
2,6 - Dimethylheptane on monochlorination produces..................derivatives.
A) 5
B) 6
C) 3
D) 4
Answer
488.7k+ views
Hint: Monochlorination is the addition of chlorine at the terminal methyl groups. The chlorine atom replaces the hydrogen from the methyl group and gets attached to the carbon of the methyl group. Monochlorination means only single chlorine is being added, although multiple chlorine atoms can bind with the molecule based on the availability of methyl groups.
Complete answer:
2,6 - Dimethylheptane is a disubstituted alkane. Two methyl groups are attached to the second and sixth carbon atoms on the chain. The structure of the 2,6 - Dimethylheptane can be drawn as-
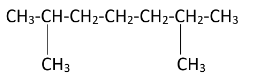
As the diagram suggests, there are four free terminal methyl groups. Monochlorination can occur on all of them. The products formed after mono chlorination will be -
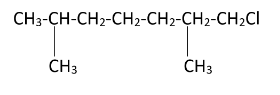
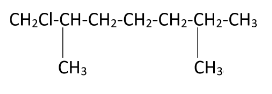
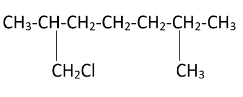
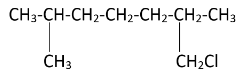
Hence, we can see that there are four possible monochlorination products.
So the correct option is D) 4.
Note:
The products formed can be named as – [7-chloro, 2,6 dimethylheptane], [1-chloro, 2,6 dimethylheptane], [2-chloromethyl, 6-methyl heptane], [6-chloromethyl, 2-methyl heptane]. Simultaneous chlorination can also occur at all the methyl groups present in the molecule resulting in tetrachloro substitution.
Complete answer:
2,6 - Dimethylheptane is a disubstituted alkane. Two methyl groups are attached to the second and sixth carbon atoms on the chain. The structure of the 2,6 - Dimethylheptane can be drawn as-
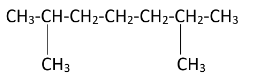
As the diagram suggests, there are four free terminal methyl groups. Monochlorination can occur on all of them. The products formed after mono chlorination will be -
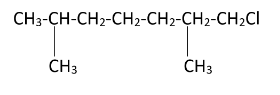
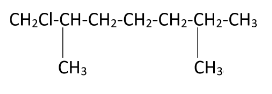
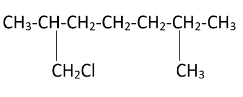
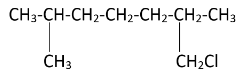
Hence, we can see that there are four possible monochlorination products.
So the correct option is D) 4.
Note:
The products formed can be named as – [7-chloro, 2,6 dimethylheptane], [1-chloro, 2,6 dimethylheptane], [2-chloromethyl, 6-methyl heptane], [6-chloromethyl, 2-methyl heptane]. Simultaneous chlorination can also occur at all the methyl groups present in the molecule resulting in tetrachloro substitution.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




