
When 3,3- dimethyl 2- butanol is heated with , the major product obtained is
(A) 2,3- dimethyl 2- butene
(B) Cis and trans isomers of 2,3 isomers of dimethyl 2-butene
(C) 2,3- dimethyl 1- butene
(D) 3,3- dimethyl 1- butene
Answer
549.9k+ views
Hint: To answer this question you must recall the reaction and its mechanism occurring when an alcohol is reacted with sulphuric acid at high temperature. Sulphuric acid is a strong dehydrating agent, i.e. it causes the loss of a water molecule. Hence, it would form an alkene when heated with water.
Complete step by step solution:
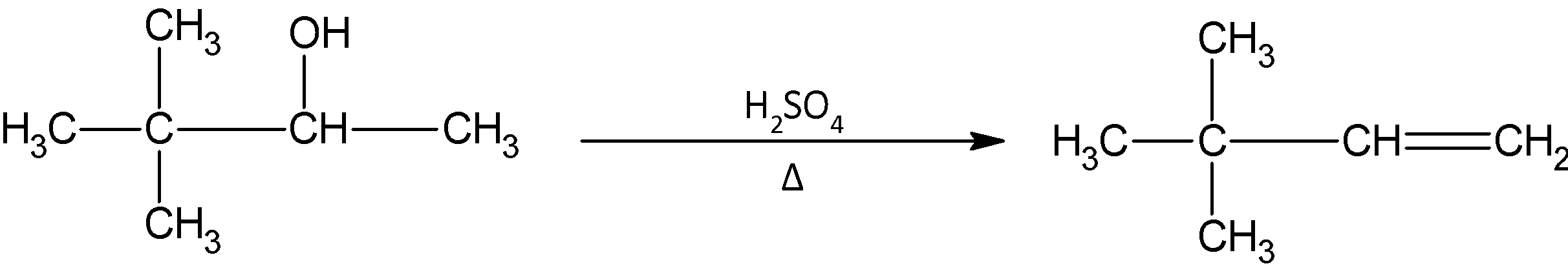
In the given question, we have 3, 3 dimethyl 2- butanol and it is reacted with sulphuric acid. We know that sulphuric acid causes the dehydration of alcohol. After the hydroxyl group departs, and we obtain the carbocation, we must decide which alkene must be formed. In this mechanism, no rearrangement takes place. Also the inner carbon atom does not have any hydrogen atom present. So the only product possible is 3, 3- dimethyl 1- butene.
The reaction occurring is given by:
Note:
The dehydration of alcohol follows the given mechanism.
The first step involves the protonation of alcohol. The oxygen atom of the hydroxyl group carries lone pairs of electrons, so the electrophilic proton formed by the sulphuric acid attacks the hydroxyl group.
The next step involves the departure of the protonated hydroxyl group as a water molecule. The departing oxygen molecule takes the shared pair of electrons with it and a carbocation is formed. This step involves the breaking carbon- oxygen bond and is thus the slowest step of the reaction and known as the rate determining step.
In the next step, the conjugate base of the acid, comes and extracts a proton from the adjacent carbon to the carbocation in such a way so as to form a more substituted and stable alkene as per the Saytzeff’s rule.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given question, we have 3, 3 dimethyl 2- butanol and it is reacted with sulphuric acid. We know that sulphuric acid causes the dehydration of alcohol. After the hydroxyl group departs, and we obtain the carbocation, we must decide which alkene must be formed. In this mechanism, no rearrangement takes place. Also the inner carbon atom does not have any hydrogen atom present. So the only product possible is 3, 3- dimethyl 1- butene.
The reaction occurring is given by:

Note:
The dehydration of alcohol follows the given mechanism.
The first step involves the protonation of alcohol. The oxygen atom of the hydroxyl group carries lone pairs of electrons, so the electrophilic proton formed by the sulphuric acid attacks the hydroxyl group.
The next step involves the departure of the protonated hydroxyl group as a water molecule. The departing oxygen molecule takes the shared pair of electrons with it and a carbocation is formed. This step involves the breaking carbon- oxygen bond and is thus the slowest step of the reaction and known as the rate determining step.
In the next step, the conjugate base of the acid, comes and extracts a proton from the adjacent carbon to the carbocation in such a way so as to form a more substituted and stable alkene as per the Saytzeff’s rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




