
A 3-4-5(or $3cm\times 4cm\times 5cm$) inclined plane is fixed to a rotating turntable. A block B rests on the inclined plane and the coefficient of static friction between the inclined plane and the block is ${{\mu }_{s}}=\dfrac{1}{4}$. The block is to remain at a position $40cm$ from the centre C of the rotation of the turntable.
The minimum angular velocity $\omega $ to keep the block from sliding down the plane (towards the centre) is ($g=10\dfrac{m}{{{s}^{2}}}$ ) ($in\,\dfrac{rad}{s}$ ):
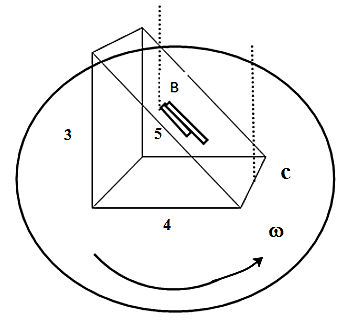

Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, we will first draw the free body diagram of the given figure in the question then; we will write all the forces acting to the block and mention the respective angles. Now, we will write an equilibrium equation and we will get two equations, putting one equation in another and solving them. We will get the value of the minimum angular velocity $\omega $ to keep the block from sliding down the plane as the block is in circular motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly we will draw free body diagram,
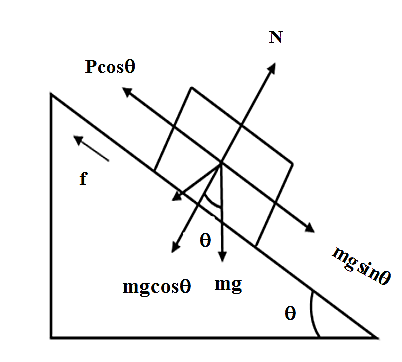
Here, N = normal reaction force
P=centrifugal force
F= static force
Now the condition of equilibrium states that:
$mg\sin \theta =P\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}N$ ………………………………. (1)
$and,N=mgcos\theta +Psin\theta $ …………………………….. (2)
$\Rightarrow $ Putting equation (2) in (1), we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =P\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}mg\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}P\sin \theta \\
& \Rightarrow P=m{{\omega }^{2}}r=(\dfrac{\sin \theta -{{\mu }_{s}}\cos \theta }{\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}\sin \theta })mg \\
& \Rightarrow {{\omega }^{2}}=(\dfrac{\sin \theta -{{\mu }_{s}}\cos \theta }{\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}\sin \theta })\dfrac{g}{r} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\omega }^{2}}=(\dfrac{\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{1}{4}\times \dfrac{4}{5}}{\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{1}{4}\times \dfrac{3}{5}})\times \dfrac{10}{0.4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\omega }^{2}}=10.3 \\
& \therefore \omega \simeq 3.2\dfrac{rad}{s} \\
\end{align}$
So, the minimum angular velocity $\omega $ to keep the block from sliding down the plane will be$3.2\dfrac{rad}{s}$.
Note: In this type of question we must have a good concept of the forces acting on the block otherwise, we will commit mistakes if wrong forces are equated. The angle of repose is defined as the angle of inclination at which the block just accelerates along an inclined surface or starts to move with the constant speed. It can also be said as the maximum angle of inclination at which body stays at rest. Always remember that the angle made by product of the weight of the body and its horizontal component is equal to the angle of inclination.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly we will draw free body diagram,

Here, N = normal reaction force
P=centrifugal force
F= static force
Now the condition of equilibrium states that:
$mg\sin \theta =P\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}N$ ………………………………. (1)
$and,N=mgcos\theta +Psin\theta $ …………………………….. (2)
$\Rightarrow $ Putting equation (2) in (1), we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow mg\sin \theta =P\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}mg\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}P\sin \theta \\
& \Rightarrow P=m{{\omega }^{2}}r=(\dfrac{\sin \theta -{{\mu }_{s}}\cos \theta }{\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}\sin \theta })mg \\
& \Rightarrow {{\omega }^{2}}=(\dfrac{\sin \theta -{{\mu }_{s}}\cos \theta }{\cos \theta +{{\mu }_{s}}\sin \theta })\dfrac{g}{r} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\omega }^{2}}=(\dfrac{\dfrac{3}{5}-\dfrac{1}{4}\times \dfrac{4}{5}}{\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{1}{4}\times \dfrac{3}{5}})\times \dfrac{10}{0.4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\omega }^{2}}=10.3 \\
& \therefore \omega \simeq 3.2\dfrac{rad}{s} \\
\end{align}$
So, the minimum angular velocity $\omega $ to keep the block from sliding down the plane will be$3.2\dfrac{rad}{s}$.
Note: In this type of question we must have a good concept of the forces acting on the block otherwise, we will commit mistakes if wrong forces are equated. The angle of repose is defined as the angle of inclination at which the block just accelerates along an inclined surface or starts to move with the constant speed. It can also be said as the maximum angle of inclination at which body stays at rest. Always remember that the angle made by product of the weight of the body and its horizontal component is equal to the angle of inclination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




