
2,3- Dimethylbutane and \[2,2\]- Dimethylbutane are:
A. Positional isomers
B. Chain isomer
C. Metamers
D. Functional isomers
Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: Isomers are these compounds who have the same molecular formula, same carbon atoms along with \[H\] atoms or other atoms but differ in physical and chemical properties are known as isomers and phenomenon is called isomerism.
\[2,3\] dimethylbutane and \[2,2-\] Dimethylbutane have similar carbon chains but have differences in methyl group attachment or positions of the same molecular formula but differ in structure .
Complete step by step answer:
If we take a look at the structure of both the molecules we will find that.
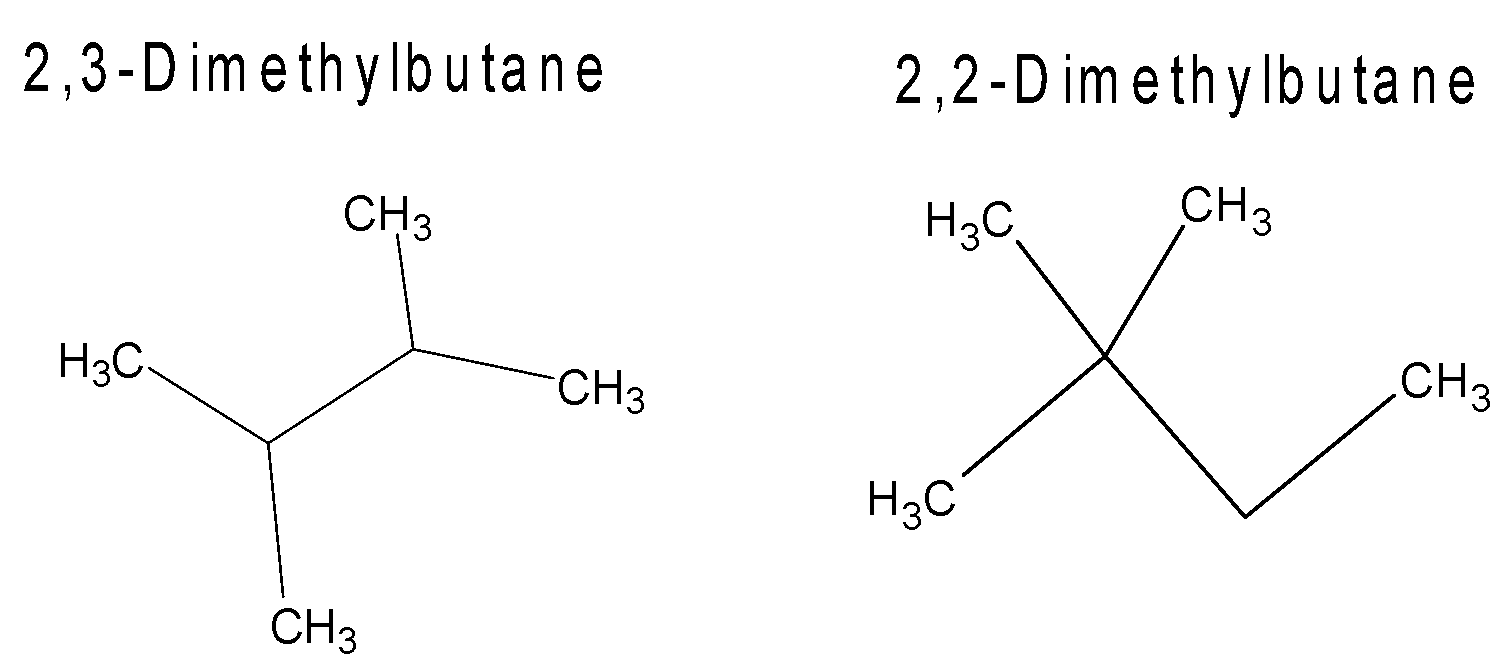
Here we can see that the position of \[1\] methyl group in both the molecules is not the same.
In \[2,3\]- dimethylbutane the methyl group is attached and \[3\] carbon of butane.
But in \[2,2-\]dimethylbutane both methyl groups are attached to \[2\] carbon of butane.
These positional isomers which have same carbon skeleton and same functional groups but differ from each other in location of the functional groups on carbon chain
Positional isomers have similar chemical properties but differ in physical properties
So here we can conclude that the molecules in the questions are showing positional isomerism the correct option is \[\left( A \right)\]
So from above we can conclude that the correct answer for this question is \['A'\].
Note: When isomerism is due difference in position of one or more functional groups or substituted groups. That is the Position isomers (also positional isomers or regioisomers) are structural isomers that can be viewed as differing only on the position of a functional group, substituent, or some other feature on a "parent" structure. Also the formation of position isomers is known as regioisomerism. The isomers are simply
\[2,3\] dimethylbutane and \[2,2-\] Dimethylbutane have similar carbon chains but have differences in methyl group attachment or positions of the same molecular formula but differ in structure .
Complete step by step answer:
If we take a look at the structure of both the molecules we will find that.

Here we can see that the position of \[1\] methyl group in both the molecules is not the same.
In \[2,3\]- dimethylbutane the methyl group is attached and \[3\] carbon of butane.
But in \[2,2-\]dimethylbutane both methyl groups are attached to \[2\] carbon of butane.
These positional isomers which have same carbon skeleton and same functional groups but differ from each other in location of the functional groups on carbon chain
Positional isomers have similar chemical properties but differ in physical properties
So here we can conclude that the molecules in the questions are showing positional isomerism the correct option is \[\left( A \right)\]
So from above we can conclude that the correct answer for this question is \['A'\].
Note: When isomerism is due difference in position of one or more functional groups or substituted groups. That is the Position isomers (also positional isomers or regioisomers) are structural isomers that can be viewed as differing only on the position of a functional group, substituent, or some other feature on a "parent" structure. Also the formation of position isomers is known as regioisomerism. The isomers are simply
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




