
A $2kg$ brick of dimension $5m \times 2.5m \times 1.5m$ is lying on the largest base. It is now made to stand with length vertical, then the amount of work done is: (taken $g = 10m/{s^2}$)
A. $35J$
B. $5J$
C. $7J$
D. $9J$
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Any object which is present above the ground is said to have potential energy. As the height of the object increases the potential energy also increases. This increase in the potential energy of the object is the work done. For the brick, the height of the brick is to be calculated with respect to the center of mass from the ground.
Formula used:
$P.E. = mgh$
$W = {(P.E.)_2} - {(P.E.)_1}$
Complete answer:
Let’s consider the initial position of the brick. It is lying on the largest base, as shown in the figure.
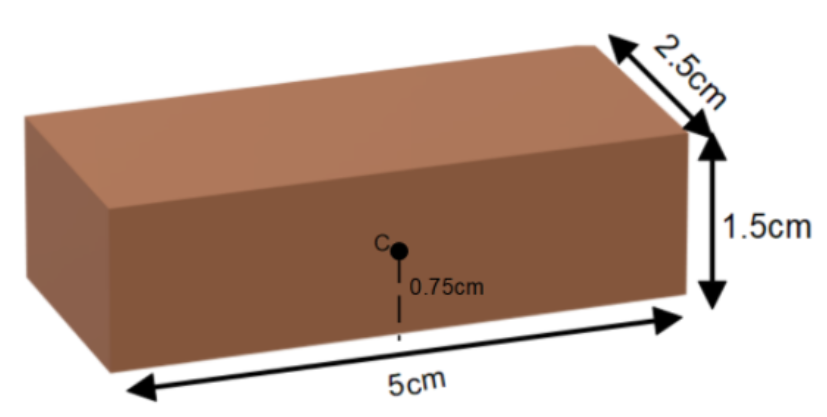
For an object of mass ‘$m$’, at a height ‘$h$’ the potential energy is given by $P.E. = mgh$.
In this case, let us assume that the potential energy of the brick is ${\left( {P.E.} \right)_1}$, given by
$\eqalign{
& {\left( {P.E.} \right)_1} = mg{h_1} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {P.E.} \right)_1} = 2kg \times 10m{s^{ - 2}} \times 0.75m \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {P.E.} \right)_1} = 15J \cr} $
Here the center of mass of the brick lies at the height ‘${h_1}$’ of $0.75m$.
Now, in the second case, the height of the brick is $5m$. So, its center of mass lies at the height ${h_2} = 2.5m$. The potential energy of the brick, in this case, is given by
$\eqalign{
& {\left( {P.E.} \right)_2} = mg{h_2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {P.E.} \right)_2} = 2kg \times 10m{s^{ - 2}} \times 2.5m \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {P.E.} \right)_2} = 50J \cr} $
The work done in changing the brick from the initial position to the final position is seen as the change in the potential energy of the brick. The work done is given by
$\eqalign{
& W = {(P.E.)_2} - {(P.E.)_1} \cr
& \Rightarrow W = 50J - 15J = 35J \cr
& \therefore W = 35J \cr} $
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:
- The change in the potential energy is the work done as per the law of conservation of energy; energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it is only converted from one form to another.
- Center of mass of an object is the point that works as if the complete mass of the object is concentrated at that point. That is the reason for considering the height of the object from the center of mass.
Formula used:
$P.E. = mgh$
$W = {(P.E.)_2} - {(P.E.)_1}$
Complete answer:
Let’s consider the initial position of the brick. It is lying on the largest base, as shown in the figure.

For an object of mass ‘$m$’, at a height ‘$h$’ the potential energy is given by $P.E. = mgh$.
In this case, let us assume that the potential energy of the brick is ${\left( {P.E.} \right)_1}$, given by
$\eqalign{
& {\left( {P.E.} \right)_1} = mg{h_1} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {P.E.} \right)_1} = 2kg \times 10m{s^{ - 2}} \times 0.75m \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {P.E.} \right)_1} = 15J \cr} $
Here the center of mass of the brick lies at the height ‘${h_1}$’ of $0.75m$.
Now, in the second case, the height of the brick is $5m$. So, its center of mass lies at the height ${h_2} = 2.5m$. The potential energy of the brick, in this case, is given by
$\eqalign{
& {\left( {P.E.} \right)_2} = mg{h_2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {P.E.} \right)_2} = 2kg \times 10m{s^{ - 2}} \times 2.5m \cr
& \Rightarrow {\left( {P.E.} \right)_2} = 50J \cr} $
The work done in changing the brick from the initial position to the final position is seen as the change in the potential energy of the brick. The work done is given by
$\eqalign{
& W = {(P.E.)_2} - {(P.E.)_1} \cr
& \Rightarrow W = 50J - 15J = 35J \cr
& \therefore W = 35J \cr} $
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:
- The change in the potential energy is the work done as per the law of conservation of energy; energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it is only converted from one form to another.
- Center of mass of an object is the point that works as if the complete mass of the object is concentrated at that point. That is the reason for considering the height of the object from the center of mass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




