
A 1.6 meters tall boy spots an object moving with the wind in a horizontal line at the height of 88.6 meters from the ground. The angle of elevation reduces to ${30^0}$. Find the distance travelled by the object during the interval.
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: In this question, we need to determine the distance travelled by the object during the interval such that it makes an angle of elevation with the tall box as 30 degrees. For this, we will use the trigonometric identity of $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{perpendiclar}}{{base}}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
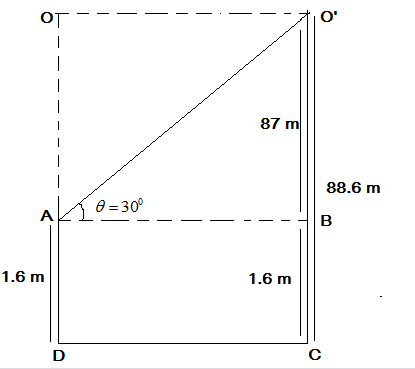
The object is flying due to wind from the point O to O’ making an angle of elevation with the 1.6 meters tall boy of 30 degrees.
From the figure, we can see that $AD = BC = 1.6{\text{ m}}$.
Also, the total height of the flying object is the sum of the height of the boy and O’B. So,
$
O'C = O'B + BC \\
88.6 = O'B + 1.6 \\
O'B = 88.6 - 1.6 \\
= 87{\text{ m}} \\
$
Following the trigonometric function of tangent in the triangle O’AB such that $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{perpendiclar}}{{base}}$. Here, perpendicular is the opposite side of the angle under consideration, and the base is the third side other than the hypotenuse. Hence, O’B is the perpendicular and AB is the base in the triangle O’AB.
So, substitute $\angle O'AB = {30^0}{\text{ and O'B = 87 m}}$ in the formula $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{perpendiclar}}{{base}}$ to determine the base of the triangle or the distance between the object and the boy.
$
\tan \theta = \dfrac{{perpendiclar}}{{base}} \\
\tan {30^0} = \dfrac{{87}}{{AB}} - - - - (i) \\
$
Now, substitute the value of the tangent of 30 degrees as $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ in the equation (i) we get-
$
\tan {30^0} = \dfrac{{87}}{{AB}} \\
\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{87}}{{AB}} \\
AB = 87\sqrt 3 {\text{ meters}} \\
$
Substitute the value of the root of 3 as 1.732 in the above equation we get-
$
AB = 87\sqrt 3 \\
= 87 \times 1.732 \\
= 150.684{\text{ meters}} \\
$
Hence, the distance travelled by the object in the meantime is 150.684 meters.
Note: Students must be careful while using the perpendicular and the base sides of the triangle. It is to be noted that the side opposite to the angle under observation is considered as the perpendicular of the triangle and the side other than the perpendicular and the hypotenuse is the base.
Complete step-by-step answer:

The object is flying due to wind from the point O to O’ making an angle of elevation with the 1.6 meters tall boy of 30 degrees.
From the figure, we can see that $AD = BC = 1.6{\text{ m}}$.
Also, the total height of the flying object is the sum of the height of the boy and O’B. So,
$
O'C = O'B + BC \\
88.6 = O'B + 1.6 \\
O'B = 88.6 - 1.6 \\
= 87{\text{ m}} \\
$
Following the trigonometric function of tangent in the triangle O’AB such that $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{perpendiclar}}{{base}}$. Here, perpendicular is the opposite side of the angle under consideration, and the base is the third side other than the hypotenuse. Hence, O’B is the perpendicular and AB is the base in the triangle O’AB.
So, substitute $\angle O'AB = {30^0}{\text{ and O'B = 87 m}}$ in the formula $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{perpendiclar}}{{base}}$ to determine the base of the triangle or the distance between the object and the boy.
$
\tan \theta = \dfrac{{perpendiclar}}{{base}} \\
\tan {30^0} = \dfrac{{87}}{{AB}} - - - - (i) \\
$
Now, substitute the value of the tangent of 30 degrees as $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ in the equation (i) we get-
$
\tan {30^0} = \dfrac{{87}}{{AB}} \\
\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{87}}{{AB}} \\
AB = 87\sqrt 3 {\text{ meters}} \\
$
Substitute the value of the root of 3 as 1.732 in the above equation we get-
$
AB = 87\sqrt 3 \\
= 87 \times 1.732 \\
= 150.684{\text{ meters}} \\
$
Hence, the distance travelled by the object in the meantime is 150.684 meters.
Note: Students must be careful while using the perpendicular and the base sides of the triangle. It is to be noted that the side opposite to the angle under observation is considered as the perpendicular of the triangle and the side other than the perpendicular and the hypotenuse is the base.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




