
1-methylcyclohexene on treatment with HCl gas gives:
(A) 1-chloro-2-methylcyclohexane
(B) 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane
(C) 1-chloro-cyclohexane
(D) None of these
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, 1- methylcyclohexene is an asymmetric alkene whereas HCl is a hydrogen halide. So, to solve this question we first need to know how the reaction between an asymmetric alkene and a hydrogen halide takes place.
Complete answer:
We know that hydrogen halides (HX) are protic acids. i.e., these acids produce protons as they ionize in solutions.
Now, when an asymmetric alkene reacts with a protic acid, the unsaturated carbon atom which has the most number of alkyl substituents will form a bond with the halide group whereas the unsaturated carbon atom which has the most number of hydrogen substituent will bind with the acidic hydrogen to form the major saturated product.
This phenomenon is known as Markovnikov's rule.
\[R-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HX\to R-CH(X)-C{{H}_{3}}\text{ (major)}\]
So, according to this rule, the reaction between 1-methylcyclohexene and hydrochloric acid (HCl) will be as follows.
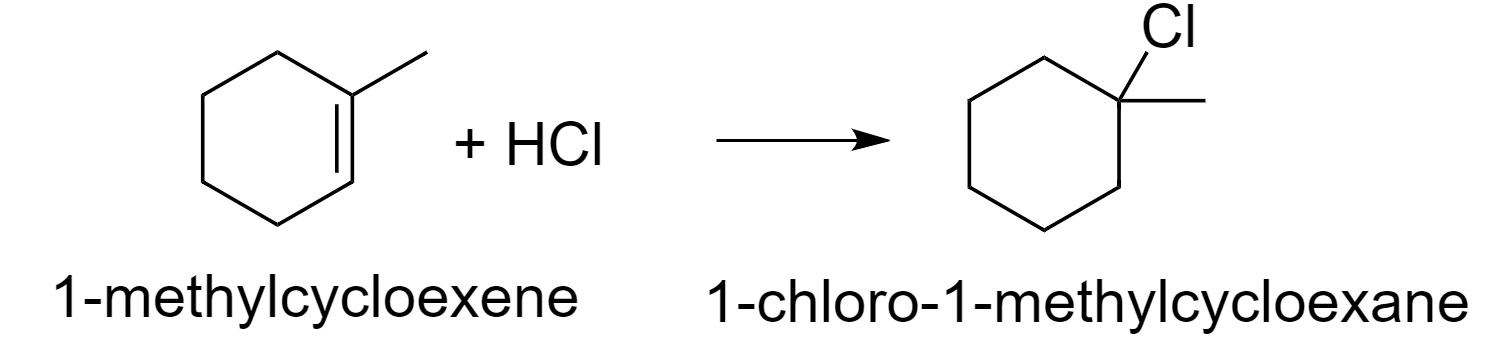
1-methylcyclohexene on treatment with HCl gas gives option (B) 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane
Additional information:
The speed of the reaction of the addition of hydrogen halide to alkene depends upon the hydrogen halide. The reaction rate increases as we go from HF to HI.
HF < HCl < HBr < HI
This is because, with the increase in the size of the halide atom, the bond strength of the hydrogen halide decreases, and the bonds break easily, which further helps in increasing the rate of the reaction.
Note:
It should be noted that when hydrogen bromide (HBr) is added to an asymmetrical alkene in the presence of an organic peroxide, the reaction follows the free radical mechanism, and the products are formed according to the anti-Markovnikov's rule which states that the protic acid is added to the more alkyl-substituted carbon atom.
Complete answer:
We know that hydrogen halides (HX) are protic acids. i.e., these acids produce protons as they ionize in solutions.
Now, when an asymmetric alkene reacts with a protic acid, the unsaturated carbon atom which has the most number of alkyl substituents will form a bond with the halide group whereas the unsaturated carbon atom which has the most number of hydrogen substituent will bind with the acidic hydrogen to form the major saturated product.
This phenomenon is known as Markovnikov's rule.
\[R-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HX\to R-CH(X)-C{{H}_{3}}\text{ (major)}\]
So, according to this rule, the reaction between 1-methylcyclohexene and hydrochloric acid (HCl) will be as follows.

1-methylcyclohexene on treatment with HCl gas gives option (B) 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane
Additional information:
The speed of the reaction of the addition of hydrogen halide to alkene depends upon the hydrogen halide. The reaction rate increases as we go from HF to HI.
HF < HCl < HBr < HI
This is because, with the increase in the size of the halide atom, the bond strength of the hydrogen halide decreases, and the bonds break easily, which further helps in increasing the rate of the reaction.
Note:
It should be noted that when hydrogen bromide (HBr) is added to an asymmetrical alkene in the presence of an organic peroxide, the reaction follows the free radical mechanism, and the products are formed according to the anti-Markovnikov's rule which states that the protic acid is added to the more alkyl-substituted carbon atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




