
5 boys and 3 girls sit in a row at random. The probability that no girls sit together is
A. $\dfrac{3}{{14}}$
B. $\dfrac{5}{{14}}$
C. $\dfrac{9}{{14}}$
D. $\dfrac{7}{{14}}$
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: We will first find the total number of ways in which all people can be arranged. Then, find the number of ways in which 3 girls can sit together by considering all three girls as a single unit. And at last, subtract the number of ways in which three girls together from the total number of ways in all persons can be arranged.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When there are $n$ objects and $n$ places, then the number of ways in which objects can be arranged is $n!$.
There are total 8 person and 8 seats, then the total number of ways in which the person can be seated is $8!$
Also, we know \[n! = n.\left( {n - 1} \right).\left( {n - 2} \right).....3.2.1\].
Then, total possible outcomes are $8! = 8.7.6.5.4.3.2.1 = 40320$,
But, we need that no two girls sit side by side.
Then, there has to be a girl between every two boys.
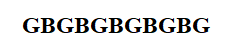
Here, we can see there are 6 positions that a girl can occupy.
Then, 3 girls can choose any of the six positions.
We will use combinations to find the number of ways in which 3 girls can be seated when no two girls can sit together.
Hence, there are $^6{C_3}$
Also, \[^n{C_r} = \dfrac{{n!}}{{r!\left( {n - r} \right)!}}\]
Then, $^6{C_3} = \dfrac{{6!}}{{3!\left( 3 \right)!}} = \dfrac{{6.5.4.3!}}{{3.2.1.3!}} = 20$
Also, the three girls and 5 boys can arrange among themselves.
Therefore, total ways in which two girls can sit such that no girls sit together.
$5!3!\left( {20} \right) = 5.4.3.2.1.3.2.1.20 = 14400$
We will calculate the probability by dividing the number of favourable outcomes by the total number of all the possible outcomes.
\[\dfrac{{14400}}{{40320}} = \dfrac{5}{{14}}\]
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: When there are $n$ distinct objects and needs to be arranged in $n$ places, then the number of ways in which these can be arranged is $n!$. Also, \[n! = n.\left( {n - 1} \right).\left( {n - 2} \right).....3.2.1\]. Since, the position of the girls and boys will also matter that’s why we have to multiply 3! and 5! by finding the total ways of arrangement.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When there are $n$ objects and $n$ places, then the number of ways in which objects can be arranged is $n!$.
There are total 8 person and 8 seats, then the total number of ways in which the person can be seated is $8!$
Also, we know \[n! = n.\left( {n - 1} \right).\left( {n - 2} \right).....3.2.1\].
Then, total possible outcomes are $8! = 8.7.6.5.4.3.2.1 = 40320$,
But, we need that no two girls sit side by side.
Then, there has to be a girl between every two boys.
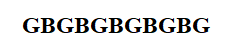
Here, we can see there are 6 positions that a girl can occupy.
Then, 3 girls can choose any of the six positions.
We will use combinations to find the number of ways in which 3 girls can be seated when no two girls can sit together.
Hence, there are $^6{C_3}$
Also, \[^n{C_r} = \dfrac{{n!}}{{r!\left( {n - r} \right)!}}\]
Then, $^6{C_3} = \dfrac{{6!}}{{3!\left( 3 \right)!}} = \dfrac{{6.5.4.3!}}{{3.2.1.3!}} = 20$
Also, the three girls and 5 boys can arrange among themselves.
Therefore, total ways in which two girls can sit such that no girls sit together.
$5!3!\left( {20} \right) = 5.4.3.2.1.3.2.1.20 = 14400$
We will calculate the probability by dividing the number of favourable outcomes by the total number of all the possible outcomes.
\[\dfrac{{14400}}{{40320}} = \dfrac{5}{{14}}\]
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: When there are $n$ distinct objects and needs to be arranged in $n$ places, then the number of ways in which these can be arranged is $n!$. Also, \[n! = n.\left( {n - 1} \right).\left( {n - 2} \right).....3.2.1\]. Since, the position of the girls and boys will also matter that’s why we have to multiply 3! and 5! by finding the total ways of arrangement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




