
A 3m long ladder weighing 20kg leans on a frictionless wall. Its feet rest on the floor 1m from the wall as shown, find the reaction forces of the wall and the floor.
Answer
531.3k+ views
Hint: Firstly we will make a free body diagram of the complete system then we resolve the different parameters into its horizontal & vertical component. Then equate them to find the required parameter.
Step by step answer: Given that, Length of ladder AB \[ = 3m\]
Weight of ladder(W) \[ = 20kg\]
Distance of ladder from wall, AE=\[1m\]
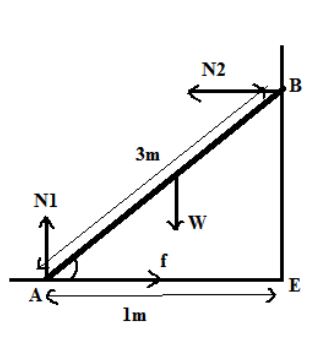
By making a free body diagram, we can understand in which direction force is acting.
\[
{N_2} = f \\
{N_1} = W \\
\]
Here \[{N_1}\] and \[{N_2}\]are the normal reactions and \[w\]is the weight of the ladder.
Now, use Pythagoras theorem,
\[\sqrt {BE^2} \] = \[\sqrt {A{B^2} - A{C^2}} \] \[ = \sqrt {{3^2} - {1^2}} \]
\[\Rightarrow BE = \sqrt 8 \] \[ = 2\sqrt 2 \]
Now, by using rotational equation,
\[W\left( {1.5\operatorname{Cos} \theta } \right) = 3{N_2}\operatorname{sin} \theta \]
Now, substitute all the given values in this equation.
\[\dfrac{{20 \times 1.5g\operatorname{Cos} \theta }}{{3\operatorname{sin} \theta }} = {N_2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {N_2} = 10g \times cot\theta \]
\[\Rightarrow {N_2} = \dfrac{{10g}}{{\operatorname{tan} \theta }}\]
From the triangle ABE, find the value of
\[\operatorname{tan} \theta \] \[ = \dfrac{{BE}}{{AB}}\]
We know, BE\[ = 2\sqrt 2 \] m
AE\[ = 1m\]
So,
\[\operatorname{tan} \theta = 2\sqrt 2 \]
Now, substitute all the values in \[{N_2}\]equation,
We get-\[\dfrac{{10 \times g}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{{10 \times 9.8}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {N_2} = 34.65N\]
So, value of \[{N_2}\] is \[ = 34.65N\]which is equal to f. so, f\[ = 34.65N\]
We know,
\[{N_1} = W\]
\[\Rightarrow {N_1} = 20 \times 9.8\]
\[ \Rightarrow {N_1} = 196N\]
Now, one reaction is in vertical direction and one force I acting in horizontal(as shown), so its resultant will be-
\[{R^2} = \] \[{\left( {196} \right)^2} + {\left( {34.65} \right)^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow R = 199N\]
This \[R = 199N\] is the resultant of these two(as shown)
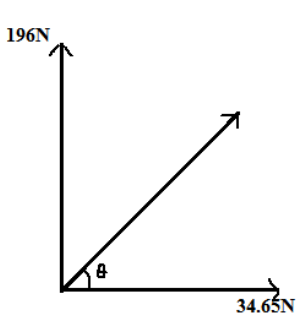
Hence, the reaction forces at A and B are 196N and 34.65N respectively.
Note: If we want to find the value of θ then we can substitute the x and y components of forces which are acting here.
So, \[\operatorname{tan} \theta = \dfrac{{196}}{{34.65}}\]
\[\operatorname{tan} \theta = 5.6\]
\[\theta = 80^\circ \]
Here normal force is a contact force that requires contact to occur, that surfaces exert to prevent solid objects from passing through each other and reaction force is the force that acts in the opposite direction.
Step by step answer: Given that, Length of ladder AB \[ = 3m\]
Weight of ladder(W) \[ = 20kg\]
Distance of ladder from wall, AE=\[1m\]

By making a free body diagram, we can understand in which direction force is acting.
\[
{N_2} = f \\
{N_1} = W \\
\]
Here \[{N_1}\] and \[{N_2}\]are the normal reactions and \[w\]is the weight of the ladder.
Now, use Pythagoras theorem,
\[\sqrt {BE^2} \] = \[\sqrt {A{B^2} - A{C^2}} \] \[ = \sqrt {{3^2} - {1^2}} \]
\[\Rightarrow BE = \sqrt 8 \] \[ = 2\sqrt 2 \]
Now, by using rotational equation,
\[W\left( {1.5\operatorname{Cos} \theta } \right) = 3{N_2}\operatorname{sin} \theta \]
Now, substitute all the given values in this equation.
\[\dfrac{{20 \times 1.5g\operatorname{Cos} \theta }}{{3\operatorname{sin} \theta }} = {N_2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {N_2} = 10g \times cot\theta \]
\[\Rightarrow {N_2} = \dfrac{{10g}}{{\operatorname{tan} \theta }}\]
From the triangle ABE, find the value of
\[\operatorname{tan} \theta \] \[ = \dfrac{{BE}}{{AB}}\]
We know, BE\[ = 2\sqrt 2 \] m
AE\[ = 1m\]
So,
\[\operatorname{tan} \theta = 2\sqrt 2 \]
Now, substitute all the values in \[{N_2}\]equation,
We get-\[\dfrac{{10 \times g}}{{2\sqrt 2 }} = \dfrac{{10 \times 9.8}}{{2\sqrt 2 }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {N_2} = 34.65N\]
So, value of \[{N_2}\] is \[ = 34.65N\]which is equal to f. so, f\[ = 34.65N\]
We know,
\[{N_1} = W\]
\[\Rightarrow {N_1} = 20 \times 9.8\]
\[ \Rightarrow {N_1} = 196N\]
Now, one reaction is in vertical direction and one force I acting in horizontal(as shown), so its resultant will be-
\[{R^2} = \] \[{\left( {196} \right)^2} + {\left( {34.65} \right)^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow R = 199N\]
This \[R = 199N\] is the resultant of these two(as shown)

Hence, the reaction forces at A and B are 196N and 34.65N respectively.
Note: If we want to find the value of θ then we can substitute the x and y components of forces which are acting here.
So, \[\operatorname{tan} \theta = \dfrac{{196}}{{34.65}}\]
\[\operatorname{tan} \theta = 5.6\]
\[\theta = 80^\circ \]
Here normal force is a contact force that requires contact to occur, that surfaces exert to prevent solid objects from passing through each other and reaction force is the force that acts in the opposite direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




