
What is the 23rd element on the periodic table? What does 23 stand for?
Answer
530.4k+ views
Hint: The elements on the periodic table are arranged in increasing order of the atomic numbers. The 23rd element is a hard, silver-grey transition metal. It is a d-block element and is rarely found in nature. Its pentoxide is used in the preparation of sulphuric acid as a catalyst for the reaction.
Complete answer:
An early attempt to organize elements was made by Mendeleev, who developed the first periodic table. But his proposed idea was based on atomic weights of elements and later it got replaced by a more precise and correct form of the periodic table given by Henry Mosley. It is known as the modern periodic table and it is based upon the fact that properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers and not atomic weights.
So, the elements are placed in the increasing order of the atomic numbers in the periodic table. Given below is an image of a modern periodic table. It contains 18 vertical groups and 7 horizontal periods.
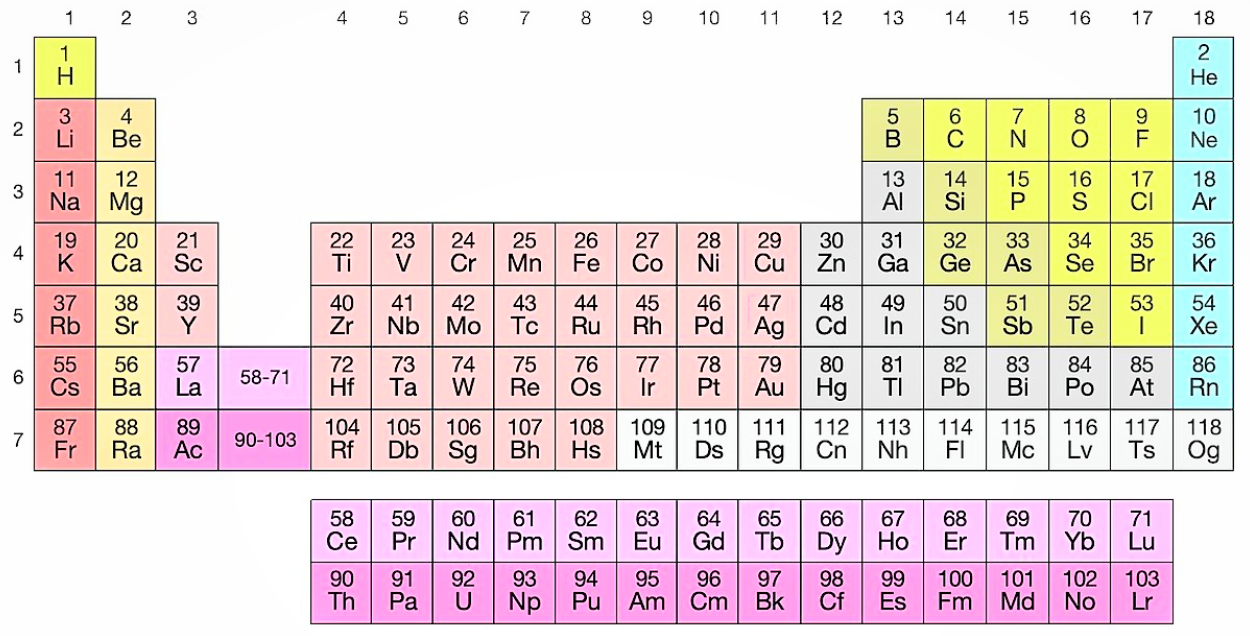
We can see from the periodic table that the 23rd element is Vanadium with the symbol “V”. It is a transition metal that is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the free metal against oxidation.
In this table, an element’s atomic number is indicated above the elemental symbol. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element and since atoms are neutral, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons.
Hence, the 23rd element on the periodic table is Vanadium, and 23 stands for atomic number or number of protons of the Vanadium atom.
Note:
The elements present between groups 3 to 12 are known as transition elements because they possess partially filled d-orbitals in their atom and secondly their properties lie between alkali and alkaline earth metals present on their left-hand side and non-metals present on the right-hand side.
Complete answer:
An early attempt to organize elements was made by Mendeleev, who developed the first periodic table. But his proposed idea was based on atomic weights of elements and later it got replaced by a more precise and correct form of the periodic table given by Henry Mosley. It is known as the modern periodic table and it is based upon the fact that properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers and not atomic weights.
So, the elements are placed in the increasing order of the atomic numbers in the periodic table. Given below is an image of a modern periodic table. It contains 18 vertical groups and 7 horizontal periods.

We can see from the periodic table that the 23rd element is Vanadium with the symbol “V”. It is a transition metal that is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the free metal against oxidation.
In this table, an element’s atomic number is indicated above the elemental symbol. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element and since atoms are neutral, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons.
Hence, the 23rd element on the periodic table is Vanadium, and 23 stands for atomic number or number of protons of the Vanadium atom.
Note:
The elements present between groups 3 to 12 are known as transition elements because they possess partially filled d-orbitals in their atom and secondly their properties lie between alkali and alkaline earth metals present on their left-hand side and non-metals present on the right-hand side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE

State BPT theorem and prove it class 10 maths CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Find the area of the minor segment of a circle of radius class 10 maths CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




