
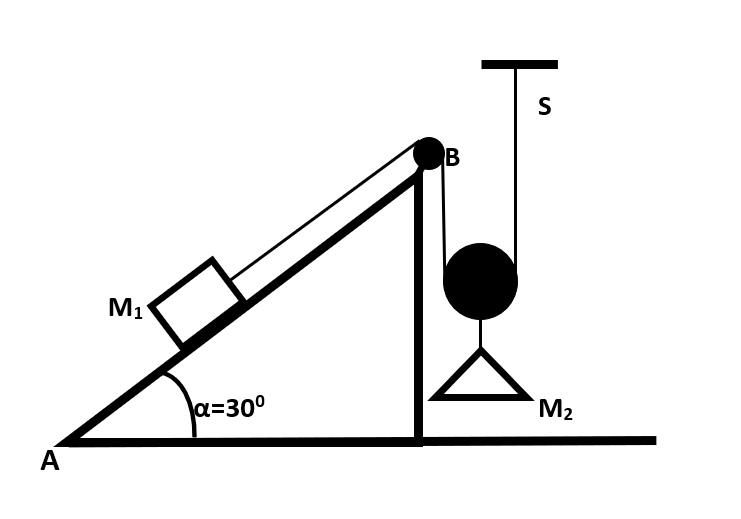
A 30kg block of mass ${{M}_{1}}$ rests on a smooth inclined plane AB. It is attached by a flexible in-extensible string over frictionless light pulley to a 45kg mass ${{M}_{2}}$and a support S. If the angle of inclination of the plane is ${{30}^{0}}$, find at what distance will the block ${{M}_{1}}$ attain the speed of $3m{{s}^{-1}}$ .

Answer
534k+ views
Hint: We will first of all relate the accelerations of the two masses and then write the force equation on these two blocks to get the required acceleration of block 1. Once, we get the acceleration, we can calculate the time taken to reach the desired speed. And then, the distance travelled by the block to reach its desired speed.
Complete answer:
Let the acceleration of block 1 be ‘a’ and the acceleration of block 2 be ‘b’. Then, we can relate these two accelerations as:
$\Rightarrow a=b$
Now, we can write the force equation on these blocks as follows:
On the block weighing 45kg, the force equation will be written as follows:
$\Rightarrow {{M}_{2}}g-2T={{M}_{2}}a$ [Since, accelerations are equal]
And on the block weighing 30kg, we have:
$\Rightarrow T-{{M}_{1}}g\sin \alpha ={{M}_{1}}a$
On multiplying the second equation by 2 and adding it to the first equation, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{M}_{2}}g-2{{M}_{1}}g\sin \alpha =(2{{M}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}})a \\
& \therefore a=\dfrac{({{M}_{2}}-2{{M}_{1}}\sin \alpha )g}{(2{{M}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}})} \\
\end{align}$
Putting the values of all the known terms, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{\left( 45-2\times 30\times \dfrac{1}{2} \right)10}{\left( 45+2\times 30 \right)} \\
& \therefore a=\dfrac{10}{7}m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, if the block starts from rest, time taken to reach a speed of $3m{{s}^{-1}}$ is:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 3=0+\dfrac{10}{7}t \\
& \therefore t=2.1s \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the distance travelled to reach this speed is equal to:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow s=0\times 2.1+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{10}{7}\times {{(2.1)}^{2}} \\
& \therefore s=3.15m \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the distance at which the block ${{M}_{1}}$ will attain a speed of $3m{{s}^{-1}}$ is 3.15 meters.
Note:
In problems like these, the tricky part is to establish the relation between the objects that are under tension. But once, this is done the problem can then be easily solved by just writing the force equations on the blocks. The total number of equations will always be greater than the total number of variables present in the problem.
Complete answer:
Let the acceleration of block 1 be ‘a’ and the acceleration of block 2 be ‘b’. Then, we can relate these two accelerations as:
$\Rightarrow a=b$
Now, we can write the force equation on these blocks as follows:
On the block weighing 45kg, the force equation will be written as follows:
$\Rightarrow {{M}_{2}}g-2T={{M}_{2}}a$ [Since, accelerations are equal]
And on the block weighing 30kg, we have:
$\Rightarrow T-{{M}_{1}}g\sin \alpha ={{M}_{1}}a$
On multiplying the second equation by 2 and adding it to the first equation, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{M}_{2}}g-2{{M}_{1}}g\sin \alpha =(2{{M}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}})a \\
& \therefore a=\dfrac{({{M}_{2}}-2{{M}_{1}}\sin \alpha )g}{(2{{M}_{1}}+{{M}_{2}})} \\
\end{align}$
Putting the values of all the known terms, we get:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{\left( 45-2\times 30\times \dfrac{1}{2} \right)10}{\left( 45+2\times 30 \right)} \\
& \therefore a=\dfrac{10}{7}m{{s}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, if the block starts from rest, time taken to reach a speed of $3m{{s}^{-1}}$ is:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 3=0+\dfrac{10}{7}t \\
& \therefore t=2.1s \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the distance travelled to reach this speed is equal to:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow s=0\times 2.1+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{10}{7}\times {{(2.1)}^{2}} \\
& \therefore s=3.15m \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the distance at which the block ${{M}_{1}}$ will attain a speed of $3m{{s}^{-1}}$ is 3.15 meters.
Note:
In problems like these, the tricky part is to establish the relation between the objects that are under tension. But once, this is done the problem can then be easily solved by just writing the force equations on the blocks. The total number of equations will always be greater than the total number of variables present in the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




