
2-chloro-2-methyl butane, on reaction with aq. KOH gives X as the major product. X is
(A) 2-butene
(B) 2-methyl-1-butene
(C) 2-methyl-2-butene
(D) 2-methyl-2-butanol
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: 2-chloro-2-methyl butane is an alkyl chloride. Its common name is tert-Amyl chloride. Tert-amyl chloride is an alkyl chloride and it is used for odorizing and flavouring, although at room temperature it has an unpleasant odour. Reaction with KOH forms an alkene.
Complete Step by step solution:
Aqueous potassium hydroxide reacts with alkyl halide. The reaction of aqueous potassium hydroxide with alkyl halide is due to the nucleophilic substitution.
Aqueous potassium hydroxide particularly is alkaline in nature. As it is alkaline, it dissociates in water to give hydroxide ion.
These hydroxide ions replace halogen atoms in alkyl halide to form alcohol. Alcoholic KOH particularly in ethanol does not undergo nucleophilic substitution. It does not replace the halogen atom by an alcohol group. It abstracts beta hydrogen and forms π bonds. This is known as elimination reaction.
The structure of 2-chloro-2-methyl butane is as follows,
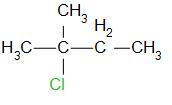
The reaction is as follows,
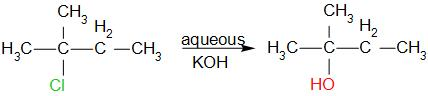
The name of the product is 2-methyl-2-butanol. Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
2-methyl-2-butanol is also called tert-amyl alcohol. It is a clear and a colourless liquid which is slightly soluble in water.
1) 2-methyl-1-butanol is sold industrially as a component of amyl alcohol. It is used as a solvent and is used for manufacturing of many chemicals.
2) 2-methyl-1-butanol occurs naturally in fruits such as grapes etc. It is derived from fuel oil. It is manufactured by oxo process or via halogenation of pentane.
Complete Step by step solution:
Aqueous potassium hydroxide reacts with alkyl halide. The reaction of aqueous potassium hydroxide with alkyl halide is due to the nucleophilic substitution.
Aqueous potassium hydroxide particularly is alkaline in nature. As it is alkaline, it dissociates in water to give hydroxide ion.
These hydroxide ions replace halogen atoms in alkyl halide to form alcohol. Alcoholic KOH particularly in ethanol does not undergo nucleophilic substitution. It does not replace the halogen atom by an alcohol group. It abstracts beta hydrogen and forms π bonds. This is known as elimination reaction.
The structure of 2-chloro-2-methyl butane is as follows,

The reaction is as follows,

The name of the product is 2-methyl-2-butanol. Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
2-methyl-2-butanol is also called tert-amyl alcohol. It is a clear and a colourless liquid which is slightly soluble in water.
1) 2-methyl-1-butanol is sold industrially as a component of amyl alcohol. It is used as a solvent and is used for manufacturing of many chemicals.
2) 2-methyl-1-butanol occurs naturally in fruits such as grapes etc. It is derived from fuel oil. It is manufactured by oxo process or via halogenation of pentane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




