
A $2m$ long wire of resistance 4 ohms ($4\Omega $ ) and diameter $0.64mm$ is coated with plastic insulation of thickness$0.66mm$. When a current $5A$ flows through the wire, find the temperature difference across the insulation in steady-state.
If $K=0.16\times {{10}^{-2}}cal/cm{}^\circ C\sec $ .
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: When current is flowing through a conductor continuously some amount of the heat will get wasted in the form of the heat. The change in the heat results in an increase in the temperature around the conductor. In terms of electronics, the heat loss can be termed as the power loss of the system.
As per the given data,
The length $\left( l \right)$ of the wire is $2m$
The resistance of the wire $4\Omega $
The diameter of the wire is $0.64mm$. (Radius is $0.32mm$)
The thickness of the plastic insulation is $0.66mm$ (so the radius from the center of the conductor will be $0.33mm$)
The value of $K=0.16\times {{10}^{-2}}cal/cm{}^\circ C\sec $ .
Complete answer:
Consider a cross-section of a conductor having the following labeled dimensions.
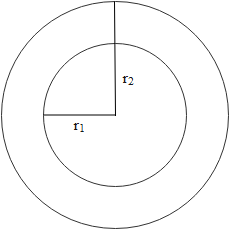
So the power loss is given as,
$P={{I}^{2}}R$
By putting the values from the given information from the question,
$\begin{align}
& P=({{5}^{2}})4 \\
& \Rightarrow P=100W \\
\end{align}$
The power loss is in the terms of heat energy only so it can be said that $100W$ power will be converted into heat.
The relation between the heat and the change in the temperature (temperature difference) is given as,
$H=\dfrac{\Delta T}{R}\quad .....(1)$
The value of R for the case of a cylindrical conductor is given as,
$R=\dfrac{\ln (\dfrac{{{r}_{2}}}{{{r}_{1}}})}{2\pi kl}$
So, after putting the value of $R$ the equation (1) can be written as,
$100=\dfrac{2\pi kl\Delta T}{\ln \left( \dfrac{{{r}_{1}}}{{{r}_{2}}} \right)}$
By putting the values from the given information in the above equation the temperature difference is given as,
$\Delta T=2.23{}^\circ C$
Thus, the required answer to the question is $2.23{}^\circ C$.
Note:
According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can never be created or destroyed; it can be just transformed from one form to another. In practical studies during any energy transfer, the energy cannot be transferred completely so the energy gets released as heat energy. Also creates a temperature difference in the material. The heat-generating property of the material is used to produce many instruments such as water heater, induction cooking plate, immersion rod, etc.
As per the given data,
The length $\left( l \right)$ of the wire is $2m$
The resistance of the wire $4\Omega $
The diameter of the wire is $0.64mm$. (Radius is $0.32mm$)
The thickness of the plastic insulation is $0.66mm$ (so the radius from the center of the conductor will be $0.33mm$)
The value of $K=0.16\times {{10}^{-2}}cal/cm{}^\circ C\sec $ .
Complete answer:
Consider a cross-section of a conductor having the following labeled dimensions.

So the power loss is given as,
$P={{I}^{2}}R$
By putting the values from the given information from the question,
$\begin{align}
& P=({{5}^{2}})4 \\
& \Rightarrow P=100W \\
\end{align}$
The power loss is in the terms of heat energy only so it can be said that $100W$ power will be converted into heat.
The relation between the heat and the change in the temperature (temperature difference) is given as,
$H=\dfrac{\Delta T}{R}\quad .....(1)$
The value of R for the case of a cylindrical conductor is given as,
$R=\dfrac{\ln (\dfrac{{{r}_{2}}}{{{r}_{1}}})}{2\pi kl}$
So, after putting the value of $R$ the equation (1) can be written as,
$100=\dfrac{2\pi kl\Delta T}{\ln \left( \dfrac{{{r}_{1}}}{{{r}_{2}}} \right)}$
By putting the values from the given information in the above equation the temperature difference is given as,
$\Delta T=2.23{}^\circ C$
Thus, the required answer to the question is $2.23{}^\circ C$.
Note:
According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can never be created or destroyed; it can be just transformed from one form to another. In practical studies during any energy transfer, the energy cannot be transferred completely so the energy gets released as heat energy. Also creates a temperature difference in the material. The heat-generating property of the material is used to produce many instruments such as water heater, induction cooking plate, immersion rod, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




