrilateral ABCD = \[6+2\times 4.58=15.2c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of the quadrilateral ABCD = \[15.2c{{m}^{2}}\]
Note: Here the square root of the numbers can be found using the long division method. Consider the term as pairs and first divide by the closest perfect square number. In the first case, we have paired number 3500 as 35 and 00. Now, for 35, we know that closet perfect square is 25, so we will divide the number with 5. Then take twice the quotient, i.e. \[2\times 5=10\]. Find the number y such that 10yxy would give the next closest number. So, we get \[109\times 9\] as 981 which is closest to 1000, then we will continue this process till we get two decimal places in the quotient.
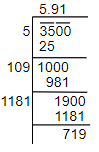
\[109\times 9=981\]
{\[110\times 10\] is invalid}

\[\begin{align}
& 84\times 4=336 \\
& 85\times 5=425 \\
& 86\times 6=516 \\
& 908\times 8=7264 \\
& 909\times 9=8181 \\
\end{align}\]
Area of triangle = \[\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\] and also the formula for area of right angled triangle, which is given by \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] base \[\times \] height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(a) From the figure, it is given a quadrilateral ABCD.
We have been given that,

AB = 9cm, BC = 12m, CD = 5m and AD = 8m.
Total area = area of \[\Delta ABD\] + area of \[\Delta BCD\]
From the figure, let us find the area of \[\Delta BCD\].
We have been given BC = 12cm and DC = 5cm. It is right angled at C. Thus \[\Delta BCD\] is a right-angled triangle.
Area of \[\Delta BCD\] = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] base \[\times \] height
Area of \[\Delta BCD\] = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] BC \[\times \] DC = \[\dfrac{1}{2}\times \] 12 \[\times \] 5 = 6 \[\times \] 5 = 30\[{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore ar\left( \Delta BCD \right)=30{{m}^{2}}\]
As \[\Delta BCD\] is a right-angled triangle, by Pythagoras theorem,
\[B{{D}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}}+D{{C}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore BD=\sqrt{B{{C}^{2}}+D{{C}^{2}}}\].
\[\therefore BD=\sqrt{{{12}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}}=\sqrt{144+25}=\sqrt{169}=13\]m.
\[\therefore \] BD = 13m.
Now let us find the area of \[\Delta ABD\], using Heron’s formula.
We know all the sides of the triangle,
AD = 8m, AB = 9m, BD = 13m.
Thus Heron’s formula gives the area as,
Area of triangle = \[\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\], where a, b, c are the sides of the triangle where a = AD = 8m, b = AB = 9m, c = BD = 13m.
s is the semi – perimeter of the triangle, where,
\[s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}=\dfrac{8+9+13}{2}=\dfrac{30}{2}=15\]m.
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABD=\sqrt{15\left( 15-8 \right)\left( 15-9 \right)\left( 15-13 \right)}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABD=\sqrt{15\times 7\times 6\times 2}=\sqrt{3\times 5\times 7\times 3\times 2\times 2}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABD=\sqrt{9\times 4\times 35}=6\sqrt{35}{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABD=6\sqrt{35}{{m}^{2}}\].
\[\therefore \] Total area of the park = \[ar\left( \Delta BCD \right)+ar\left( \Delta ABD \right)\].
\[\therefore \] Total area of the park = \[30+6\sqrt{35}\].
\[\therefore \] Total area of the park = \[30+6\times 5.91=65.46{{m}^{2}}\].
Thus, we got the total area of the park as \[65.46{{m}^{2}}\].
(b) We have been given the side of the quadrilateral as AB = 3cm, BC = 4cm, CD = 4cm, DA = 5cm and AC = 5cm.

\[\therefore \] Area of quadrilateral ABCD = area of \[\Delta ABC\] + area of \[\Delta ADC\].
We can use Heron’s formula for finding area,
Area of triangle = \[\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\]
First let us find the area of \[\Delta ABC\].
From the figure, a = AB = 3cm,
b = BC = 4cm,
c = AC = 5cm.
\[\therefore s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}=\dfrac{3+4+5}{2}=\dfrac{12}{2}\]= 6cm
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABC\] = \[\sqrt{s\left( s-a \right)\left( s-b \right)\left( s-c \right)}\]
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABC\] = \[\sqrt{6\left( 6-3 \right)\left( 6-4 \right)\left( 6-5 \right)}=\sqrt{6\times 3\times 2\times 1}=\sqrt{36}=6c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore \] Area of \[\Delta ABC\] = \[6c{{m}^{2}}\]
Now let us find the area of \[\Delta ABC\].
From the figure, a = AD = 5cm
b = DC = 4cm,
c = AC = 5cm.
\[\therefore s=\dfrac{a+b+c}{2}=\dfrac{5+4+5}{2}=\dfrac{14}{2}\]= 7cm
\[\therefore ar\left( \Delta ADC \right)=\sqrt{7\left( 7-5 \right)\left( 7-4 \right)\left( 7-5 \right)}=\sqrt{7\times 2\times 3\times 2}=2\sqrt{21}c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore ar\left( \Delta ADC \right)=2\sqrt{21}c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of the quadrilateral ABCD = \[ar\left( \Delta ABC \right)+ar\left( \Delta ADC \right)\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of the quadrilateral ABCD = \[6+2\sqrt{21}\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of the quadrilateral ABCD = \[6+2\times 4.58=15.2c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\therefore \] Total area of the quadrilateral ABCD = \[15.2c{{m}^{2}}\]
Note: Here the square root of the numbers can be found using the long division method. Consider the term as pairs and first divide by the closest perfect square number. In the first case, we have paired number 3500 as 35 and 00. Now, for 35, we know that closet perfect square is 25, so we will divide the number with 5. Then take twice the quotient, i.e. \[2\times 5=10\]. Find the number y such that 10yxy would give the next closest number. So, we get \[109\times 9\] as 981 which is closest to 1000, then we will continue this process till we get two decimal places in the quotient.
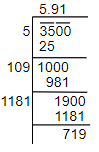
\[109\times 9=981\]
{\[110\times 10\] is invalid}

\[\begin{align}
& 84\times 4=336 \\
& 85\times 5=425 \\
& 86\times 6=516 \\
& 908\times 8=7264 \\
& 909\times 9=8181 \\
\end{align}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




