
A 5gm lump of clay, moving with a velocity of 10 cm/s towards east, collides head-on with another 2gm lump of clay moving with 15 cm/s towards west. After the collision, the two lumps stick together. What will be the velocity of the compound lump?
A. 5 cm/s towards east
B. 5 cm/s towards west
C. 2.88 cm/s towards east
D. 2.5 cm/s towards west
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: For this question we need to have the knowledge of Conservation of momentum which states that for two or more bodies in an isolated system acting upon each other, their total momentum remains constant unless an external force is applied. Hence, momentum can neither be created nor be destroyed.
Step by step solution:
1. In the diagram drawn below $m_1$ be the mass of 5gm which is moving with a velocity of 10 cm/s towards east and $m_2$ be the mass of 2gm moving with velocity 15 cm/s towards west.
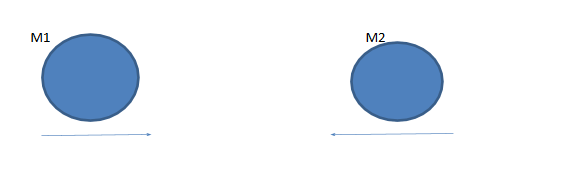
2. Now after collision the two masses stick together, that is they combine to form a new lump of clay weighing (5+2) = 7gm. So now we will apply the law of conservation of momentum.
Initial momentum=final momentum
${p_i} = {p_f}$
${m_1}{v_1} + {m_2}{v_2} = MV$ …………….equation 1
Where $M = {m_1} + {m_2}$ and V=velocity of the compound lump.
3. Substituting the values in equation 1, we get
$ \Rightarrow $ $5 \times 10 + 2 \times ( - 15) = (5 + 2) \times V$ (- sign is because both the lumps are moving in the opposite directions)
$ \Rightarrow $ $50 - 30 = 7 \times V$
$ \Rightarrow $ $20 = 7 \times V$
$ \Rightarrow $ $V = \dfrac{{20}}{7} = 2.8$m/s
4. Now it's direction will be east because by taking the east direction as reference direction we got positive velocity. If we had taken otherwise then velocity would have come negative and hence we have taken other directions than the reference direction.
That means option C is correct.
Note: Here we could also take the velocity of the 1st mass as negative and another one as negative then also we would get the same answer. It totally depends on us which direction we are taking as a reference direction.
Step by step solution:
1. In the diagram drawn below $m_1$ be the mass of 5gm which is moving with a velocity of 10 cm/s towards east and $m_2$ be the mass of 2gm moving with velocity 15 cm/s towards west.
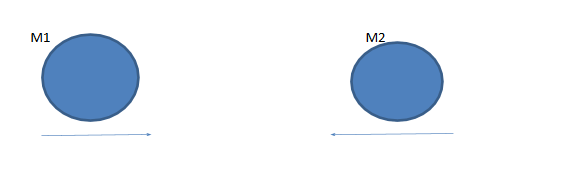
2. Now after collision the two masses stick together, that is they combine to form a new lump of clay weighing (5+2) = 7gm. So now we will apply the law of conservation of momentum.
Initial momentum=final momentum
${p_i} = {p_f}$
${m_1}{v_1} + {m_2}{v_2} = MV$ …………….equation 1
Where $M = {m_1} + {m_2}$ and V=velocity of the compound lump.
3. Substituting the values in equation 1, we get
$ \Rightarrow $ $5 \times 10 + 2 \times ( - 15) = (5 + 2) \times V$ (- sign is because both the lumps are moving in the opposite directions)
$ \Rightarrow $ $50 - 30 = 7 \times V$
$ \Rightarrow $ $20 = 7 \times V$
$ \Rightarrow $ $V = \dfrac{{20}}{7} = 2.8$m/s
4. Now it's direction will be east because by taking the east direction as reference direction we got positive velocity. If we had taken otherwise then velocity would have come negative and hence we have taken other directions than the reference direction.
That means option C is correct.
Note: Here we could also take the velocity of the 1st mass as negative and another one as negative then also we would get the same answer. It totally depends on us which direction we are taking as a reference direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




