
A 2kg block is dropped from a height 0.4m on a spring of force constant k=1960 N/m. The maximum compression of spring is
A. 0.1m
B. 0.2m
C. 0.3m
D. 0.4m
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: We apply the conservation of energy equation to obtain the maximum compression of the spring. Loss in gravitational potential energy is equal to the potential energy stored in the spring. You have to solve a quadratic equation to calculate the maximum compression.
Formulas used:
\[{{K}_{i}}+{{P}_{i}}+{{W}_{nc}}+O{{E}_{i}}={{K}_{f}}+{{P}_{f}}+O{{E}_{f}}\]
$mg(h+x)=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
Complete step by step answer:
The conservation of energy is a classic concept of physics. It states that within a system the total amount of energy remains constant. Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. The conservation of energy formula is:
\[{{K}_{i}}+{{P}_{i}}+{{W}_{nc}}+O{{E}_{i}}={{K}_{f}}+{{P}_{f}}+O{{E}_{f}}\]………. (1)
where \[{{K}_{i}}\]is initial kinetic energy, \[{{P}_{i}}\] is initial potential energy, \[{{W}_{nc}}\]is work done by non-conservative forces, \[O{{E}_{i}}\] is other initial energies, \[{{K}_{f}}\]is final kinetic energy, \[{{P}_{f}}\]is final potential energy, \[O{{E}_{f}}\] is other final energies.
The diagram below depicts our system:
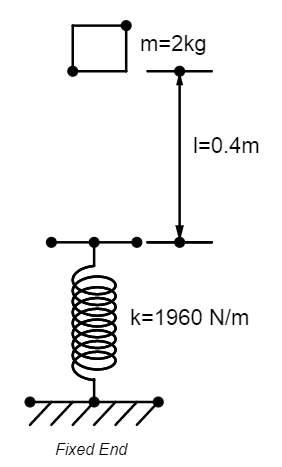
We have, mass of the block = 2 kg; height (h) = 0.4m; force constant (k) = 1960N/m.
Let us consider x to be the maximum compression of the spring. So the total distance travelled by the block during free fall is$(h+x)$.
By using the law of conservation of energy, we have loss in gravitational potential energy equal to the potential energy stored in the spring.
$mg(h+x)=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
Let us substitute the given values in the above equation
$2\times 10(0.4+x)=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1960\times {{x}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 20x+8=980{{x}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 980{{x}^{2}}+20x+8=0$
So now we have to solve a quadratic equation with a=980, b=20, c=8
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-20\pm \sqrt{{{20}^{2}}-4\times 980}\times 8}{2\times 980}$
$\Rightarrow x=0.1m$
So the correct option is (a).
Note: The loss in the gravitational potential energy might be confused to be negative but it is $+mg(h+x)$ because during a free fall g is negative which makes the entire formula positive. Students should focus on giving directions to the forces which results in change in magnitude.
Formulas used:
\[{{K}_{i}}+{{P}_{i}}+{{W}_{nc}}+O{{E}_{i}}={{K}_{f}}+{{P}_{f}}+O{{E}_{f}}\]
$mg(h+x)=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
Complete step by step answer:
The conservation of energy is a classic concept of physics. It states that within a system the total amount of energy remains constant. Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. The conservation of energy formula is:
\[{{K}_{i}}+{{P}_{i}}+{{W}_{nc}}+O{{E}_{i}}={{K}_{f}}+{{P}_{f}}+O{{E}_{f}}\]………. (1)
where \[{{K}_{i}}\]is initial kinetic energy, \[{{P}_{i}}\] is initial potential energy, \[{{W}_{nc}}\]is work done by non-conservative forces, \[O{{E}_{i}}\] is other initial energies, \[{{K}_{f}}\]is final kinetic energy, \[{{P}_{f}}\]is final potential energy, \[O{{E}_{f}}\] is other final energies.
The diagram below depicts our system:

We have, mass of the block = 2 kg; height (h) = 0.4m; force constant (k) = 1960N/m.
Let us consider x to be the maximum compression of the spring. So the total distance travelled by the block during free fall is$(h+x)$.
By using the law of conservation of energy, we have loss in gravitational potential energy equal to the potential energy stored in the spring.
$mg(h+x)=\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
Let us substitute the given values in the above equation
$2\times 10(0.4+x)=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1960\times {{x}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 20x+8=980{{x}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 980{{x}^{2}}+20x+8=0$
So now we have to solve a quadratic equation with a=980, b=20, c=8
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-20\pm \sqrt{{{20}^{2}}-4\times 980}\times 8}{2\times 980}$
$\Rightarrow x=0.1m$
So the correct option is (a).
Note: The loss in the gravitational potential energy might be confused to be negative but it is $+mg(h+x)$ because during a free fall g is negative which makes the entire formula positive. Students should focus on giving directions to the forces which results in change in magnitude.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




