
A \[60\,{\text{kg}}\] body is pushed with just enough to start it moving across a floor and the same force continues to act afterwards. The coefficient of the static friction and sliding friction are \[0.5\] and \[0.4\] respectively. The acceleration of the body is:
(A) \[9.8\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
(B) \[3.2\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
(C) \[1\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
(D) \[5\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: First of all, we will find the limiting friction and the kinetic friction separately. Then we will find out the net accelerating force by subtracting these two quantities. We will find the acceleration by using Newton’s second law of motion.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, we are provided with the following data:
The mass of the body is \[60\,{\text{kg}}\] .
The coefficient of the static friction and sliding friction are \[0.5\] and \[0.4\] respectively.
We are asked to find the acceleration of the body.
For better understanding, we draw a diagram which shows all the forces acting on the body. The weight of the body acts in the downward direction. The normal reaction acts upwards. The force applied acts towards right.
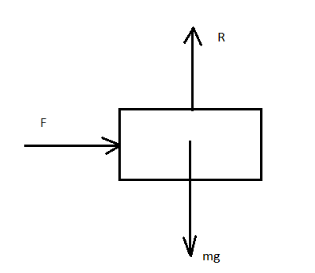
First, we will find the limiting friction, which is given by the formula:
\[{F_{\text{l}}} = {\mu _{\text{s}}}R\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{F_{\text{l}}}\] indicates limiting friction.
\[{\mu _{\text{s}}}\] indicates coefficient of the static friction.
\[R\] indicates normal reaction.
Substituting the required values in the equation (1), we get:
\[
{F_{\text{l}}} = {\mu _{\text{s}}}R \\
{F_{\text{l}}} = {\mu _{\text{s}}}mg \\
{F_{\text{l}}} = 0.5 \times 60 \times 10\,{\text{N}} \\
{F_{\text{l}}} = 300\,{\text{N}} \\
\]
The value of limiting friction is found to be \[300\,{\text{N}}\] .
For the second case, we find the kinetic friction:
\[{F_{\text{k}}} = {\mu _{\text{k}}}mg\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{F_{\text{k}}}\] indicates kinetic friction.
\[{\mu _{\text{k}}}\] indicates coefficient of the kinetic friction.
\[mg\] indicates weight force.
Substituting the required values in the equation (1), we get:
\[
{F_{\text{k}}} = {\mu _{\text{k}}}mg \\
{F_{\text{k}}} = 0.4 \times 60 \times 10\,{\text{N}} \\
{F_{\text{k}}} = 240\,{\text{N}} \\
\]
The value of kinetic friction is found to be \[240\,{\text{N}}\] .
The force applied force is \[300\,{\text{N}}\] .
So, we need to find the net accelerating force which is the difference of limiting friction and the kinetic friction.
So, we can write:
\[F = {F_{\text{l}}} - {F_{\text{k}}}\] …… (2)
Where,
\[F\] indicates the net accelerating force.
\[{F_{\text{l}}}\] indicates the limiting force.
\[{F_{\text{k}}}\] indicates the kinetic friction.
Substituting the required values in the equation (2), we get:
\[
F = {F_{\text{l}}} - {F_{\text{k}}} \\
ma = 300 - 240 \\
a = \dfrac{{60}}{{60}} \\
a = 1\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}} \\
\]
Hence, the acceleration of the body is found to be \[1\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\] .
The correct option is C..
Note: While solving this problem, we need to understand that limiting friction is different from kinetic friction. Limiting friction is the maximum friction that is generated between two static surfaces which are in contact. Kinetic friction is that force which acts between two surfaces when they are moving.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given question, we are provided with the following data:
The mass of the body is \[60\,{\text{kg}}\] .
The coefficient of the static friction and sliding friction are \[0.5\] and \[0.4\] respectively.
We are asked to find the acceleration of the body.
For better understanding, we draw a diagram which shows all the forces acting on the body. The weight of the body acts in the downward direction. The normal reaction acts upwards. The force applied acts towards right.

First, we will find the limiting friction, which is given by the formula:
\[{F_{\text{l}}} = {\mu _{\text{s}}}R\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{F_{\text{l}}}\] indicates limiting friction.
\[{\mu _{\text{s}}}\] indicates coefficient of the static friction.
\[R\] indicates normal reaction.
Substituting the required values in the equation (1), we get:
\[
{F_{\text{l}}} = {\mu _{\text{s}}}R \\
{F_{\text{l}}} = {\mu _{\text{s}}}mg \\
{F_{\text{l}}} = 0.5 \times 60 \times 10\,{\text{N}} \\
{F_{\text{l}}} = 300\,{\text{N}} \\
\]
The value of limiting friction is found to be \[300\,{\text{N}}\] .
For the second case, we find the kinetic friction:
\[{F_{\text{k}}} = {\mu _{\text{k}}}mg\] …… (1)
Where,
\[{F_{\text{k}}}\] indicates kinetic friction.
\[{\mu _{\text{k}}}\] indicates coefficient of the kinetic friction.
\[mg\] indicates weight force.
Substituting the required values in the equation (1), we get:
\[
{F_{\text{k}}} = {\mu _{\text{k}}}mg \\
{F_{\text{k}}} = 0.4 \times 60 \times 10\,{\text{N}} \\
{F_{\text{k}}} = 240\,{\text{N}} \\
\]
The value of kinetic friction is found to be \[240\,{\text{N}}\] .
The force applied force is \[300\,{\text{N}}\] .
So, we need to find the net accelerating force which is the difference of limiting friction and the kinetic friction.
So, we can write:
\[F = {F_{\text{l}}} - {F_{\text{k}}}\] …… (2)
Where,
\[F\] indicates the net accelerating force.
\[{F_{\text{l}}}\] indicates the limiting force.
\[{F_{\text{k}}}\] indicates the kinetic friction.
Substituting the required values in the equation (2), we get:
\[
F = {F_{\text{l}}} - {F_{\text{k}}} \\
ma = 300 - 240 \\
a = \dfrac{{60}}{{60}} \\
a = 1\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}} \\
\]
Hence, the acceleration of the body is found to be \[1\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\] .
The correct option is C..
Note: While solving this problem, we need to understand that limiting friction is different from kinetic friction. Limiting friction is the maximum friction that is generated between two static surfaces which are in contact. Kinetic friction is that force which acts between two surfaces when they are moving.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




