
How do 1s, 2s and 3s orbitals differ from each other?
Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint :We know that the electron is not present in a fixed circular path. The orbital wave function for an electron in an atom has no physical significance. It is simply a mathematical function of the coordinates of the electron.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
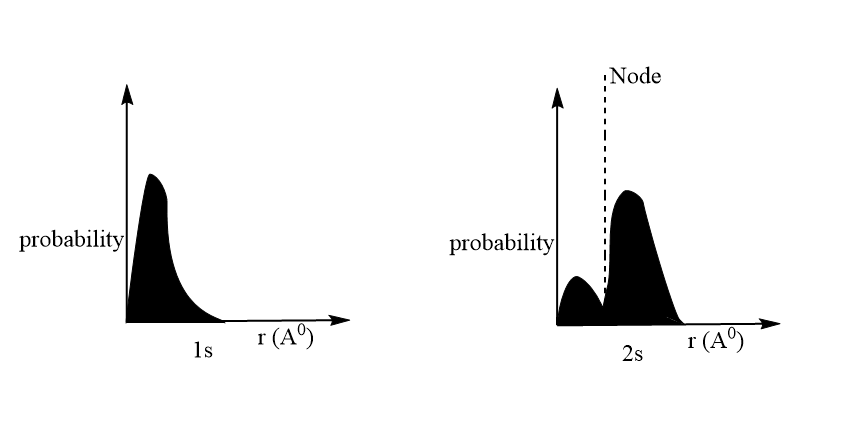
1s orbital, the wave function continuously decreases with the increase in the distance.
2s orbital the wave function decreases until it reaches a point where it becomes zero and then becomes negative. So, here it is seen that wavefunction Is both positive and negative for 2s orbital depending upon the distance.
From the graph it is clear that, in 1s orbital the probability to find the electron decreases away from the nucleus.
For, 2s-orbitals- The graph shows that the probability of finding the electron first decreases with the increase in the value of r, becomes zero at appointment and then increases. The region where this probability density function reduces to zero is called the nodal surface or a node. The graph is similar to that of wave function versus distance except that it is positive throughout because the square of the negative value is always positive.
The 3s orbital: It is the largest among the others. It holds more electrons than the rest. It has a different shape. It has different orientation in space than the 2s orbital. It has ground state electron configuration. That electron is unpaired. It has the lowest energy state of an atom.
Note :
The region where this probability density function reduces to zero is called the nodal surface or a node. The graph is similar to that of wave function versus distance except that it is positive throughout because the square of the negative value is always positive.
Complete Step By Step Answer:

1s orbital, the wave function continuously decreases with the increase in the distance.
2s orbital the wave function decreases until it reaches a point where it becomes zero and then becomes negative. So, here it is seen that wavefunction Is both positive and negative for 2s orbital depending upon the distance.
From the graph it is clear that, in 1s orbital the probability to find the electron decreases away from the nucleus.
For, 2s-orbitals- The graph shows that the probability of finding the electron first decreases with the increase in the value of r, becomes zero at appointment and then increases. The region where this probability density function reduces to zero is called the nodal surface or a node. The graph is similar to that of wave function versus distance except that it is positive throughout because the square of the negative value is always positive.
The 3s orbital: It is the largest among the others. It holds more electrons than the rest. It has a different shape. It has different orientation in space than the 2s orbital. It has ground state electron configuration. That electron is unpaired. It has the lowest energy state of an atom.
Note :
The region where this probability density function reduces to zero is called the nodal surface or a node. The graph is similar to that of wave function versus distance except that it is positive throughout because the square of the negative value is always positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




