
A $10kg$ block is pulled along a frictionless surface in the form of an arc or a circle of radius $10m$ The applied force is of $200N$ as shown in the figure. If the block started from rest at A, the velocity at B would be: $(g = 10m{s^{ - 2}})$
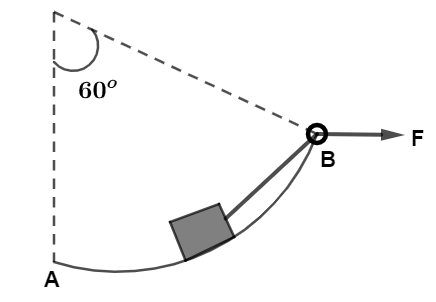
(A) $\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}}$
(B) $10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}}$
(C) $100\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}}$
(D) None of these

Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we will first find the work done by the applied force and the potential energy of block due to rise in height by drawing free body diagram and later will use the concept that work done will be equal to that of net energy used of the body.
Complete answer:
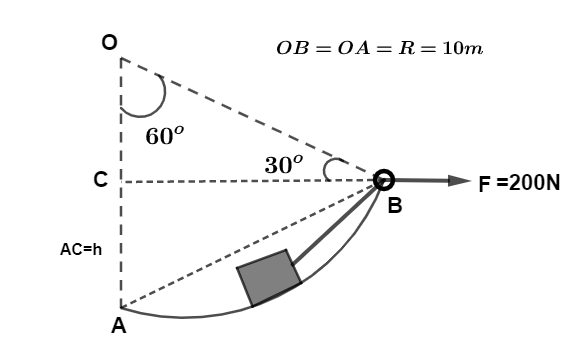
Let us first draw the diagram as:
$OA = OB = R = 10m$ radius if circular arc given in question.
Let AC be the height from point A to which block is raised to reach point B.
Since, In $\Delta OAB$ $OA = OB$ so remaining angles $\angle OAB = \angle OBA = {60^0}$ which makes triangle OAB a equilateral triangle such that distance covered by the block due to applied force $F = 200N$ will be $AB = OA = R = 10m$ hence, work done by the force is given by,
$W = F.AB$
on putting the values we get,
$W = 2000J \to (i)$
Now, mass of the block is given by $m = 10kg$
acceleration due to gravity is $g = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
and height to which block is raised is $AC = h$
now, in right angle triangle OCB we have,
$\sin {30^0} = \dfrac{{OC}}{{OB}}$ we know $\sin {30^0} = \dfrac{1}{2},OB = R = 10m$ on putting these values we get,
$\dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{OC}}{{10}}$
$ \Rightarrow OC = 5m$ now the height h can be written as from diagram we have,
$AC = OA - OC$
$AC = h = 10 - 5 = 5m$
so height is given by $h = 5m$
hence, potential energy of the block is
$P.E = mgh$ on putting the values we get,
$P.E = 10 \times 10 \times 5$
$ \Rightarrow P.E = 500J \to (ii)$
Now, the kinetic energy of the block while it’s at rest at point A is $K.{E_A} = 0$
Let K.E of the block at point B with velocity v is $K.{E_B} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} \to (iii)$
Now, Sum of all energy of the block will be equal to work done by the applied force so, net energy on the block is sum of potential energy and change in Kinetic energy so,
$W = P.E + K.{E_B} - K.{E_A}$
on putting the values of these parameters from equation (i) , (ii) and (ii) we get,
$2000 = 500 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times {v^2} - 0$
$2000 - 500 = 5{v^2}$
$1500 = 5{v^2}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {300} $
$ \Rightarrow v = 10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}}$
Hence, the correct option is (B) $10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}}$.
Note: It should be remembered that, the work done by a body is equal to change in energy of a body is referred as Work Energy theorem. and also when two sides of a triangle are equal then the opposite angles of these sides are also equal is an property of triangles. In an equilateral triangle all sides are equal and all angles are of ${60^0}$ each.
Complete answer:
Let us first draw the diagram as:
$OA = OB = R = 10m$ radius if circular arc given in question.
Let AC be the height from point A to which block is raised to reach point B.
Since, In $\Delta OAB$ $OA = OB$ so remaining angles $\angle OAB = \angle OBA = {60^0}$ which makes triangle OAB a equilateral triangle such that distance covered by the block due to applied force $F = 200N$ will be $AB = OA = R = 10m$ hence, work done by the force is given by,
$W = F.AB$
on putting the values we get,
$W = 2000J \to (i)$
Now, mass of the block is given by $m = 10kg$

acceleration due to gravity is $g = 10m{s^{ - 2}}$
and height to which block is raised is $AC = h$
now, in right angle triangle OCB we have,
$\sin {30^0} = \dfrac{{OC}}{{OB}}$ we know $\sin {30^0} = \dfrac{1}{2},OB = R = 10m$ on putting these values we get,
$\dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{OC}}{{10}}$
$ \Rightarrow OC = 5m$ now the height h can be written as from diagram we have,
$AC = OA - OC$
$AC = h = 10 - 5 = 5m$
so height is given by $h = 5m$
hence, potential energy of the block is
$P.E = mgh$ on putting the values we get,
$P.E = 10 \times 10 \times 5$
$ \Rightarrow P.E = 500J \to (ii)$
Now, the kinetic energy of the block while it’s at rest at point A is $K.{E_A} = 0$
Let K.E of the block at point B with velocity v is $K.{E_B} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} \to (iii)$
Now, Sum of all energy of the block will be equal to work done by the applied force so, net energy on the block is sum of potential energy and change in Kinetic energy so,
$W = P.E + K.{E_B} - K.{E_A}$
on putting the values of these parameters from equation (i) , (ii) and (ii) we get,
$2000 = 500 + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \times {v^2} - 0$
$2000 - 500 = 5{v^2}$
$1500 = 5{v^2}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {300} $
$ \Rightarrow v = 10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}}$
Hence, the correct option is (B) $10\sqrt 3 m{s^{ - 1}}$.
Note: It should be remembered that, the work done by a body is equal to change in energy of a body is referred as Work Energy theorem. and also when two sides of a triangle are equal then the opposite angles of these sides are also equal is an property of triangles. In an equilateral triangle all sides are equal and all angles are of ${60^0}$ each.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




