
A 10kg monkey is climbing a massless rope attached to a \[15\,{\text{kg}}\] mass over a tree limb. The mass is lying on the ground. In order to raise the mass from the ground it must climb with
A. Uniform acceleration greater than \[{\text{5}}\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
B. Uniform acceleration greater than \[{\text{2}}{\text{.5}}\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
C. High speed
D. Uniform acceleration greater than \[10\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\]
Answer
564.3k+ views
Hint: Here, we have to find the acceleration required by the monkey to raise the mass from the ground. First draw a free body diagram for the problem and balance the forces to find the value of tension of the rope and use this value to find the minimum acceleration required by the monkey to climb the rope.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, mass of the monkey, \[m = 10\,{\text{kg}}\], Mass attached to the rope, \[M = 15\,{\text{kg}}\].
Let the minimum acceleration required by the monkey to climb the rope be \[a\], acceleration due to gravity be \[g = 10\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\] and \[T\] be the tension of the rope.Now, let us draw the free body diagram for the problem.
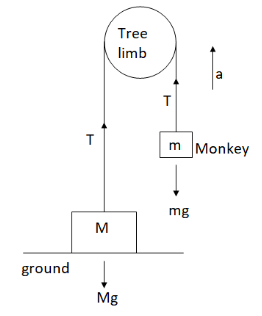
The mass \[M\] is at rest, so tension of the rope should be equal to the weight of mass \[M\]that is,
\[T = Mg\]
Putting the values of \[M\] and \[g\] we get,
\[T = 15 \times 10\,{\text{N}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = 150\,{\text{N}}\] …………………(i)
Now, for the monkey we have from the figure,
\[T - mg = ma\]
Putting the values of \[T\], \[m\] and \[g\], we get
\[150 - 10 \times 10 = 10a\]
\[ \Rightarrow 150 - 100 = 10a\]
\[ \Rightarrow 50 = 10a\]
\[ \Rightarrow 10a = 50\]
\[ \therefore a = 5\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\]
Therefore, the minimum acceleration required by the monkey to climb the rope is \[5\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\]. So, to raise the mass from the ground the monkey must climb with acceleration greater than \[5\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\].
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: For such types of questions, first draw a free body diagram showing all the forces acting on the system with its direction, as it will help us to visualize the problem. Then observing the diagram we can balance the forces to get our required result. Also, while drawing a free body diagram carefully assign the direction of the forces.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, mass of the monkey, \[m = 10\,{\text{kg}}\], Mass attached to the rope, \[M = 15\,{\text{kg}}\].
Let the minimum acceleration required by the monkey to climb the rope be \[a\], acceleration due to gravity be \[g = 10\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\] and \[T\] be the tension of the rope.Now, let us draw the free body diagram for the problem.

The mass \[M\] is at rest, so tension of the rope should be equal to the weight of mass \[M\]that is,
\[T = Mg\]
Putting the values of \[M\] and \[g\] we get,
\[T = 15 \times 10\,{\text{N}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = 150\,{\text{N}}\] …………………(i)
Now, for the monkey we have from the figure,
\[T - mg = ma\]
Putting the values of \[T\], \[m\] and \[g\], we get
\[150 - 10 \times 10 = 10a\]
\[ \Rightarrow 150 - 100 = 10a\]
\[ \Rightarrow 50 = 10a\]
\[ \Rightarrow 10a = 50\]
\[ \therefore a = 5\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\]
Therefore, the minimum acceleration required by the monkey to climb the rope is \[5\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\]. So, to raise the mass from the ground the monkey must climb with acceleration greater than \[5\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{{\text{ - 2}}}}\].
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: For such types of questions, first draw a free body diagram showing all the forces acting on the system with its direction, as it will help us to visualize the problem. Then observing the diagram we can balance the forces to get our required result. Also, while drawing a free body diagram carefully assign the direction of the forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




