
A $0.21H$ inductor and a $88\Omega $ resistor are connected in series to a $220V$ , $50Hz$ AC source. Find out the current in the circuit and the phase angle between the current and the source voltage respectively.
It is recommended to use $\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}$
$\begin{align}
& A.2A,{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{3}{4} \\
& B.14.4A,{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{7}{8} \\
& C.14.4A,{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{8}{7} \\
& D.3.28A,{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{2}{11} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: The impedance of a circuit can be found by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of resistance and inductive reactance. Using this, find the impedance of the circuit. Then find the current through the circuit. The tangent of the phase angle is given as the inductive reactance divided by the resistance. These may help you to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer:
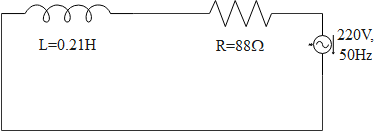
The impedance of a circuit can be found using the equation,
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{X}_{L}}^{2}}$
Where $R$ be the resistance and ${{X}_{L}}$ be the inductive reactance.
It is already mentioned in the question that,
$\begin{align}
& R=88\Omega \\
& L=0.21H \\
\end{align}$
Where $L$be the inductance of the inductor.
The inductive reactance can be found using the formula,\[2A\]
${{X}_{L}}=2\pi fL$
$f=50Hz$
Where $f$be the frequency of the circuit
Let us substitute the parameters in the equation,
${{X}_{L}}=2\pi \times 50\times 0.21=65.973\Omega $
So let us use this in the equation of impedance,
$Z=\sqrt{{{88}^{2}}+{{65.973}^{2}}}=110\Omega $
Now let us calculate the current flowing through the circuit, which is given as,
$I=\dfrac{V}{Z}$
Where the voltage is given as,
$V=220V$
Using this value in the equation of current will give,
$I=\dfrac{220}{110}=2A$
Now the phase angle is given by the equation,
$\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{{{X}_{L}}}{R} \right)$
Substituting the values of the terms in the equation will give,
\[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{65.973}{88} \right)\]
Simplifying will give,
\[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)\]
Therefore the current in the circuit is obtained as \[2A\] and the phase angle is obtained as\[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)\].
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note:
Inductive reactance is given as the prevention of the variation in current through an element. In an AC circuit, in the case of an ideal inductor, the preventive or the opposition effect on change in current flow will cause a delay or a phase shift. This is happening in the alternating current with respect to their alternating voltage.
Complete step by step answer:

The impedance of a circuit can be found using the equation,
$Z=\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+{{X}_{L}}^{2}}$
Where $R$ be the resistance and ${{X}_{L}}$ be the inductive reactance.
It is already mentioned in the question that,
$\begin{align}
& R=88\Omega \\
& L=0.21H \\
\end{align}$
Where $L$be the inductance of the inductor.
The inductive reactance can be found using the formula,\[2A\]
${{X}_{L}}=2\pi fL$
$f=50Hz$
Where $f$be the frequency of the circuit
Let us substitute the parameters in the equation,
${{X}_{L}}=2\pi \times 50\times 0.21=65.973\Omega $
So let us use this in the equation of impedance,
$Z=\sqrt{{{88}^{2}}+{{65.973}^{2}}}=110\Omega $
Now let us calculate the current flowing through the circuit, which is given as,
$I=\dfrac{V}{Z}$
Where the voltage is given as,
$V=220V$
Using this value in the equation of current will give,
$I=\dfrac{220}{110}=2A$
Now the phase angle is given by the equation,
$\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{{{X}_{L}}}{R} \right)$
Substituting the values of the terms in the equation will give,
\[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{65.973}{88} \right)\]
Simplifying will give,
\[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)\]
Therefore the current in the circuit is obtained as \[2A\] and the phase angle is obtained as\[\theta ={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{3}{4} \right)\].
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note:
Inductive reactance is given as the prevention of the variation in current through an element. In an AC circuit, in the case of an ideal inductor, the preventive or the opposition effect on change in current flow will cause a delay or a phase shift. This is happening in the alternating current with respect to their alternating voltage.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




