
A $2m$ wide truck is moving with a uniform speed ${v_0} = 8m{s^{ - 1}}$ along a straight horizontal road. A pedestrian starts to cross over the road with a uniform speed $v$ when the truck is $4m$ away from him. The minimum value of $v$ so that he can cross the road safely is
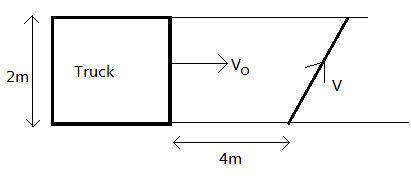
A. $2.62m{s^{ - 1}}$
B. $4.6m{s^{ - 1}}$
C. $3.57m{s^{ - 1}}$
D. $1.414m{s^{ - 1}}$

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Split the velocity of the pedestrian in horizontal and vertical components. The distance to be travelled by the pedestrian is $2m$ . The truck is moving horizontally, so for the pedestrian to safely cross the road; the horizontal distance by the pedestrian $(x)\,m$ must at least equal to the distance travelled by the truck $(x + 4)m$ .
Complete step by step answer:
Please note that the pedestrian will take the same time to travel in the vertical direction as much time taken to travel in a horizontal direction. But in the meantime the truck will also move some distance. We know for sure that the pedestrian has to travel a vertical distance of $2m$ .
Consider that the pedestrian travels at an angle $\theta $ with the horizontal as shown below:
And let's split the velocity of the pedestrian.
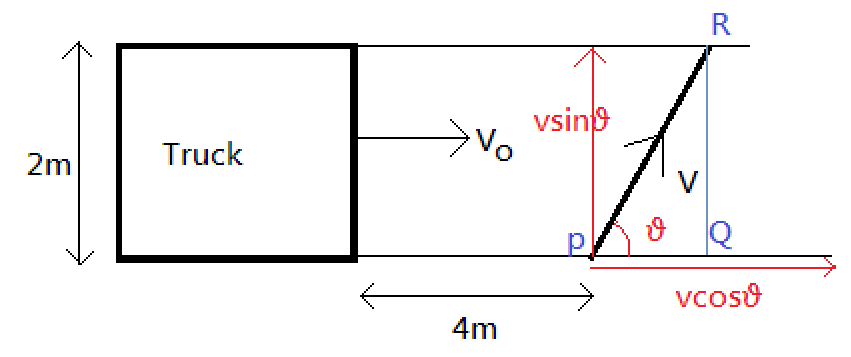
Note that the distance $PQ = 2\cot \theta $
For vertical direction.
Velocity of the pedestrian $ = v\sin \theta $ and the distance to be travelled $ = 2m$
So, the time taken will be:
${t_p} = \dfrac{2}{{v\sin \theta }}$
Where ${t_p}$ is the time taken by pedestrians.
At the same time the truck will move some horizontal distance. The truck will move a total distance of $4m + PQ = 4 + 2\cot \theta $
The minimum time taken by pedestrians to cross vertical distance will be the same as the time taken by the truck to cover $4 + 2\cot \theta $ distance.
$ \Rightarrow {t_p} = \dfrac{2}{{v\sin \theta }} = \dfrac{{4 + 2\cot \theta }}{8}$
Solving this equation, we will get the minimum velocity for the pedestrian to cross safely.
$$v = \dfrac{8}{{(2\sin \theta + \cos \theta )}}$$ --equation $1$
By properties of differentiation, the minimum velocity is obtained when
$$\dfrac{{dv}}{{d\theta }} = 0$$
$$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dv}}{{d\theta }} = \dfrac{{ - 8}}{{(2\sin \theta + \cos \theta )}} \times \left( {2\cos \theta - \sin \theta } \right) = 0$$
$$ \Rightarrow \left( {2\cos \theta - \sin \theta } \right) = 0$$
$$\sin \theta = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}\,;\,\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}$$
Substituting these values in equation $1$ , we get
$v = \dfrac{8}{{2 \times \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }} + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}}}$
$v = \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
$v = 3.57m{s^{ - 1}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In such types of questions, remember that the vertical distance is fixed. So, time can be calculated. Now the truck too takes the same time to reach the pedestrian.
Also remember that this is the minimum speed.
The mean time the truck will also move some distance.
Complete step by step answer:
Please note that the pedestrian will take the same time to travel in the vertical direction as much time taken to travel in a horizontal direction. But in the meantime the truck will also move some distance. We know for sure that the pedestrian has to travel a vertical distance of $2m$ .
Consider that the pedestrian travels at an angle $\theta $ with the horizontal as shown below:
And let's split the velocity of the pedestrian.

Note that the distance $PQ = 2\cot \theta $
For vertical direction.
Velocity of the pedestrian $ = v\sin \theta $ and the distance to be travelled $ = 2m$
So, the time taken will be:
${t_p} = \dfrac{2}{{v\sin \theta }}$
Where ${t_p}$ is the time taken by pedestrians.
At the same time the truck will move some horizontal distance. The truck will move a total distance of $4m + PQ = 4 + 2\cot \theta $
The minimum time taken by pedestrians to cross vertical distance will be the same as the time taken by the truck to cover $4 + 2\cot \theta $ distance.
$ \Rightarrow {t_p} = \dfrac{2}{{v\sin \theta }} = \dfrac{{4 + 2\cot \theta }}{8}$
Solving this equation, we will get the minimum velocity for the pedestrian to cross safely.
$$v = \dfrac{8}{{(2\sin \theta + \cos \theta )}}$$ --equation $1$
By properties of differentiation, the minimum velocity is obtained when
$$\dfrac{{dv}}{{d\theta }} = 0$$
$$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dv}}{{d\theta }} = \dfrac{{ - 8}}{{(2\sin \theta + \cos \theta )}} \times \left( {2\cos \theta - \sin \theta } \right) = 0$$
$$ \Rightarrow \left( {2\cos \theta - \sin \theta } \right) = 0$$
$$\sin \theta = \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }}\,;\,\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}$$
Substituting these values in equation $1$ , we get
$v = \dfrac{8}{{2 \times \dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 5 }} + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 5 }}}}$
$v = \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 5 }}$
$v = 3.57m{s^{ - 1}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In such types of questions, remember that the vertical distance is fixed. So, time can be calculated. Now the truck too takes the same time to reach the pedestrian.
Also remember that this is the minimum speed.
The mean time the truck will also move some distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




