
A 25-feet ladder leans against a building. As the bottom of the ladder at a point \[A\] slides away from the building, the top of the ladder, \[B\], slides from a height of \[24\] feet above the ground to a height of \[16\] feet. How many feet did the bottom of the ladder slide?
Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: In order to find the distance the ladder has slided, we will be applying the Pythagoras theorem. By applying the Pythagoras theorem, we will be finding the distance from the building to the actual point of the ladder firstly. Then we will be finding the distance from the building to the point at which the ladder has slided. Then we will be finding the distance it has slided by subtracting the distance to the second point from the distance to first or actual point.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now let us learn about the Pythagoras theorem. It is a theorem which basically defines the relation between the sides of a right-angled triangle. It helps in finding the length of an unknown side of a triangle. It generally states that the square of sum of two sides of a triangle is equal to the square of the hypotenuse.
Now let us find the distance the ladder has slided.
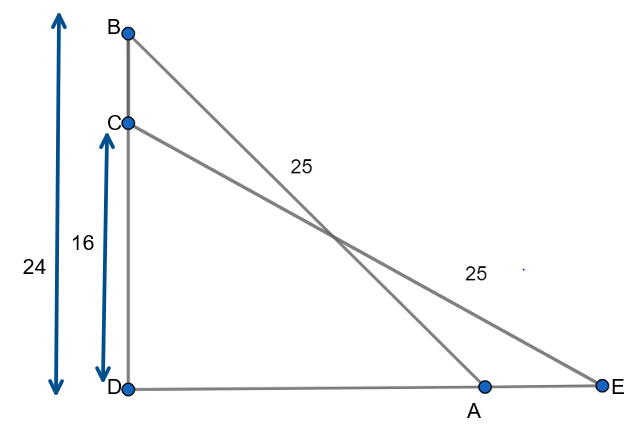
Let us consider \[\Delta ABC\]
We know that from Pythagoras theorem that \[A{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}-B{{D}^{2}}\]
Now upon substituting the values, we get
\[\Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}={{25}^{2}}-{{24}^{2}}\]
Upon solving this, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}={{25}^{2}}-{{24}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}=625-576 \\
& \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}=49 \\
& \Rightarrow AD=\sqrt{49} \\
& \Rightarrow AD=7 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] The distance from the building to the actual point is \[7\]feet.
Now let us find the distance from the building to the new position of the ladder after sliding .
Now let us consider \[\Delta CDE\]
So we know that from Pythagoras theorem that \[\Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}=C{{E}^{2}}-C{{D}^{2}}\]
Now upon substituting the values, we get
\[\Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}={{25}^{2}}-{{16}^{2}}\]
Upon solving this, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}={{25}^{2}}-{{16}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}=625-256 \\
& \Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}=369 \\
& \Rightarrow DE=\sqrt{369} \\
& \Rightarrow DE=19.2 \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us find the distance from the original position to the new position.
\[\Rightarrow 19.2-7=12.2\]
\[\therefore \] The bottom ladder has slided \[12.2\] feet.
Note: We must note that we can apply the Pythagoras theorem only when the problem statement given forms a right-angled triangle. The required distances or the lengths can be found easily. We can find the distance by finding out the length of \[AD\] and \[AE\] and then adding them up gives us the required answer too.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now let us learn about the Pythagoras theorem. It is a theorem which basically defines the relation between the sides of a right-angled triangle. It helps in finding the length of an unknown side of a triangle. It generally states that the square of sum of two sides of a triangle is equal to the square of the hypotenuse.
Now let us find the distance the ladder has slided.

Let us consider \[\Delta ABC\]
We know that from Pythagoras theorem that \[A{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}-B{{D}^{2}}\]
Now upon substituting the values, we get
\[\Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}={{25}^{2}}-{{24}^{2}}\]
Upon solving this, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}={{25}^{2}}-{{24}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}=625-576 \\
& \Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}=49 \\
& \Rightarrow AD=\sqrt{49} \\
& \Rightarrow AD=7 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\therefore \] The distance from the building to the actual point is \[7\]feet.
Now let us find the distance from the building to the new position of the ladder after sliding .
Now let us consider \[\Delta CDE\]
So we know that from Pythagoras theorem that \[\Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}=C{{E}^{2}}-C{{D}^{2}}\]
Now upon substituting the values, we get
\[\Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}={{25}^{2}}-{{16}^{2}}\]
Upon solving this, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}={{25}^{2}}-{{16}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}=625-256 \\
& \Rightarrow D{{E}^{2}}=369 \\
& \Rightarrow DE=\sqrt{369} \\
& \Rightarrow DE=19.2 \\
\end{align}\]
Now let us find the distance from the original position to the new position.
\[\Rightarrow 19.2-7=12.2\]
\[\therefore \] The bottom ladder has slided \[12.2\] feet.
Note: We must note that we can apply the Pythagoras theorem only when the problem statement given forms a right-angled triangle. The required distances or the lengths can be found easily. We can find the distance by finding out the length of \[AD\] and \[AE\] and then adding them up gives us the required answer too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?




