
2-butyne gives $B$ with Lindlar’s catalyst and $A$ with $Na$ in liquid ammonia. $A$ and $B$ are geometric isomers $(MeCH=CHMe)$ then:
A. $A$ is trans, $B$ is cis
B. $A$ is cis, $B$ is trans
C. $A$ is trans, $B$ is trans
D. $A$ is cis, $B$ is cis
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Recall the mechanism of reduction of alkynes by the sodium in liquid ammonia. How the electron is gained and its location affects the stereochemistry of the end product.
Complete step by step answer:
We have 2-butyne that gets converted to 2-butene in the 2 reactions that are mentioned. The geometry of the product is dependent on what kind of catalyst is used while the reduction hydrogenation of the alkyne takes place.
Lindlar’s catalyst comprises of the following molecules: $PdCaC{{O}_{3}}$, $PbO{{(CC{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}$, and quinoline. Usually, the reduction hydrogenation of alkynes continues till an alkane is formed, but when the Lindlar’s catalyst is used, the reduction is arrested at the stage when an alkene is formed. A cis-alkene is formed whenever an alkyne is reduced with this catalyst. The reaction that will occur here is:

Whenever sodium is used with liquid ammonia to reduce alkynes, a trans product is obtained. The reason for this lies in the mechanism of how the reduction takes place. Sodium donates an electron to one of the triple bonded carbon atoms. Due to this, a lone pair is formed and the repulsion between this lone pair and the electron on the other triple bonded carbon increases and they assume a trans configuration. All the further reaction takes place in this state and the end product obtained will be trans. The reaction that will occur here is:
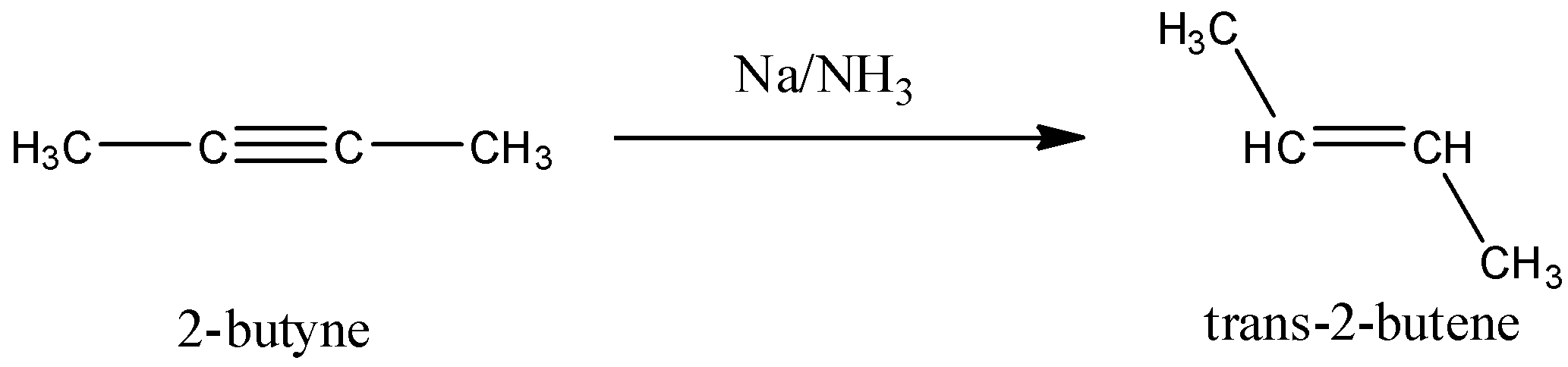
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Note that the exact mechanism of how exactly the reduction of alkenes occurs due to the Lindlar’s catalyst is not known. But it has always been observed that the products are cis in nature and not trans.
Complete step by step answer:
We have 2-butyne that gets converted to 2-butene in the 2 reactions that are mentioned. The geometry of the product is dependent on what kind of catalyst is used while the reduction hydrogenation of the alkyne takes place.
Lindlar’s catalyst comprises of the following molecules: $PdCaC{{O}_{3}}$, $PbO{{(CC{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}$, and quinoline. Usually, the reduction hydrogenation of alkynes continues till an alkane is formed, but when the Lindlar’s catalyst is used, the reduction is arrested at the stage when an alkene is formed. A cis-alkene is formed whenever an alkyne is reduced with this catalyst. The reaction that will occur here is:

Whenever sodium is used with liquid ammonia to reduce alkynes, a trans product is obtained. The reason for this lies in the mechanism of how the reduction takes place. Sodium donates an electron to one of the triple bonded carbon atoms. Due to this, a lone pair is formed and the repulsion between this lone pair and the electron on the other triple bonded carbon increases and they assume a trans configuration. All the further reaction takes place in this state and the end product obtained will be trans. The reaction that will occur here is:
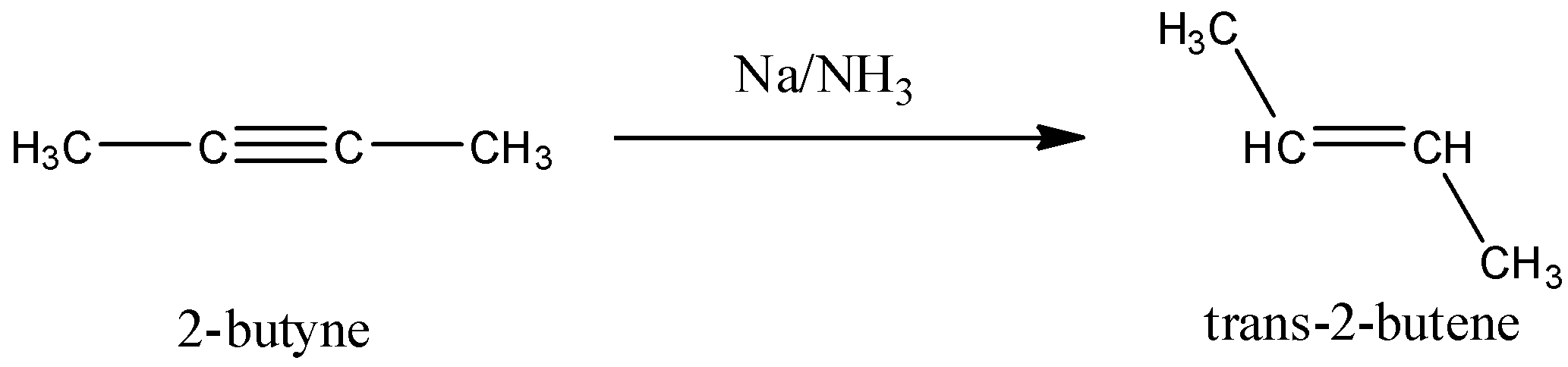
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Note that the exact mechanism of how exactly the reduction of alkenes occurs due to the Lindlar’s catalyst is not known. But it has always been observed that the products are cis in nature and not trans.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




